|
Dyotropic Reaction
A dyotropic reaction (from the Greek ''dyo'', meaning two) in organic chemistry is a type of organic reaction and more specifically a pericyclic valence isomerization in which two sigma bonds simultaneously migrate intramolecularly. The reaction type is of some relevance to organic chemistry because it can explain how certain reactions occur and because it is a synthetic tool in the synthesis of organic molecules for example in total synthesis. It was first described by Manfred T. Reetz in 1971 In a type I reaction two migrating groups interchange their relative positions and a type II reaction involves migration to new bonding sites without positional interchange. Type I rearrangements In type I rearrangements (Y-A-B-X conversion to X-A-B-Y) the two migrating groups are oriented trans to each other and as a result of the rearrangement they migrate to opposite sides. The first example of a dyotropic rearrangement involving a carbon-carbon bond was reported by Cyril A. Grob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyotropic Rearrangement
A dyotropic reaction (from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''dyo'', meaning two) in organic chemistry is a type of organic reaction and more specifically a pericyclic valence isomerization in which two sigma bonds simultaneously migrate Intramolecular reaction, intramolecularly. The reaction type is of some relevance to organic chemistry because it can explain how certain reactions occur and because it is a synthetic tool in the synthesis of organic molecules for example in total synthesis. It was first described by Manfred T. Reetz in 1971 In a type I reaction two substituent, migrating groups interchange their relative positions and a type II reaction involves migration to new bonding sites without positional interchange. Type I rearrangements In type I rearrangements (Y-A-B-X conversion to X-A-B-Y) the two migrating groups are oriented trans configuration, trans to each other and as a result of the rearrangement they migrate to opposite sides. The first example of a dyotropic rearr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvetica Chimica Acta
''Helvetica Chimica Acta'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of chemistry established by the Swiss Chemical Society. It is published online by John Wiley & Sons. The journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.164. History *August 6, 1901: Founding of the Swiss Chemical Society *1911: IUPAC refused SCG as a member, no own journal *September 11, 1917: SCG founded HCA *1917–1948: First editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing ...: Friedrich Fichter (1869–1952) *Spring 1918: Fasciculus I of Volume I of HCA was issued *1948–1971: Emile Cherbuliez (1891–1985) *1970: English allowed as fourth language *1971–1983: Edgardo Giovannini (1909–2004) *1983–2015: M. Volkan Kisakürek *2015-2016: Richard J. Smith *2016–2021: Jeffrey W. Bode and Christophe Copér ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo A
Leo A (also known as Leo III) is an irregular galaxy that is part of the Local Group. It lies 2.6 million light-years from Earth, and was discovered by Fritz Zwicky in 1942. The estimated mass of this galaxy is solar masses, with at least 80% consisting of dark matter. It is one of the most isolated galaxies in the Local Group and shows no indications of an interaction or merger for several billion years. However, Leo A is nearly unique among irregular galaxies in that more than 90% of its stars formed more recently than 8 billion years ago, suggesting a rather unusual evolutionary history. The presence of RR Lyrae variables shows that the galaxy has an old stellar population that is up to 10 billion years in age. The neutral hydrogen in this galaxy occupies in a volume similar to its optical extent, and is distributed in a squashed, uneven ring. The galaxy is not rotating and the hydrogen is moving about in random clumps. The proportion of elements with higher atomic numbers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
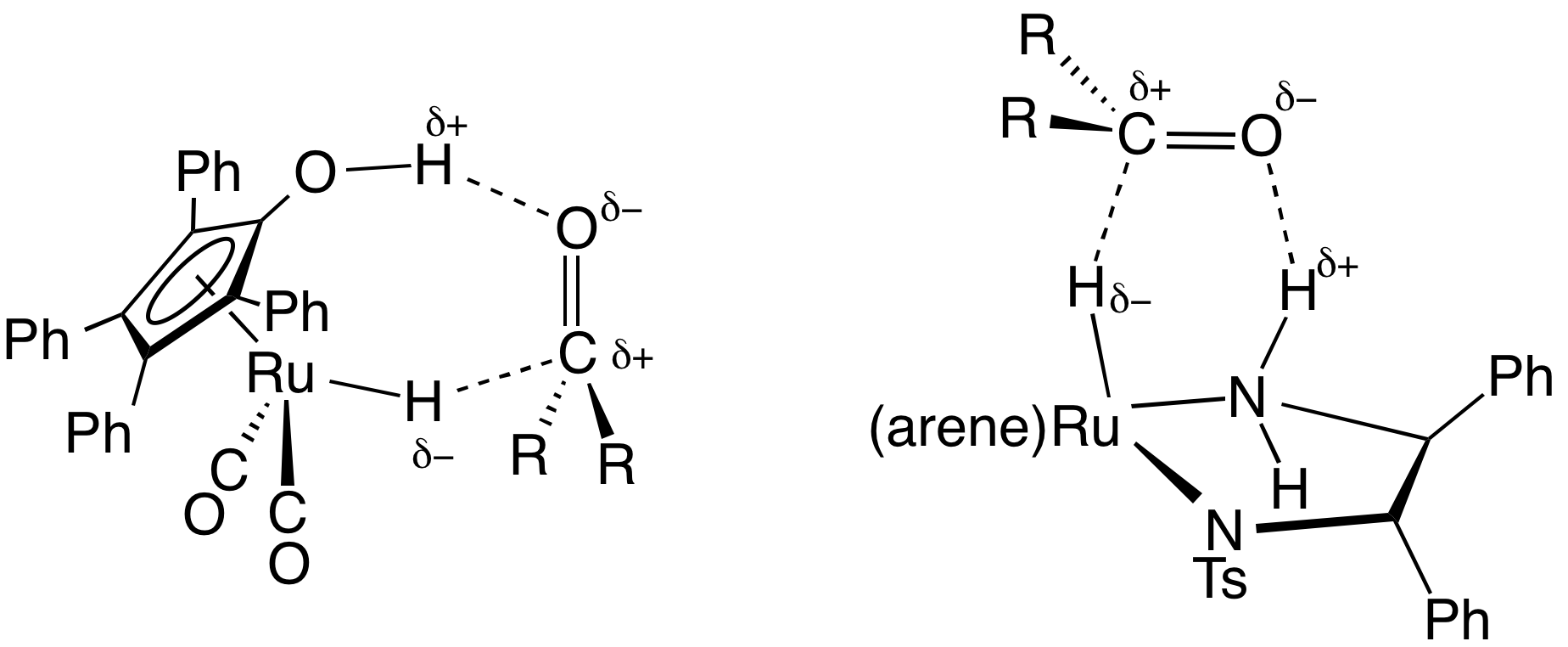
Transfer Hydrogenation
In chemistry, transfer hydrogenation is a chemical reaction involving the addition of hydrogen to a compound from a source other than molecular . It is applied in laboratory and industrial organic synthesis to saturate organic compounds and reduce ketones to alcohols, and imines to amines. It avoids the need for high-pressure molecular used in conventional hydrogenation. Transfer hydrogenation usually occurs at mild temperature and pressure conditions using organic or organometallic catalysts, many of which are chiral, allowing efficient asymmetric synthesis. It uses hydrogen donor compounds such as formic acid, isopropanol or dihydroanthracene, dehydrogenating them to , acetone, or anthracene respectively. Often, the donor molecules also function as solvents for the reaction. A large scale application of transfer hydrogenation is coal liquefaction using "donor solvents" such as tetralin. Organometallic catalysts In the area of organic synthesis, a useful family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2-Wittig Rearrangement
A 1,2-Wittig rearrangement is a categorization of chemical reactions in organic chemistry, and consists of a 1,2-rearrangement of an ether with an alkyllithium compound. The reaction is named for Nobel Prize winning chemist Georg Wittig. : \mathsf The intermediate product is an alkoxy lithium salt and the final product an alcohol. When R" is a good leaving group and electron withdrawing group such as a cyanide (CN) group,''Preparation of aryl benzyl ketones by ,2Wittig rearrangement'' Alan R. Katritzky, Yuming Zhang, Sandeep K. Singh Arkivoc pp. 146–50 2002 (viilink this group is eliminated and the corresponding ketone is formed. : \mathsf Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism centers on the formation of a free radical pair with lithium migrating from the carbon atom to the oxygen atom. The R radical then recombines with the ketyl.''Wittig Rearrangement of Lithiated Allyl Aryl Ethers: A Mechanistic Study'' Sven Strunk, Manfred Schlosser European Journal of Organic Chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrolactone
Butyrolactone may refer to: * ''beta''-Butyrolactone * ''gamma''-Butyrolactone (GBL) {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
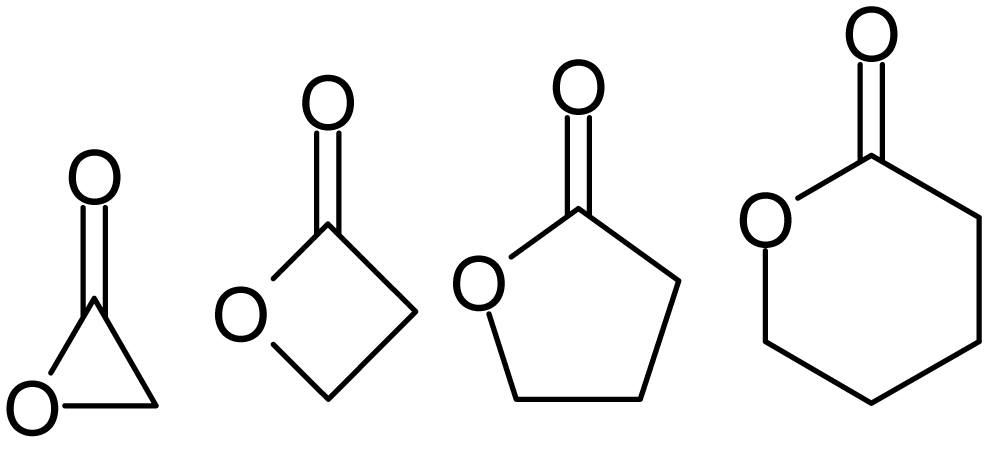
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concerted
In chemistry, a concerted reaction is a chemical reaction in which all bond breaking and bond making occurs in a single step. Reactive intermediates or other unstable high energy intermediates are not involved. Concerted reaction rates tend not to depend on solvent polarity ruling out large buildup of charge in the transition state. The reaction is said to progress through a concerted mechanism as all bonds are formed and broken ''in concert''. Pericyclic reactions, the S2 reaction, and some rearrangements - such as the Claisen rearrangement - are concerted reactions. The rate of the SN2 reaction is second order overall due to the reaction being bimolecular (i.e. there are two molecular species involved in the rate-determining step). The reaction does not have any intermediate steps, only a transition state In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition State
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked with the double dagger ‡ symbol. As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxide anion: The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state. Peter Atkins and Julio de Paula, ''Physical Chemistry'' (8th ed., W.H. Freeman 2006), p.809 According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products. History of concept The concept of a transition state has been important in many theories of the rates at which chemical react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutarotation
Mutarotation is the change in the ''optical rotation'' because of the change in the equilibrium between two anomers, when the corresponding stereocenters interconvert. Cyclic sugars show mutarotation as α and β anomeric forms interconvert. The optical rotation of the solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution. Mutarotation was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1844, when he noticed that the specific rotation of aqueous sugar solution changes with time. Measurement The α and β anomers are diastereomers of each other and usually have different specific rotations. A solution or liquid sample of a pure α anomer will rotate plane polarised light by a different amount and/or in the opposite direction than the pure β anomer of that compound. The optical rotation of the solution depends on the optical rotation of each anomer and their ratio in the solution. For example, if a solution of β-D- glucopyranose is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |