|
Dynamic Topography
The term dynamic topography is used in geodynamics to refer the elevation differences caused by the flow within Earth's mantle. Definition In geodynamics, ''dynamic topography'' refers to topography generated by the motion of zones of differing degrees of buoyancy (convection) in Earth's mantle. It is also seen as the residual topography obtained by removing the isostatic contribution from the observed topography (i.e., the topography that cannot be explained by an isostatic equilibrium of the crust or the lithosphere resting on a fluid mantle) and all observed topography due to post-glacial rebound. Elevation differences due to dynamic topography are frequently on the order of a few hundred meters to a couple of kilometers. Large scale surface features due to dynamic topography are mid-ocean ridges and oceanic trenches. Other prominent examples include areas overlying mantle plumes such as the African superswell. The mid-ocean ridges are high due to dynamic topography because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodynamics
Geodynamics is a subfield of geophysics dealing with dynamics of the Earth. It applies physics, chemistry and mathematics to the understanding of how mantle convection leads to plate tectonics and geologic phenomena such as seafloor spreading, mountain building, volcanoes, earthquakes, faulting. It also attempts to probe the internal activity by measuring magnetic fields, gravity, and seismic waves, as well as the mineralogy of rocks and their isotopic composition. Methods of geodynamics are also applied to exploration of other planets. Overview Geodynamics is generally concerned with processes that move materials throughout the Earth. In the Earth's interior, movement happens when rocks melt or deform and flow in response to a stress field.Turcotte, D. L. and G. Schubert (2014). "Geodynamics." This deformation may be brittle, elastic, or plastic, depending on the magnitude of the stress and the material's physical properties, especially the stress relaxation time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
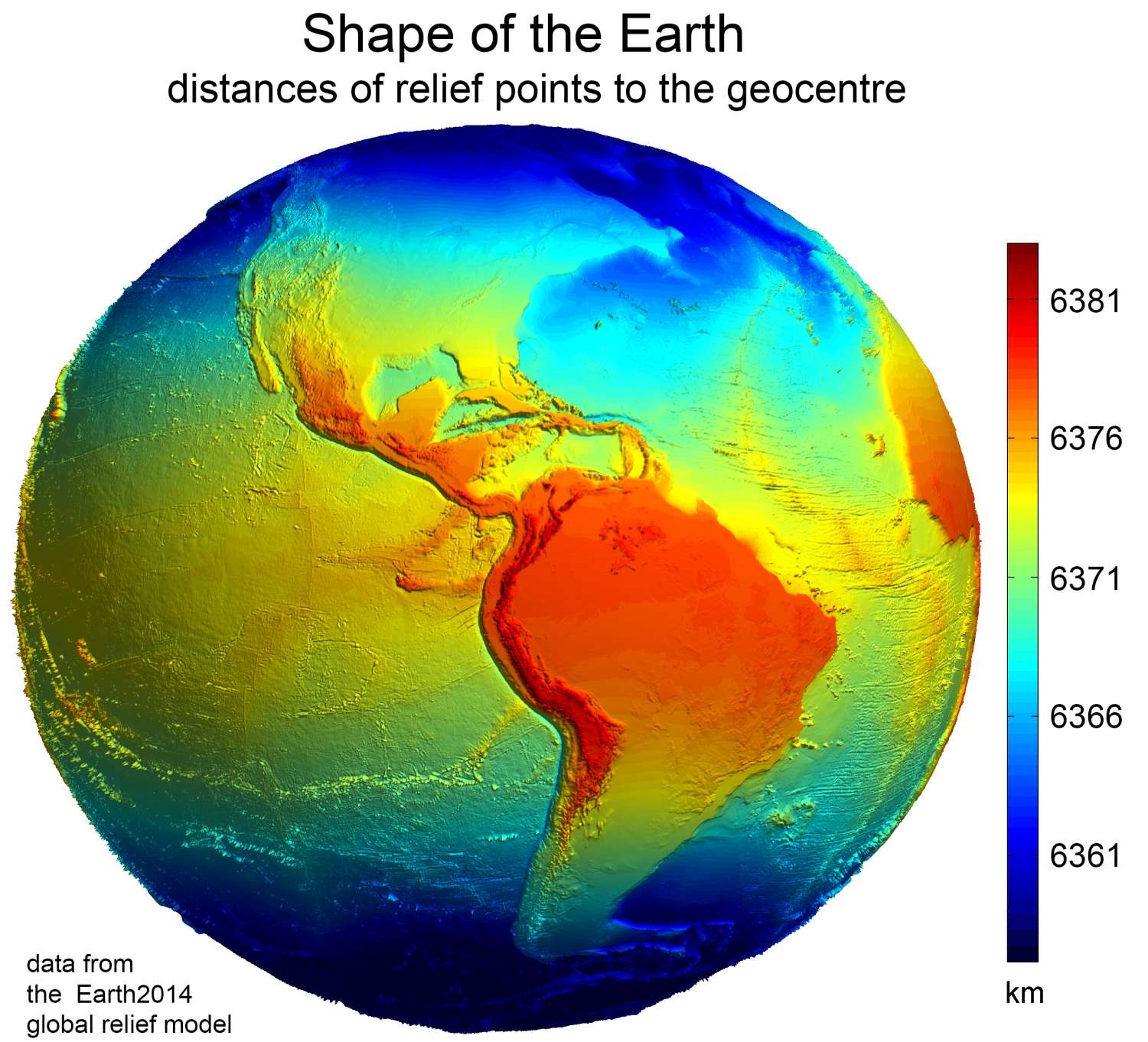
Figure Of The Earth
Figure of the Earth is a term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A sphere is a well-known historical approximation of the figure of the Earth that is satisfactory for many purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including ellipsoid) have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, hydrographers, and geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely complicated. The Pythagorean concept of a spherical Earth offers a simple surface that is easy to deal with math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epeirogenic Movement
In geology, epeirogenic movement (from Greek ''epeiros'', land, and ''genesis'', birth) is upheavals or depressions of land exhibiting long wavelengths and little folding apart from broad undulations. The broad central parts of continents are called cratons, and are subject to epeirogeny. The movement may be one of subsidence toward, or of uplift from, the centre of the Earth. The movement is caused by a set of forces acting along an Earth radius, such as those contributing to isostasy and faulting in the lithosphere. Epeirogenic movement can be permanent or transient. Transient uplift can occur over a thermal anomaly due to convecting anomalously hot mantle, and disappears when convection wanes. Permanent uplift can occur when igneous material is injected into the crust, and circular or elliptical structural uplift (that is, without folding) over a large radius (tens to thousands of km) is one characteristic of a mantle plume. In contrast to epeirogenic movemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slab Window
In geology, a slab window is a gap that forms in a subducted oceanic plate when a mid-ocean ridge meets with a subduction zone and plate divergence at the ridge and convergence at the subduction zone continue, causing the ridge to be subducted.Thorkelson, Derek J., 1996, Subduction of diverging plates and the principles of slab window formation, '' Tectonophysics'', v. 255, p. 47-63 Formation of a slab window produces an area where the crust of the over-riding plate is lacking a rigid lithospheric mantle component and thus is exposed to hot asthenospheric mantle (for a diagram of this, see the link below). This produces anomalous thermal, chemical and physical effects in the mantle that can dramatically change the over-riding plate by interrupting the established tectonic and magmatic regimes. In general, the data used to identify possible slab windows comes from seismic tomography and heat flow studies.van Wijk, J.W., Govers, R., Furlong, K.P., 2001, Three-dimensional thermal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile Triple Junction
The Chile Triple Junction (or Chile Margin Triple Junction) is a geologic triple junction located on the seafloor of the Pacific Ocean off Taitao and Tres Montes Peninsula on the southern coast of Chile. Here three tectonic plates meet: the South American Plate, the Nazca Plate and the Antarctic Plate. This triple junction is unusual in that it consists of a mid-oceanic ridge, the Chile Rise, being subducted under the South American Plate at the Peru–Chile Trench. The Chile Triple Junction is the boundary between the Chilean Rise and the Chilean margin, where the Nazca, Antarctic, and South American plates meet at the trench. Tectonic plate movement The Antarctic Plate started to subduct beneath South America 14 million years ago in the Miocene epoch forming the Chile Triple Junction. At first the Antarctic Plate subducted only in the southernmost tip of Patagonia, meaning that the Chile Triple Junction lay near the Strait of Magellan. As the southern part of Nazca Plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics (journal)
''Tectonics'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of geology focusing on tectonics. It is published by the American Geophysical Union in collaboration with the European Geosciences Union. The journal is edited by John Geissman (University of Texas at Dallas), Laurent Jolivet (Institut des Sciences de la Terre de Paris), Nathan Niemi (University of Michigan) and Taylor Schildgen (University of Potsdam). Abtrascting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following bibliographic databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.58. References External links * Publications established in 1982 English-language journals Geology journals American Geophysical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomorphology (journal)
''Geomorphology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal about geomorphology Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or .... External links * Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Elsevier academic journals English-language journals Geomorphology journals {{Geomorphology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three period (geology), periods of the Cenozoic era (geology), Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ago to the present. The Quaternary Period is divided into two epochs: the Pleistocene (2.58 million years ago to 11.7 thousand years ago) and the Holocene (11.7 thousand years ago to today, although a third epoch, the Anthropocene, has been proposed but is not yet officially recognised by the ICS). The Quaternary Period is typically defined by the cyclic growth and decay of continental ice sheets related to the Milankovitch cycles and the associated climate and environmental changes that they caused. Research history In 1759 Giovanni Arduino (geologist), Giovanni Arduino proposed that the geological strata of northern Italy could be divided into four successive formations or "orders" ( it, quattro ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regression (geology)
A marine regression is a geological process occurring when areas of submerged seafloor are exposed above the sea level. The opposite event, marine transgression, occurs when flooding from the sea covers previously-exposed land. Evidence of marine regressions and transgressions occurs throughout the fossil record, and the fluctuations are thought to have caused or contributed to several mass extinctions, such as the Permian-Triassic extinction event (250 million years ago) and Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (66 Ma). During the Permian-Triassic extinction, the largest extinction event in the Earth's history, the global sea level fell 250 m (820 ft). A major regression could itself cause marine organisms in shallow seas to go extinct, but mass extinctions tend to involve both terrestrial and aquatic species, and it is harder to see how a marine regression could cause widespread extinctions of land animals. Regressions are, therefore, seen as correlates or symptoms of majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgression (geology)
A marine transgression is a geologic event during which sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, which results in flooding. Transgressions can be caused by the land sinking or by the ocean basins filling with water or decreasing in capacity. Transgressions and regressions may be caused by tectonic events such as orogenies, severe climate change such as ice ages or isostatic adjustments following removal of ice or sediment load. During the Cretaceous, seafloor spreading created a relatively shallow Atlantic basin at the expense of deeper Pacific basin. That reduced the world's ocean basin capacity and caused a rise in sea level worldwide. As a result of the sea level rise, the oceans transgressed completely across the central portion of North America and created the Western Interior Seaway from the Gulf of Mexico to the Arctic Ocean. The opposite of transgression is regression in which the sea level falls relative to the land and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers in the west and deserts, tablelands and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel, and the Drake Passage to the south. The Colorado and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago of Tierra del Fuego is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |