|
Dynamic Data Driven Application System
"'Dynamic Data Driven Applications Systems" ("'DDDAS'") is a paradigm whereby the computation and instrumentation aspects of an application system are dynamically integrated with a feedback control loop, in the sense that instrumentation data can be dynamically incorporated into the executing model of the application, and in reverse the executing model can control the instrumentation. Several closely related concepts predate DDDAS, including: * N-armed bandit problems (Thompson 1933, Gittins 1979) and, subsequently, Reinforcement Learning: * Chernoff'Sequential Design of Experiments* Fedorov's Design of Experiments (70s), where the experiments determine the parameters and the parameters guide the experiments, including for data and model selection. * MacKay's Information-based Active Data Selection (1991) is where the expected informativeness of candidate measurements is used to select salient ones for learning, improving the expected informativeness. * Active Learning (the 80s-90 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederica Darema
Frederica Darema is a Greek American physicist. She proposed the SPMD programming model in 1984 and Dynamic Data Driven Application Systems (DDDAS) in 2000. She was elected IEEE Fellow in 2004. Biography Darema received her BS degree from the School of Physics and Mathematics of the University of Athens - Greece, and MS and Ph. D. degrees in Theoretical Nuclear Physics from the Illinois Institute of Technology and the University of California at Davis, respectively, where she attended as a Fulbright Scholar and a Distinguished Scholar. After Physics Research Associate positions at the University of Pittsburgh and Brookhaven National Laboratory, she received an APS Industrial Fellowship and became a Technical Staff Member in the Nuclear Sciences Department at Schlumberger Doll Research. Subsequently, in 1982, she joined the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center as a Research Staff Member in the Computer Sciences Department and later-on she established and became the manager of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. With an annual budget of about $8.3 billion (fiscal year 2020), the NSF funds approximately 25% of all federally supported basic research conducted by the United States' colleges and universities. In some fields, such as mathematics, computer science, economics, and the social sciences, the NSF is the major source of federal backing. The NSF's director and deputy director are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate, whereas the 24 president-appointed members of the National Science Board (NSB) do not require Senate confirmation. The director and deputy director are responsible for administration, planning, budgeting and day-to-day operations of the foundation, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Assimilation
Data assimilation is a mathematical discipline that seeks to optimally combine theory (usually in the form of a numerical model) with observations. There may be a number of different goals sought – for example, to determine the optimal state estimate of a system, to determine initial conditions for a numerical forecast model, to interpolate sparse observation data using (e.g. physical) knowledge of the system being observed, to set numerical parameters based on training a model from observed data. Depending on the goal, different solution methods may be used. Data assimilation is distinguished from other forms of machine learning, image analysis, and statistical methods in that it utilizes a dynamical model of the system being analyzed. Data assimilation initially developed in the field of numerical weather prediction. Numerical weather prediction models are equations describing the dynamical behavior of the atmosphere, typically coded into a computer program. In order to use t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Systems
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial control systems which are used for controlling processes or machines. The control systems are designed via control engineering process. For continuously modulated control, a feedback controller is used to automatically control a process or operation. The control system compares the value or status of the process variable (PV) being controlled with the desired value or setpoint (SP), and applies the difference as a control signal to bring the process variable output of the plant to the same value as the setpoint. For sequential and combinational logic, software logic, such as in a programmable logic controller, is used. Open-loop and closed-loop control There are two common classes of control action: open loop and closed loop. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
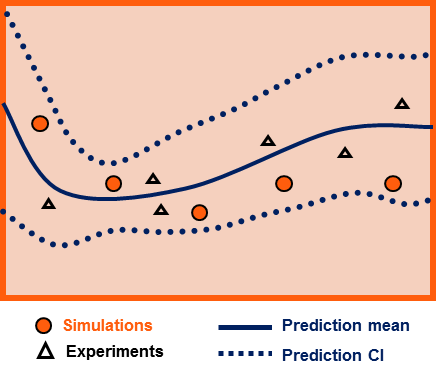
Uncertainty Quantification
Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is the science of quantitative characterization and reduction of uncertainties in both computational and real world applications. It tries to determine how likely certain outcomes are if some aspects of the system are not exactly known. An example would be to predict the acceleration of a human body in a head-on crash with another car: even if the speed was exactly known, small differences in the manufacturing of individual cars, how tightly every bolt has been tightened, etc., will lead to different results that can only be predicted in a statistical sense. Many problems in the natural sciences and engineering are also rife with sources of uncertainty. Computer experiments on computer simulations are the most common approach to study problems in uncertainty quantification. Sources Uncertainty can enter mathematical models and experimental measurements in various contexts. One way to categorize the sources of uncertainty is to consider: ; Parame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)