|
Dwm Dual Monitor
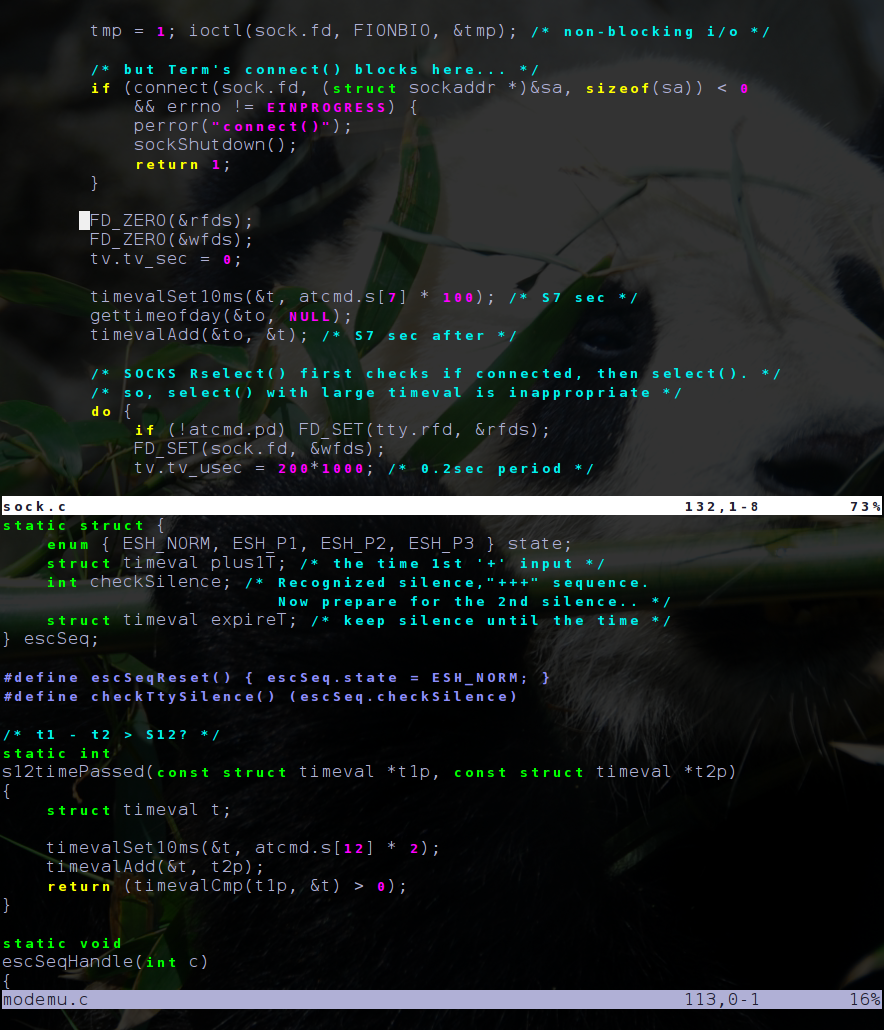
dwm is a minimalism (computing), minimalist dynamic window manager for the X Window System developed by suckless.org, Suckless that has influenced the development of several other X window managers, including xmonad and Awesome (window manager), awesome. It is externally similar to wmii, but internally much simpler. dwm is written purely in C (programming language), C for performance and lacks any configuration interface besides editing the source code. One of the project's guidelines is that the source code is intended never to exceed 2000 Source lines of code, SLOC, and options meant to be user-configurable are all contained in a single header file. Features dwm supports multiple workspaces and, unlike ratpoison, allows moving and resizing windows with the mouse. Older versions of dwm displayed their Standard streams#Standard input (stdin), stdin in a status bar, along the edge of the screen. Recent versions instead display the root window's name, which can be set by inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Urxvt
Rxvt (acronym for our extended virtual terminal) is a terminal emulator for the X Window System, and in the form of a Cygwin port, for Windows. History Rxvt was originally written by Rob Nation and later extensively modified by Mark Olesen, who took over maintenance for several years. It is intended to be a slimmed-down alternate for xterm, omitting some of its little-used features, like Tektronix 4014 emulation and toolkit-style configurability. The latter refers to the Xt resource mechanism, e.g., for binding keys. Rxvt is an extended version of the older xvt terminal emulator by John Bovey of the University of Kent. The name originally stood for "Rob's xvt" (with XVT stands for 'X Virtual Terminal'), but was later re-dubbed "our xvt" (pronounced like the letters r-x-v-t). Features Aside from features such as those controlled by resource files, rxvt's terminal emulation differs from xterm in two important ways: *It emulates a VT102, rather than a VT220. That means that it han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Source Lines Of Code
Source lines of code (SLOC), also known as lines of code (LOC), is a software metric used to measure the size of a computer program by counting the number of lines in the text of the program's source code. SLOC is typically used to predict the amount of effort that will be required to develop a program, as well as to estimate programming productivity or maintainability once the software is produced. Measurement methods Multiple useful comparisons involve only the order of magnitude of lines of code in a project. Using lines of code to compare a 10,000-line project to a 100,000-line project is far more useful than when comparing a 20,000-line project with a 21,000-line project. While it is debatable exactly how to measure lines of code, discrepancies of an order of magnitude can be clear indicators of software complexity or man-hours. There are two major types of SLOC measures: physical SLOC (LOC) and logical SLOC (LLOC). Specific definitions of these two measures vary, but the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Path (variable)
PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like operating systems, DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, specifying a set of directories where executable programs are located. In general, each executing process or user session has its own PATH setting. History Multics originated the idea of a search path. The early Unix shell only looked for program names in /bin, but by Version 3 Unix the directory was too large and /usr/bin, and a search path, became part of the operating system. Unix and Unix-like On POSIX and Unix-like operating systems, the $PATH variable is specified as a list of one or more directory names separated by colon (:) characters. Directories in the PATH-string are not meant to be escaped, making it impossible to have directories with : in their name. The /bin, /usr/bin, and /usr/local/bin directories are typically included in most users' $PATH setting (although this varies from implementation to implementation). The superuser also typically has /sbin and /usr/sbin en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Key Combination
In computing, a keyboard shortcut (also hotkey/hot key or key binding) is a software-based assignment of an action to one or more keys on a computer keyboard. Most operating systems and applications come with a default set of keyboard shortcuts, some of which may be modified by the user in the settings. Keyboard configuration software allows users to create and assign macros to key combinations which can perform more complex sequences of actions. Some older keyboards had a physical macro key specifically for this purpose. Terminology The precise words used for these assignments and their meaning can vary depending on the context. For example, Microsoft has generally used ''keyboard shortcuts'' for Windows and Microsoft Office since the transition to 64-bit for Windows 7. However, they used ''hot keys'' prior to that and continue to do so in their 32-bit API for developing 'classic desktop apps'. Meanwhile, Lenovo and ASUS each have keyboard configuration software made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Menu (computing)
In user interface design, a menu is a list of options presented to the user. Navigation A user chooses an option from a menu by using an input device. Some input methods require linear navigation: the user must move a cursor or otherwise pass from one menu item to another until reaching the selection. On a computer terminal, a reverse video bar may serve as the cursor. Touch user interfaces and menus that accept codes to select menu options without navigation are two examples of non-linear interfaces. Some of the input devices used in menu interfaces are touchscreens, keyboards, mice, remote controls, and microphones. In a voice-activated system, such as interactive voice response, a microphone sends a recording of the user's voice to a speech recognition system, which translates it to a command. Types of menus A computer using a command line interface may present a list of relevant commands with assigned short-cuts (digits, numbers or characters) on the screen. Ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Patch (software)
A patch is data that is intended to be used to modify an existing software resource such as a program or a file, often to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities. A patch may be created to improve functionality, usability, or performance. A patch is typically provided by a vendor for updating the software that they provide. A patch may be created manually, but commonly it is created via a tool that compares two versions of the resource and generates data that can be used to transform one to the other. Typically, a patch needs to be applied to the specific version of the resource it is intended to modify, although there are exceptions. Some patching tools can detect the version of the existing resource and apply the appropriate patch, even if it supports multiple versions. As more patches are released, their cumulative size can grow significantly, sometimes exceeding the size of the resource itself. To manage this, the number of supported versions may be limited, or a complete c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Focus-follows-mouse
In a computing graphical user interface (GUI), a component has focus when it is selected to receive input from the user by an event such as a mouse button click or keypress. Moving the focus away from a specific user interface element is known as a blur event in relation to this element. Typically, the focus is withdrawn from an element by giving another element the focus. This means that focus and blur events are virtually simultaneous in relation to different user interface elements, one that becomes focused and one that is "blurred" (in the computing, not visual, sense). The concept is similar to a cursor in a text-based environment. However, when considering a graphical interface, there is also a mouse pointer involved. Moving the mouse will typically move the mouse pointer without changing the focus. The focus can usually be changed by clicking on a component that can receive focus with the mouse. Many desktops also allow the focus to be changed with the keyboard. By convent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dmenu
dwm is a minimalist dynamic window manager for the X Window System developed by Suckless that has influenced the development of several other X window managers, including xmonad and awesome. It is externally similar to wmii, but internally much simpler. dwm is written purely in C for performance and lacks any configuration interface besides editing the source code. One of the project's guidelines is that the source code is intended never to exceed 2000 SLOC, and options meant to be user-configurable are all contained in a single header file. Features dwm supports multiple workspaces and, unlike ratpoison, allows moving and resizing windows with the mouse. Older versions of dwm displayed their stdin in a status bar, along the edge of the screen. Recent versions instead display the root window's name, which can be set by independent processes. This is often used to show information that would appear in the notification area of other desktop environments—a clock, syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Desktop Environments
A desktop traditionally refers to: * The surface of a desk (often to distinguish office appliances that fit on a desk, such as photocopiers and printers, from larger equipment covering its own area on the floor) Desktop may refer to various computer terms: * Desktop computer, a personal computer designed to fit on a desk * Desktop metaphor, a style of graphical user interface modeled after a physical work surface **Desktop environment, software that provides a comprehensive computer user interface **.desktop file, providing configuration details for a program in a desktop environment **Remote desktop software, software that provides remote access to a computer's desktop * Client (computing), sometimes referred to as a desktop to distinguish the client from a server * Desktop (word processor), a program for the ZX Spectrum See also * * *Laptop {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Notification Area
The taskbar is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, displaying and facilitating switching between running programs. The taskbar and the associated Start Menu were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard. The taskbar is an exemplar of a category of always-visible graphical user interface elements that provide access to fundamental operating system functions and information. At the time of its introduction in 1995, the taskbar was unique among such elements because it provided the user with a means of switching between running programs through a single click of the pointing device. Since the introduction of Windows 95, other operating systems have incorporated graphical user interface elements that closely resemble the taskbar or have similar features. The designs vary, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Root Window
In the X Window System, a window is the region of the screen where drawing can occur. The root window covers the entire screen surface. Every window created is contained within it, forming a hierarchy with the root window at the very top. All other windows are either children or descendants of it. Since every window covers the part of its parent it is staying on, all other windows appear to be above the root window. As a result, the root window is visible as the part of the screen that is behind all other windows. In other words, the root window forms the background of the screen. An image can be used as the wallpaper of the screen by setting it as the background image of the root window. This can be done for example using the xsetroot or the xv programs. The direct children of the root window are called ''top-level windows''. These windows are usually drawn with a decorative frame and a title bar (which are actually added by the window manager). The top-level windows are, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |