|
Dutch Colonial Revival Architecture
Dutch Colonial is a style of domestic architecture, primarily characterized by gambrel roofs having curved eaves along the length of the house. Modern versions built in the early 20th century are more accurately referred to as "Dutch Colonial Revival", a subtype of the Colonial Revival style. History The modern use of the term is to indicate a broad gambrel roof with flaring eaves that extend over the long sides, resembling a barn in construction. The early houses built by settlers were often a single room, with additions added to either end (or short side) and very often a porch along both long sides. Typically, walls were made of stone and a chimney was located on one or both ends. Common were double-hung sash windows with outward swinging wood shutters and a central double Dutch door. Settlers of the Dutch colonies in New York, Delaware, New Jersey, and western Connecticut built these homes in ways familiar to the regions of Europe from which they came, like the Low Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Colonial Revival House In Plainfield, New Jersey
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to: * Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands ** Dutch people as an ethnic group () ** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship () ** Dutch language () * In specific terms, it reflects the Kingdom of the Netherlands ** Dutch Caribbean ** Netherlands Antilles Dutch may also refer to: Places * Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States * Pennsylvania Dutch Country People Ethnic groups * Pennsylvania Dutch, a group of early German immigrants to Pennsylvania Specific people * Dutch (nickname), a list of people * Johnny Dutch (born 1989), American hurdler and field athlete * Dutch Schultz (1902–1935), American mobster born Arthur Simon Flegenheimer * Dutch Mantel, ring name of American retired professional wrestler Wayne Maurice Keown (born 1949) * Dutch Savage, ring name of professional wrestler and promoter Frank Stewart (1935–2013) Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
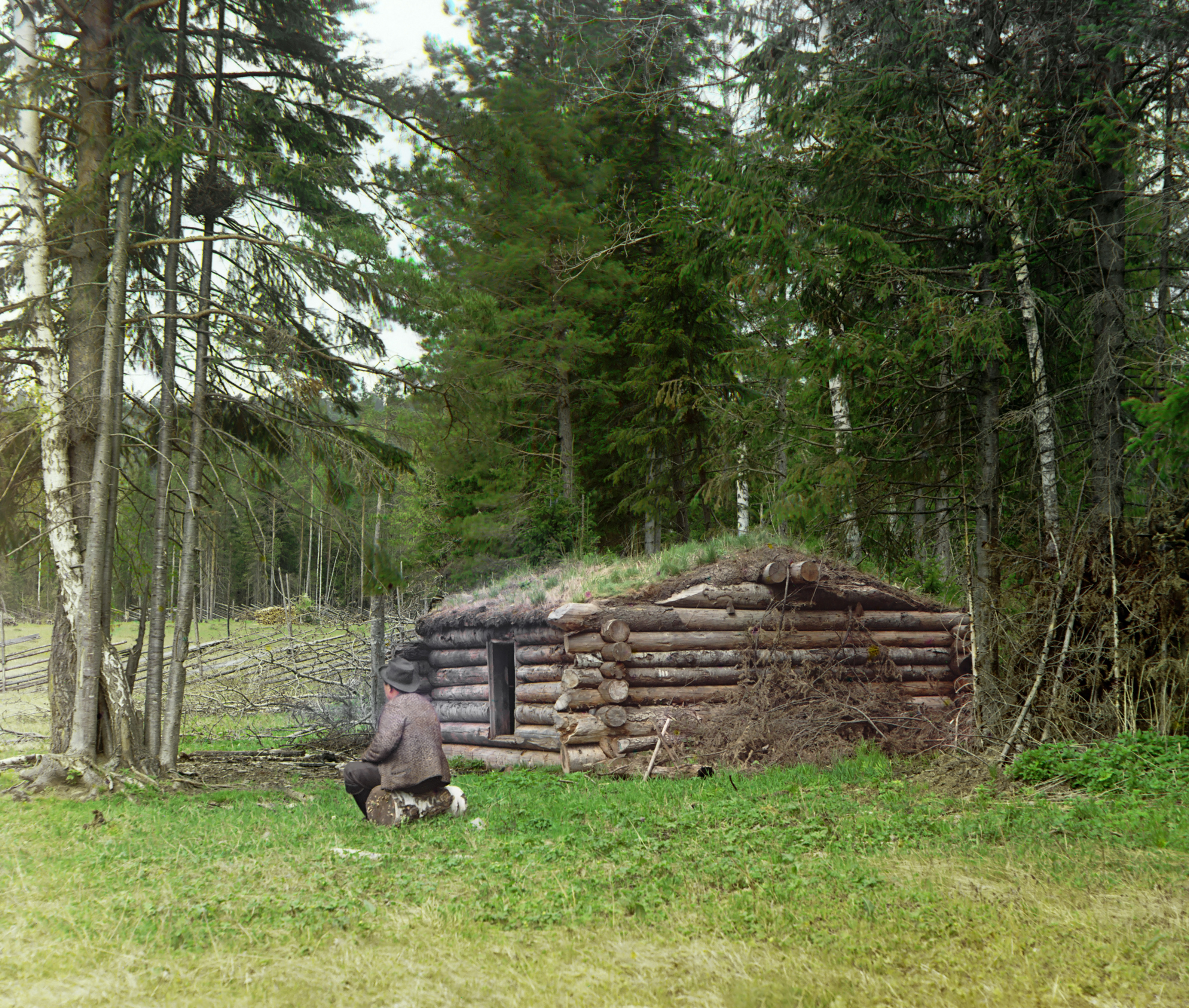
Log Cabin
A log cabin is a small log house, especially a minimally finished or less architecturally sophisticated structure. Log cabins have an ancient history in Europe, and in America are often associated with first-generation home building by settlers. History Europe Construction with logs was described by Roman architect Vitruvius Pollio in his architectural treatise ''De Architectura''. He noted that in Pontus in present-day northeastern Turkey, dwellings were constructed by laying logs horizontally overtop of each other and filling in the gaps with "chips and mud". Log cabin construction has its roots in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe. Although their precise origin is uncertain, the first log structures were probably being built in Northern Europe by the Bronze Age around 3500 BC. C. A. Weslager describes Europeans as having: A medieval log cabin was considered movable property, evidenced by the relocation of Espåby in 1557, where the buildings were disassembled, transpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transom (architectural)
In architecture, a transom is a transverse horizontal structural beam or bar, or a crosspiece separating a door from a window above it. This contrasts with a mullion, a vertical structural member. Transom or transom window is also the customary American English, U.S. word used for a transom light, the window over this crosspiece. In British English, Britain, the transom light is usually referred to as a fanlight, often with a semi-circular shape, especially when the window is segmented like the slats of a folding hand fan. A prominent example of this is at the main entrance of 10 Downing Street, the official residence of the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. History In Gothic architecture, early Gothic Church (building), ecclesiastical work, transoms are found only in belfry (architecture), belfry unglazed windows or spire lights, where they were deemed necessary to strengthen the mullions in the absence of the iron wiktionary:stay, stay bars, which in glazed windows served a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhang (architecture)
In architecture, an overhang is a protruding structure that may provide protection for lower levels. Overhangs on two sides of Pennsylvania Dutch barns protect doors, windows, and other lower-level structures. Overhangs on all four sides of barns and larger, older farmhouses are common in Swiss architecture. An overhanging eave is the edge of a roof, protruding outwards from the side of the building, generally to provide weather protection. History Overhangs are also common in medieval Indian architecture—especially Mughal architecture of the 16th–18th century, where they are called '' chhajja'', often supported by ornate corbels and also seen in Hindu temple architecture. Later, these were adopted by Indo-Saracenic architecture, which flourished during the British Raj. Extensive overhangs were incorporated in early Buddhist architecture; were seen in early Buddhist temples; and later became part of Tibetan architecture, Chinese architecture, and eventually, traditional Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeastern US
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is census regions United States Census BureauLocated on the Atlantic coast of North America, the region borders Canada to its north, the Southern United States to its south, the Midwestern United States to its west, and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The Northeast is one of the four regions defined by the U.S. Census Bureau for the collection and analysis of statistics. The Census Bureau defines the region as including the six New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont, and three lower North-Eastern states of New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania. Some expanded definitions of the region include Mid-Atlantic locations such as Delaware, Maryland, Northern Virginia, and Washington, D.C. The region is the base for the Northeast megalopolis, which includes many of the nation's largest metropolitan areas, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Public Library
The New York Public Library (NYPL) is a public library system in New York City. With nearly 53 million items and 92 locations, the New York Public Library is the second-largest public library in the United States behind the Library of Congress and the List of largest libraries, fifth-largest public library in the world. It is a private, non-governmental, independently managed, nonprofit corporation operating with both private and public financing. The library has branches in the boroughs of the Bronx, Manhattan, and Staten Island and affiliations with academic and professional libraries in the New York metropolitan area. The city's other two boroughs, Brooklyn and Queens, are not served by the New York Public Library system, but rather by their respective borough library systems: the Brooklyn Public Library and the Queens Public Library. The branch libraries are open to the general public and consist of Lending library, circulating libraries. The New York Public Library also has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Fire Of New York
The 1835 Great Fire of New York was one of three fires that rendered extensive damage to New York City in the 18th and 19th centuries. The fire occurred in the middle of an economic boom, covering 17 city blocks, killing two people, and destroying hundreds of buildings, with an estimated $20 million of property damage (equivalent to $ million in ). Background By 1835, New York City was the premier American city, and its financial prowess surpassed that of Philadelphia or Boston. The opening of the Erie Canal ten years earlier connected New York to raw materials and commercial interests in the Midwest and allowed the city to rise to prominence as a market hub. Over half of the country's exports left through New York Harbor, while more than a third of American imports arrived there. Insurance companies, investment firms, real estate companies and others made New York their home. As the city expanded northward and its economic significance increased, fire was a major concer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Fire Of New York (1776)
The Great Fire of New York was a devastating fire that burned through the night of September 20, 1776, and into the morning of September 21, on the West Side (Manhattan), West Side of what then constituted New York City at the Lower Manhattan, southern end of the island of Manhattan. It broke out in the early days of the military occupation of the city by Kingdom of Great Britain, British forces during the American Revolutionary War. The fire destroyed from 10 to 25 percent of the buildings in the city, while some unaffected parts of the city were plundered. Many people believed or assumed that one or more people deliberately started the fire, for a variety of different reasons. British leaders accused revolutionaries acting within the city and state, and many residents assumed that one side or the other had started it. The fire had long-term effects on the British occupation of the city, which did not end until 1783. Background The American Revolutionary War began in April 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
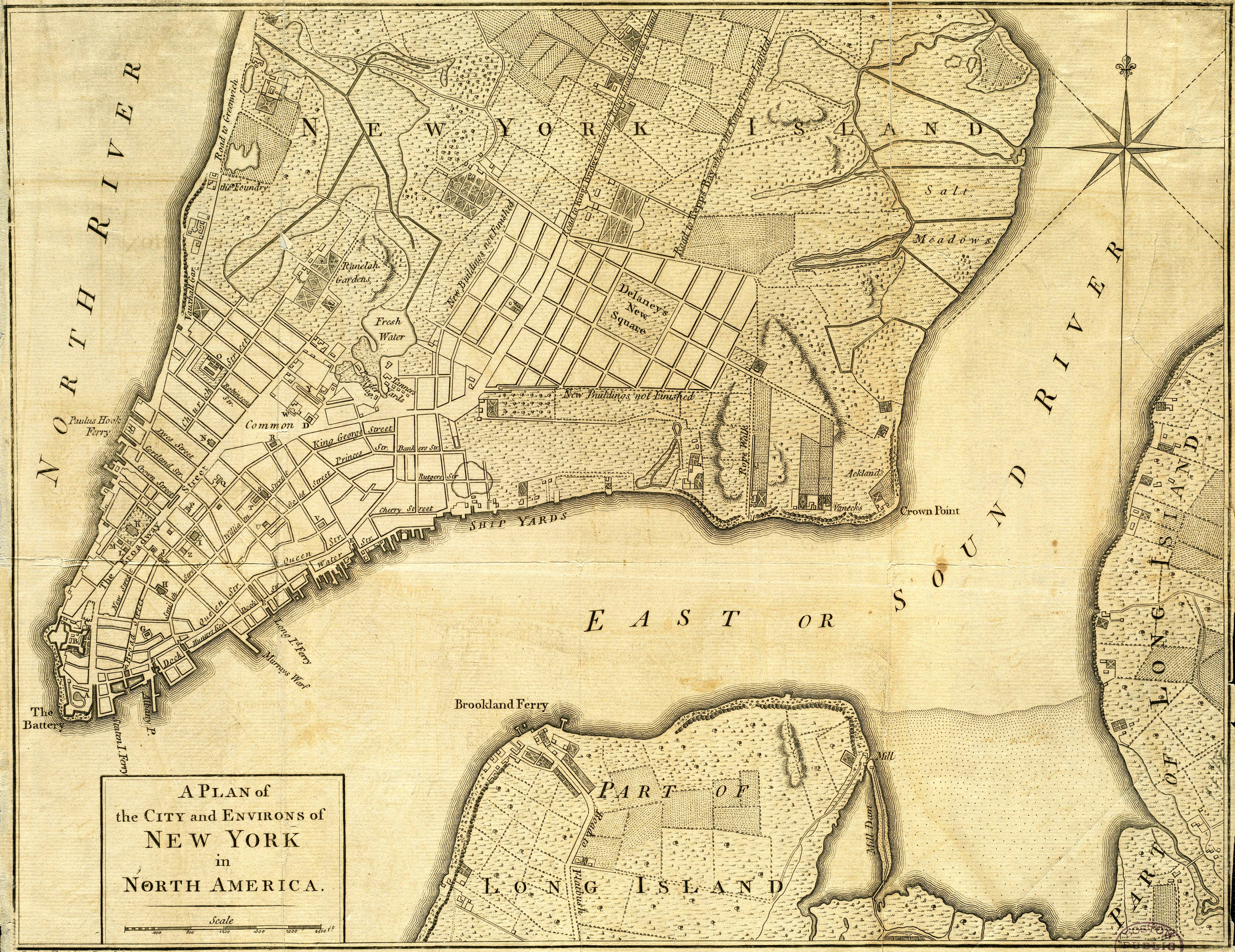
New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), factory'' gave rise to the settlement around Fort Amsterdam. The fort was situated on the strategic southern tip of the island of Manhattan and was meant to defend the fur trade operations of the Dutch West India Company in the North River (Hudson River). In 1624, it became a provincial extension of the Dutch Republic and was designated as the capital of the province in 1625. New Amsterdam became a city when it received Town privileges, municipal rights on February 2, 1653. By 1655, the population of New Netherland had grown to 9000 Dutch people, with 1,500 living in New Amsterdam. By 1664, the population of New Netherland had risen to almost 9,000 people, 2,500 of whom lived in New Amsterdam, 1,000 lived near Fort Orange (New Netherland), F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary
A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically (or by Semitic root, consonantal root for Semitic languages or radical-and-stroke sorting, radical and stroke for Logogram, logographic languages), which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, Bilingual dictionary, translation, etc.Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fourth Edition, 2002 It is a Lexicography, lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data. A broad distinction is made between general and specialized dictionaries. Specialized dictionaries include words in specialist fields, rather than a comprehensive range of words in the language. Lexical items that describe concepts in specific fields are usually called terms instead of words, although there is no consensus whether lexicology and terminology are two different fields of study. In theory, general dictionarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West End Collegiate Church 77 Jeh
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''vest'' in Romanian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב (maarav) 'west' from עֶרֶב (erev) 'evening'. West is sometimes abbreviated as W. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |