|
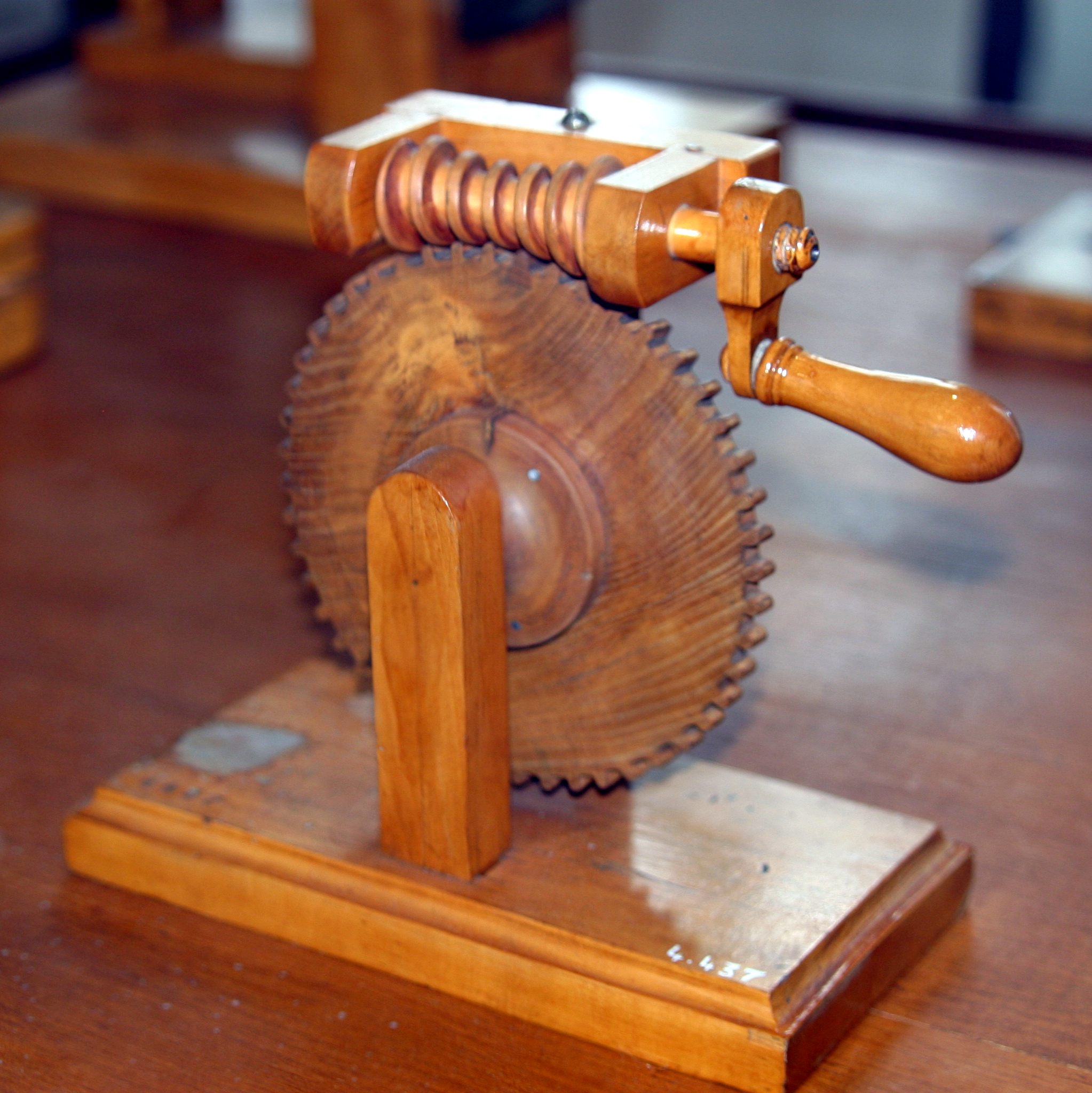
Duplex Worm
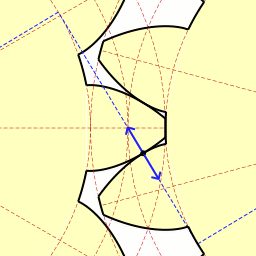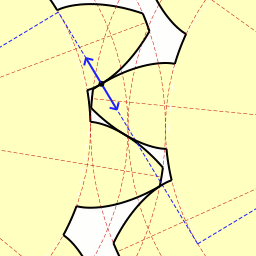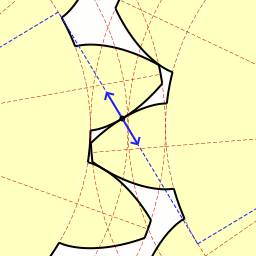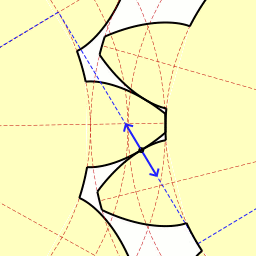
A duplex worm or dual lead worm is a worm gear set where the two flanks are manufactured with slightly different modules and/or diameter quotients. As a result of this, different lead angles on both tooth profiles are obtained, so that the tooth thickness is continuously increasing all over the worm length, while the gap between two threads is decreasing. This allows control of backlash. At the worm wheel, the different modules result in different addendum modification coefficients and rolling circle diameters at both flanks. Because of this the profiles are different at the front and at the rear flank. The thickness of each tooth and the tooth gaps remain constant at the circumference of the wheel. Backlash adjustment is done by shifting the worm axially, so that the section of the worm with the needed tooth thickness will be in contact with the wheel, giving the desired backlash (fig. 1). This way, backlash can be easily adjusted to any desired value when mounting the gear, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Worm Gear
A worm drive is a gear arrangement in which a worm (which is a gear in the form of a screw) meshes with a worm wheel (which is similar in appearance to a spur gear). The two elements are also called the worm screw and worm gear. The terminology is often confused by imprecise use of the term ''worm gear'' to refer to the worm, the worm wheel, or the worm drive as a unit. The worm drive or "endless screw" was invented by either Archytas of Terentum, Apollonius of Perga, or Archimedes, the last one being the most probable author.Witold Rybczynski, '' One good turn : a natural history of the screwdriver and the screw''. London, 2000. Page 139. The worm drive later appeared in the Indian subcontinent, for use in roller cotton gins, during the Delhi Sultanate in the thirteenth or fourteenth centuries.Irfan Habib''Economic History of Medieval India, 1200–1500'', page 53 Pearson Education Explanation A gearbox designed using a worm and worm wheel is considerably smaller than on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlash (engineering)
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash, play, or slop, is a clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be defined as "the maximum distance or angle through which any part of a mechanical system may be moved in one direction without applying appreciable force or motion to the next part in mechanical sequence."p. 1-8 An example, in the context of gears and gear trains, is the amount of clearance between mated gear teeth. It can be seen when the direction of movement is reversed and the slack or lost motion is taken up before the reversal of motion is complete. It can be heard from the railway couplings when a train reverses direction. Another example is in a valve train with mechanical tappets, where a certain range of lash is necessary for the valves to work properly. Depending on the application, backlash may or may not be desirable. Some amount of backlash is unavoidable in nearly all reversing mechanical couplings, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlash (gear)
In mechanical engineering, backlash, sometimes called lash, play, or slop, is a clearance or lost motion in a mechanism caused by gaps between the parts. It can be defined as "the maximum distance or angle through which any part of a mechanical system may be moved in one direction without applying appreciable force or motion to the next part in mechanical sequence."p. 1-8 An example, in the context of gears and gear trains, is the amount of clearance between mated gear teeth. It can be seen when the direction of movement is reversed and the slack or lost motion is taken up before the reversal of motion is complete. It can be heard from the railway couplings when a train reverses direction. Another example is in a valve train with mechanical tappets, where a certain range of lash is necessary for the valves to work properly. Depending on the application, backlash may or may not be desirable. Some amount of backlash is unavoidable in nearly all reversing mechanical couplings, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schnecken Spieleinstellung
Schnecken are a type of sweet bun or roll of German origin. Today schnecken can be commonly found in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, France, Israel, southern Brazil and the USA. The name ''Schnecken'' means ''snail A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastro ...s'' in German and refers to the shape of the pastry. The bun is still common in Germany and Austria (in some regions as ''Schneckennudel''), where the name is ''Schnecke'' (which is the German singular of ''Schnecken''), and in other parts of northern Europe. They are more commonly known as ''escargots'' (snails) or ''pain au raisin'' in France. Popular variants are Nussschnecken (filled with nuts and often raisins as well), Mohnschnecken (with a poppyseed filling) and Zimtschnecken, which are quite similar to cinnamon r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccentric (mechanism)
In mechanical engineering, an eccentric is a circular disk (''eccentric sheave'') solidly fixed to a rotating axle with its centre offset from that of the axle (hence the word "eccentric", out of the center). It is used most often in steam engines, and used to convert rotary motion into linear reciprocating motion to drive a sliding valve or pump ram. To do so, an eccentric usually has a groove at its circumference closely fitted a circular collar (''eccentric strap''). An attached ''eccentric rod'' is suspended in such a way that its other end can impart the required reciprocating motion. A return crank fulfills the same function except that it can only work at the end of an axle or on the outside of a wheel whereas an eccentric can also be fitted to the body of the axle between the wheels. Unlike a cam, which also converts rotary into linear motion at almost any rate of acceleration and deceleration, an eccentric or return crank can only impart an approximation of simple harmoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involute Gear
The involute gear profile is the most commonly used system for gearing today, with cycloid gearing still used for some specialties such as clocks. In an involute gear, the profiles of the teeth are ''involutes of a circle.'' The involute of a circle is the spiraling curve traced by the end of an imaginary taut string unwinding itself from that stationary circle called the base circle, or (equivalently) a triangle wave projected on the circumference of a circle. The involute gear profile was a fundamental advance in machine design, since unlike with other gear systems, the tooth profile of an involute gear depends only on the number of teeth on the gear, pressure angle, and pitch. That is, a gear's profile does not depend on the gear it mates with. Thus, n and m tooth involute spur gears with a given pressure angle and pitch will mate correctly, independently of n and m. This dramatically reduces the number of shapes of gears that need to be manufactured and kept in inventory. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Table
A rotary table is a precision work positioning device used in metalworking. It enables the operator to drill or cut work at exact intervals around a fixed (usually horizontal or vertical) axis. Some rotary tables allow the use of index plates for indexing operations, and some can also be fitted with dividing plates that enable regular work positioning at divisions for which indexing plates are not available. A rotary fixture used in this fashion is more appropriately called a dividing head (indexing head). Construction The table shown is a manually operated type. Powered tables under the control of CNC machines are now available, and provide a fourth axis to CNC milling machines. Rotary tables are made with a solid base, which has provision for clamping onto another table or fixture. The actual table is a precision-machined disc to which the work piece is clamped ( T slots are generally provided for this purpose). This disc can rotate freely, for indexing, or under the control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milling Machine
Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying direction on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of different operations and machines, on scales from small individual parts to large, heavy-duty gang milling operations. It is one of the most commonly used processes for machining custom parts to precise tolerances. Milling can be done with a wide range of machine tools. The original class of machine tools for milling was the milling machine (often called a mill). After the advent of computer numerical control (CNC) in the 1960s, milling machines evolved into ''machining centers'': milling machines augmented by automatic tool changers, tool magazines or carousels, CNC capability, coolant systems, and enclosures. Milling centers are generally classified as vertical machining centers (VMCs) or horizontal machining centers (HMCs). The integra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Press
A forming press, commonly shortened to press, is a machine tool that changes the shape of a work-piece by the application of pressure. The operator of a forming press is known as a press-tool setter, often shortened to tool-setter. Presses can be classified according to * their mechanism: hydraulic, mechanical, pneumatic; * their function: forging presses, stamping presses, press brakes, punch press, etc. * their structure, e.g. Knuckle-joint press, screw press * their controllability: conventional vs. servo-presses Shop Press Typically consisting of a simple rectangular frame, often fabricated from C-channel or tubing, containing a bottle jack or hydraulic cylinder to apply pressure via a ram to a work-piece. Often used for general-purpose forming work in the auto mechanic shop, machine shop, garage or basement shops, etc. Typical shop presses are capable of applying between 1 and 30 tons pressure, depending on size and construction. Lighter-duty versions are often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |