|
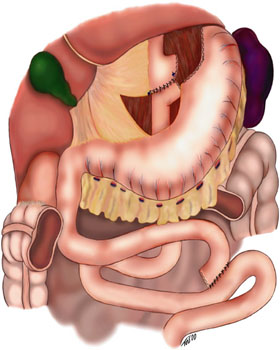
Duodenal-jejunal Bypass Liner
A duodenal-jejunal bypass liner, commonly called an EndoBarrier, is an implantable medical device in the form of a thin flexible 60 cm-long tube that creates a physical barrier between ingested food and the duodenum/ proximal jejunum. The duodenal-jejunal bypass liner prevents the interaction of food with enzymes and hormones in the proximal intestine to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity. The duodenal-jejunal bypass liner is delivered endoscopically and has been tested on the morbidly obese (those with a body mass index MIgreater than 40) as well as obese patients with a BMI less than 40, particularly those with difficult-to-manage type 2 diabetes. Despite a handful of serious adverse events such as gastrointestinal bleeding, abdominal pain, and device migration — all resolved with device removal — initial clinical trials have produced promising results in the treatment's ability to improve weight loss and glucose homeostasis outcomes. __TOC__ How it works The device is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implant (medicine)
An implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a Organ transplant, transplant, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a Biomaterial, biomedical material such as titanium, silicone, or apatite depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics, e.g. artificial pacemaker and cochlear implants. Some implants are Biological activity, bioactive, such as Subcutaneous tissue, subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stents. Applications Implants can roughly be categorized into groups by application: Sensory and neurological Perception, Sensory and Neurotechnology#Implant technologies, neurological implants are used for disorders affecting the major senses and the br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitinol
Nickel titanium, also known as Nitinol, is a metal alloy of nickel and titanium, where the two elements are present in roughly equal atomic percentages. Different alloys are named according to the weight percentage of nickel; e.g., Nitinol 55 and Nitinol 60. It exhibits the shape memory effect and superelasticity at different temperatures. Nitinol alloys exhibit two closely related and unique properties: the shape memory effect and superelasticity (also called pseudoelasticity). Shape memory is the ability of Nitinol to undergo deformation at one temperature, stay in its deformed shape when the external force is removed, then recover its original, undeformed shape upon heating above its "transformation temperature". Superelasticity is the ability for the metal to undergo large deformations and immediately return to its undeformed shape upon removal of the external load. Nitinol can deform 10–30 times as much as ordinary metals and return to its original shape. Whether Nitinol be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), also known as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide or gastric inhibitory peptide (also abbreviated as GIP), is an inhibiting hormone of the secretin family of hormones. While it is a weak inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, its main role is to stimulate insulin secretion. GIP, along with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), belongs to a class of molecules referred to as incretins. Synthesis and transport GIP is derived from a 153-amino acid proprotein encoded by the GIP gene and circulates as a biologically active 42-amino acid peptide. It is synthesized by K cells, which are found in the mucosa of the duodenum and the jejunum of the gastrointestinal tract. Like all endocrine hormones, it is transported by blood. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptors are seven-transmembrane proteins found on beta-cells in the pancreas. Functions It has traditionally been named ''gastrointestinal inhibitory peptide'' or ''gastric inhibitory pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucagon-like Peptide-1
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30- or 31-amino-acid-long peptide hormone deriving from the tissue-specific posttranslational processing of the proglucagon peptide. It is produced and secreted by intestinal enteroendocrine L-cells and certain neurons within the nucleus of the solitary tract in the brainstem upon food consumption. The initial product GLP-1 (1–37) is susceptible to amidation and proteolytic cleavage, which gives rise to the two truncated and equipotent biologically active forms, GLP-1 (7–36) amide and GLP-1 (7–37). Active GLP-1 protein secondary structure includes two α-helices from amino acid position 13–20 and 24–35 separated by a linker region. Alongside glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP), GLP-1 is an incretin; thus, it has the ability to decrease blood sugar levels in a glucose-dependent manner by enhancing the secretion of insulin. Beside the insulinotropic effects, GLP-1 has been associated with numerous regulatory and protective e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic). ''Ileum ''is derived from the Greek word ''eilein'', meaning "to twist up tightly". Structure The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine. It follows the jejunum and ends at the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum communicates with the cecum of the large intestine through the ileocecal valve. The ileum, along with the jejunum, is suspended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery refers to a technique in which the stomach is divided into a small upper pouch and a much larger lower "remnant" pouch and then the small intestine is rearranged to connect to both. Surgeons have developed several different ways to reconnect the intestine, thus leading to several different gastric bypass procedures (GBP). Any GBP leads to a marked reduction in the functional volume of the stomach, accompanied by an altered physiological and physical response to food. The operation is prescribed to treat morbid obesity (defined as a body mass index greater than 40), type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, and other comorbid conditions. ''Bariatric surgery'' is the term encompassing ''all'' of the surgical treatments for morbid obesity, not just gastric bypasses, which make up only one class of such operations. The resulting weight loss, typically dramatic, markedly reduces comorbidities. The long-term mortality rate of gastric bypass patients has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery (or weight loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. Long term weight loss through the standard of care procedures ( Roux en-Y bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch) is largely achieved by altering gut hormone levels responsible for hunger and satiety, leading to a new hormonal weight set point. Bariatric surgery is the most effective treatment causing weight loss and reducing complications of obesity. As of October 2022, the American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) and International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity (IFSO) recommend bariatric surgery for adults with a body mass index (BMI) >35, regardless of obesity-associated conditions, and recommend considering surgery for people with BMI 30.0-34.9 who have metabolic disease. This is a recent change in guidelines (October 2022), so other guideline-producing organizations and health insurance plans may t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chyme
Chyme or chymus (; from Greek χυμός ''khymos'', "juice") is the semi-fluid mass of partly digested food that is expelled by a person's stomach, through the pyloric valve, into the duodenum '''' (the beginning of the ). Chyme results from the mechanical and chemical breakdown of a bolus and consists of partially digested food, water, |
Blood Sugar
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blood of a 70 kg (154 lb) human at all times. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level at the expense of glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle. In humans, a blood glucose level of 4 grams, or about a teaspoon, is critical for normal function in a number of tissues, and the human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasting, sedentary individuals. A persistent elevation in blood glucose leads to glucose toxicity, which contributes to cell dysfunction and the pathology grouped together as complications of diabetes. Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Device
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as c. 7000 BC in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it wasn't until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres. The BMI may be determined using a table or chart which displays BMI as a function of mass and height using contour lines or colours for different BMI categories, and which may use other units of measurement (converted to metric units for the calculation). The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as ''underweight'', ''normal weight'', ''overweight'', or ''obese'' based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult BMI classifications are underweight (under 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 24.9), overweight (25 to 29.9), and obese (30 or more). When used to predict an individual's health, rather than as a statistical measurement for groups, the BMI has limitations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoscope
An endoscope is an inspection instrument composed of image sensor, optical lens, light source and mechanical device, which is used to look deep into the body by way of openings such as the mouth or anus. A typical endoscope applies several modern technologies including optics, ergonomics, precision mechanics, electronics, and software engineering. With an endoscope, it is possible to observe lesions that cannot be detected by X-ray, making it useful in medical diagnosis. Endoscopes use tubes which are only a few millimeters thick to transfer illumination in one direction and high-resolution images in real time in the other direction, resulting in minimally invasive surgeries. It is used to examine the internal organs like the throat or esophagus. Specialized instruments are named after their target organ. Examples include the cystoscope (bladder), nephroscope (kidney), bronchoscope (bronchus), arthroscope (joints) and colonoscope (colon), and laparoscope (abdomen or pelvis). They c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |