|
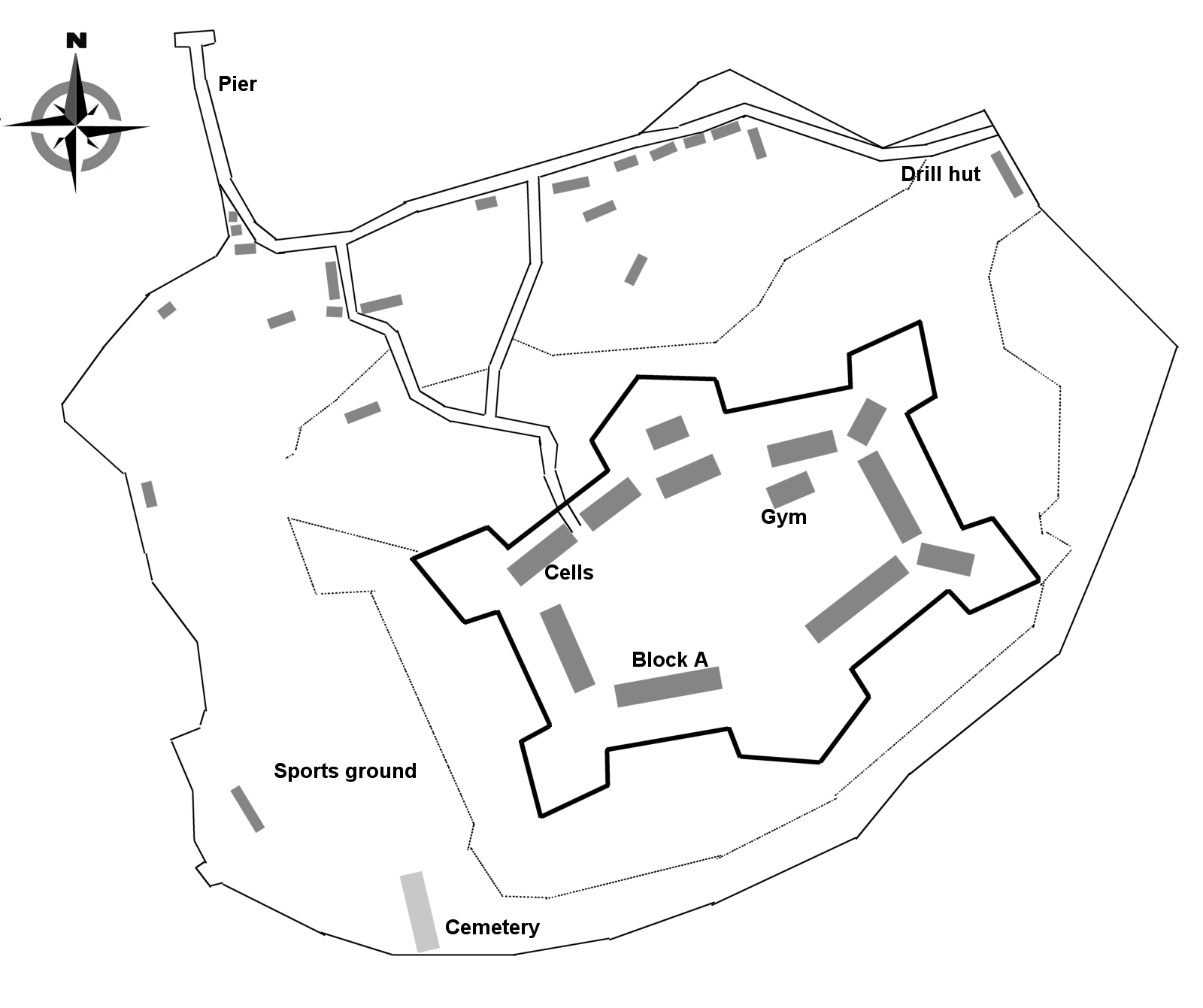
Dundalk Gaol
Dundalk Gaol is a former gaol (prison) in Dundalk, County Louth, Ireland. The men's wing is now "The Oriel Centre", the women's wing is the Louth County Archive and the Governor's House now a Garda station. __TOC__ History Built in 1853 to help with the overcrowding of the gaol already in place at Crow Street - which is now Dundalk Town Hall. It was designed by John Neville and cost £23,000 to be constructed. The gaol was opened on 19 January 1854. For approximately 60 years the gaol functioned largely as an unremarkable county gaol, averaging 25 prisoners at any one time, with few sentences of more than 2 years. During the 1870s it became the practice to send major offenders to a convict prison in Dublin, and a number of county gaols were closed. This caused an overcrowding problem and a Royal Commission Report of 1877 recommended more prisons and even portable iron jails. Also Australia was refusing to accept any more Irish convicts. This led to the extension of prisons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol (dated, standard English, Australian, and historically in Canada), penitentiary (American English and Canadian English), detention center (or detention centre outside the US), correction center, correctional facility, lock-up, hoosegow or remand center, is a facility in which inmates (or prisoners) are confined against their will and usually denied a variety of freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for various crimes. Prisons are most commonly used within a criminal justice system: people charged with crimes may be imprisoned until their trial; those pleading or being found guilty of crimes at trial may be sentenced to a specified period of imprisonment. In simplest terms, a prison can also be described as a building in which people are legally held as a punishment for a crime they have committed. Prisons can also be used as a tool of political repression by authoritarian regimes. Their perceived opponents may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dundalk
Dundalk ( ; ga, Dún Dealgan ), meaning "the fort of Dealgan", is the county town (the administrative centre) of County Louth, Ireland. The town is on the Castletown River, which flows into Dundalk Bay on the east coast of Ireland. It is halfway between Dublin and Belfast, close to the border with Northern Ireland. It is the eighth largest urban area in Ireland, with a population of 39,004 as of the 2016 census. Having been inhabited since the Neolithic period, Dundalk was established as a Norman stronghold in the 12th century following the Norman invasion of Ireland, and became the northernmost outpost of The Pale in the Late Middle Ages. The town came to be nicknamed the "Gap of the North" where the northernmost point of the province of Leinster meets the province of Ulster. The modern street layout dates from the early 18th century and owes its form to James Hamilton (later 1st Earl of Clanbrassil). The legends of the mythical warrior hero Cú Chulainn are set in the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ga, An Lú) is a coastal county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of Meath to the south, Monaghan to the west, Armagh to the north and Down to the north-east, across Carlingford Lough. It is the smallest county in Ireland by land area and the 17th most populous, with just over 139,100 residents as of 2022. The county is named after the village of Louth. Louth County Council is the local authority for the county. History County Louth is named after the village of Louth, which in turn is named after Lugh, a god of the ancient Irish. Historically, the placename has had various spellings; , , and (see Historic Names List, for full listing). is the modern simplified spelling. The county is steeped in myth, legend and history, and is a setting in the epic. Later it saw the influence of the Vikings, as seen in the name of Carlingford Lough. They also established a longphort a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest on Earth. Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garda Síochána
(; meaning "the Guardian(s) of the Peace"), more commonly referred to as the Gardaí (; "Guardians") or "the Guards", is the national police service of Ireland. The service is headed by the Garda Commissioner who is appointed by the Irish Government. Its headquarters are in Dublin's Phoenix Park. Since the formation of the in 1923, it has been a predominantly unarmed force, and more than three-quarters of the force do not routinely carry firearms. As of 31 December 2019, the police service had 14,708 sworn members (including 458 sworn Reserve members) and 2,944 civilian staff. Operationally, the is organised into four geographical regions: the East, North/West, South and Dublin Metropolitan regions. The force is the main law enforcement agency in the state, acting at local and national levels. Its roles include crime detection and prevention, drug enforcement, road traffic enforcement and accident investigation, diplomatic and witness protection responsibilities. It also pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spike Island, County Cork
Spike Island ( gle, Inis Píc) is an island of in Cork Harbour, Ireland. Originally the site of a monastic settlement, the island is dominated by an 18th-century bastion fort now named Fort Mitchel. The island's strategic location within the harbour meant it was used at times for defence and as a prison. Since the early 21st century the island has been developed as a heritage tourist attraction, with €5.5 million investment in exhibition and visitor spaces and accompanying tourism marketing. There were in excess of 81,000 visitors to the island during 2019, a 21% increase on 2018 numbers. Spike Island was named top European tourist attraction at the 2017 World Travel Awards. History Early history The principal evidence for a monastic foundation on Spike Island comes from Archdall's ''Moanasticon Hibernicum'', which states that Saint Mochuada founded a monastery there in the 7th century. While this may be correct, another passage from the "Life of St Mochuada" implies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Northern Division Of The Irish Republican Army
The Fourth Northern Division of the Irish Republican Army operated in an area covering parts of counties Louth, Armagh, Monaghan, and Down during the Irish War of Independence and Civil War. Frank Aiken was commander and Pádraig Quinn was the quartermaster general. John McCoy was Adjutant General for the division. After McCoy was shot and captured by British Crown forces in 1921, Seán F. Quinn, Pádraig's brother, took over the position. At the outbreak of the Civil War, the Fourth Northern Division was neutral and in control of the Dundalk military barracks after the British Army vacated it on 13 April 1922. Aiken was in Dublin with Richard Mulcahy ( Chief of Staff of the IRA until the split), arguing against the Free State taking military action against a large anti-treaty IRA force which had taken over the Four Courts. Mulcahy ordered Aiken back to Dundalk. On 4 July, Aiken wrote to Mulcahy stating the Fourth Northern Division would stay neutral, called for an end to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Republican Army (1922–69)
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various paramilitary organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dedicated to irredentism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions, to such a degree that many subsequent paramilitary organisations have been known by that title – most notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austin Stack
Augustine Mary Moore Stack (7 December 1879 – 27 April 1929) was an Irish republican and politician who served as Minister for Home Affairs from 1921 to 1922. He was a Teachta Dála (TD) from 1918 to 1927. Early life Stack was born in Ballymullen, Tralee, County Kerry, to William Stack, an attorney's clerk, and Nanette O'Neill. He was educated at the Christian Brothers School in Tralee. At the age of fourteen, he left school and became a clerk in a solicitor's office. A gifted Gaelic footballer, he captained the Kerry team to All-Ireland victory in 1904. He also served as President of the Kerry Gaelic Athletic Association County Board. Activism He became politically active in 1908 when he joined the Irish Republican Brotherhood. In 1916, as commandant of the Kerry Brigade of the Irish Volunteers, he made preparations for the landing of arms by Roger Casement. He was made aware that Casement was arrested on Easter Saturday and was being held in Tralee. He made no attempt to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Aiken
Francis Thomas Aiken (13 February 1898 – 18 May 1983) was an Irish revolutionary and politician. He was chief of staff of the Anti-Treaty IRA at the end of the Irish Civil War. Aiken later served as Tánaiste from 1965 to 1969 and Minister for External Affairs from 1951 to 1954 and 1957 to 1969. Previously he had held the posts of Minister for Finance from 1945 to 1948, Minister for the Co-ordination of Defensive Measures 1939 to 1945, Minister for Defence from 1932 to 1939, and was also Minister for Lands and Fisheries from June–November 1936. He was a Teachta Dála (TD) for the Louth constituency from 1923 to 1973, making him the second longest-serving member of Dáil Éireann and the longest-serving cabinet minister. Originally a member of Sinn Féin, he was later a founding member of Fianna Fáil. Early life Early years Frank Aiken was born on 13 February 1898 at Carrickbracken, Camlough, County Armagh, Ireland, the seventh and youngest child of James Aiken, a builde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Civil War
The Irish Civil War ( ga, Cogadh Cathartha na hÉireann; 28 June 1922 – 24 May 1923) was a conflict that followed the Irish War of Independence and accompanied the establishment of the Irish Free State, an entity independent from the United Kingdom but within the British Empire. The civil war was waged between the Provisional Government of Ireland (1922), Provisional Government of Ireland and the Irish Republican Army (1922–1969), Irish Republican Army (IRA) over the Anglo-Irish Treaty. The Provisional Government (which became the Free State in December 1922) supported the terms of the treaty, while the Anglo-Irish Treaty#Dáil debates, anti-treaty opposition saw it as a betrayal of the Irish Republic which had been proclaimed during the Easter Rising of 1916. Many of those who fought on both sides in the conflict had been members of the IRA during the War of Independence. The Civil War was won by the pro-treaty Free State forces, who benefited from substantial quantities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seán Treacy
Seán Allis Treacy ( ga, Seán Ó Treasaigh; 14 February 1895 – 14 October 1920) was one of the leaders of the Third Tipperary Brigade of the IRA during the Irish War of Independence. He was one of a small group whose actions initiated that conflict in 1919. He was killed in October 1920, on Talbot Street in Dublin, in a shootout with British troops during an aborted British Secret Service surveillance operation. Although sometimes written as Tracey, as inscribed on the commemorative plaque in Talbot Street, or even as Tracy, his surname is more usually spelt 'Treacy'. Early life and Irish Republicanism Born as John Treacy, Seán Allis Treacy came from a small-farming background in Soloheadbeg in west Tipperary and grew up in Hollyford. He was the son of farmer Denis Treacy and Bridget Allis. He left school aged 14 and worked as a farmer, also developing deep patriotic convictions; locally, he was seen as a promising farmer, calm, direct, ready to experiment with new met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)