|
Duncan McNeill, 1st Baron Colonsay
Duncan McNeill, 1st Baron Colonsay FRSE (20 August 1793 – 31 January 1874) was a Scottish advocate, judge and Tory politician. He was Lord Justice General and Lord President of the Court of Session between 1852 and 1867. His younger brother was the physician and diplomat Sir John McNeill. Background and education McNeill was born on the island of Oronsay in the Inner Hebrides, the son of John McNeill (1767–1846), laird of Colonsay and Oronsay, and his wife Hester (née McNeill). Educated at St Andrew's University where he graduated MA in 1809.. He served his apprenticeship in Edinburgh under Michael Linning WS, based at 6 St James Square. He became a member of the Faculty of Advocates in 1816. He was the presumptive father of philosopher Edmund Montgomery. Political, legal and judicial career He was Advocate Depute in Edinburgh 1820 to 1824. MacNeill was appointed Sheriff of Perthshire in 1824. He served under Sir Robert Peel as Solicitor General for Scotland from 1834 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duncan McNeill, 1st Baron Colonsay
Duncan McNeill, 1st Baron Colonsay FRSE (20 August 1793 – 31 January 1874) was a Scottish advocate, judge and Tory politician. He was Lord Justice General and Lord President of the Court of Session between 1852 and 1867. His younger brother was the physician and diplomat Sir John McNeill. Background and education McNeill was born on the island of Oronsay in the Inner Hebrides, the son of John McNeill (1767–1846), laird of Colonsay and Oronsay, and his wife Hester (née McNeill). Educated at St Andrew's University where he graduated MA in 1809.. He served his apprenticeship in Edinburgh under Michael Linning WS, based at 6 St James Square. He became a member of the Faculty of Advocates in 1816. He was the presumptive father of philosopher Edmund Montgomery. Political, legal and judicial career He was Advocate Depute in Edinburgh 1820 to 1824. MacNeill was appointed Sheriff of Perthshire in 1824. He served under Sir Robert Peel as Solicitor General for Scotland from 1834 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheriff Of Perth
The Sheriff of Perth was historically a royal official, appointed for life, who was responsible for enforcing justice in Perth, Scotland. Prior to 1748 most sheriffdoms were held on a hereditary basis. From that date, following the Jacobite uprising of 1745, the hereditary sheriffs were replaced by salaried sheriff-deputes, qualified advocates who were members of the Scottish Bar. Following consecutive reorganisations of the Scottish sheriffdoms the position became the Sheriff of Perthshire in 1747 and the Sheriff of Perth & Angus in 1934. The sheriffdom was dissolved in 1975 and replaced by that of Tayside, Central and Fife. Sheriffs of Perth *Kenneth (1164) *Roger de Mortimer of Aberdour (1209) *John de Moray (1210) * Geoffrey de Inverkunglas (1219) *John Hay of Naughton (1226-1228) *William Blund (1228) *Malcolm of Moray (1236) *Adam de Lochore *William de Munfichet (1245) *John Hay of Naughton (1246) *William de Lauder (1251) *David de Lochore (1255) * Gilbert de la Hay (12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pau, Pyrénées-Atlantiques
Pau (, ) is a Communes of France, commune overlooking the Pyrenees, and prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Pyrénées-Atlantiques, regions of France, region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine, France. The city is located in the heart of the former sovereign principality of Béarn, of which it was the capital from 1464. Pau lies on the Gave de Pau, and is located from the Atlantic Ocean and from Spain. This position gives it a striking panorama across the mountain range of the Pyrenees, especially from its landmark "Boulevard des Pyrénées", as well as the hillsides of Jurançon AOC, Jurançon. According to Alphonse de Lamartine, "Pau has the world's most beautiful view of the earth just as Naples has the most beautiful view of the sea." The site has been occupied since at least the Roman Gaul, Gallo-Roman era. However the first references to Pau as a settlement only occur in the first half of the 12th century. The town developed from the construction of its Château ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Highland And Agricultural Society Of Scotland
The Royal Highland and Agricultural Society of Scotland (RHASS) was founded in Edinburgh in 1784 as the Highland Society of Edinburgh. The Society had its root in 1723 when the Society of Improvers of the Knowledge of Agriculture in Scotland was created in Edinburgh.Scottish Garden Buildings by Tim Buxbaum p.15 It was remodelled and renamed in 1784 largely in reaction to the subsistence crises of 1782/3 when many of the estates in the highlands and islands of Scotland were not producing enough food to feed tenants. The Society is responsible for organising the annual Royal Highland Show. Famous members include Sir Walter Scott and James MacDonald, secretary from 1893 to 1912. See also * Highland Society of London * Royal Highland Showground The Royal Highland Centre, originally the Royal Highland Showground, is an exhibition centre and showground located at Ingliston in the western outskirts of Edinburgh, Scotland, adjacent to Edinburgh Airport and the A8. History The Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
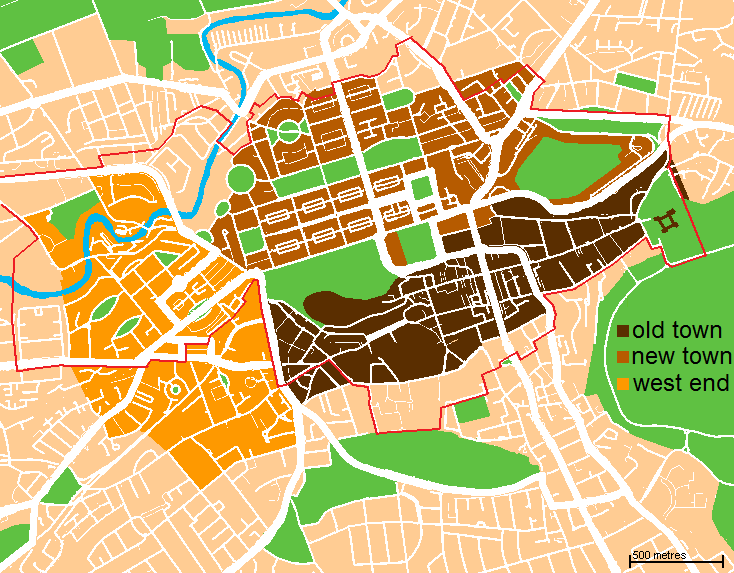
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh University
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's four ancient universities and the sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played an important role in Edinburgh becoming a chief intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the "Athens of the North." Edinburgh is ranked among the top universities in the United Kingdom and the world. Edinburgh is a member of several associations of research-intensive universities, including the Coimbra Group, League of European Research Universities, Russell Group, Una Europa, and Universitas 21. In the fiscal year ending 31 July 2021, it had a total income of £1.176 billion, of which £3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Shank More
John Shank More (sometimes written as John Schank More) LL.D FRSE RSA (1784–1861) was the Chair of Scots Law at the University of Edinburgh which he held from 1843 to 1861. He was involved in the anti-slavery movement and was Vice-President of the Royal Scottish Society of Arts. Life More was born in North Shields in County Durham, the son of Reverend George More (1744-1827), for some time Presbyterian minister at South Shields, and his wife Catharine (1749-1827). His parents retired to Edinburgh around 1805, living at 82 Nicolson Street. His parents later moved to 4 Hill Square. He was called to the Bar in 1806. He married Mary Gillespie (1784-1849) in 1811. They initially lived near his parents at 32 Nicolson Street. In the 1820s he was living at 19 Great King Street. He edited Charles Erskine’s ''Principles'' and Stair’s ''Institutions''. He was considered "a suitably learned man who inspired some affection in his students despite the dullness of his lecturing sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
73 Great King Street, Edinburgh
73 may refer to: * 73 (number) * one of the years 73 BC, AD 73, 1973, 2073 * ''73'' (magazine), a United States-based amateur radio magazine * 73 Best regards, a popular Morse code abbreviation * ''No. 73'', a British 1980s children's TV show *Nickname for the Boeing 737 airplane *73 Bristol–Cribbs Causeway The 73 is a bus route that operates between Bristol Temple Meads railway station and Cribbs Causeway. History The former 74 bus route was merged with the 73 from 1 September 2013. The frequency of the combined route was a bus every 10 minute ..., a bus route in England See also * List of highways numbered * {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of Session
The senators of the College of Justice are judges of the College of Justice, a set of legal institutions involved in the administration of justice in Scotland. There are three types of senator: Lords of Session (judges of the Court of Session); Lords Commissioners of Justiciary (judges of the High Court of Justiciary); and the Chairman of the Scottish Land Court. Whilst the High Court and Court of Session historically maintained separate judiciary, these are now identical, and the term ''Senator'' is almost exclusively used in referring to the judges of these courts. Senators of the college use the title ''Lord'' or ''Lady'' along with a surname or a territorial name. Note, however, that some senators have a peerage title, which would be used instead of the senatorial title. All senators of the college have the honorific, ''The Honourable'', before their titles, while those who are also privy counsellors or peers have the honorific, ''The Right Honourable''. Senators are made p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senator Of The College Of Justice
The senators of the College of Justice are judges of the College of Justice, a set of legal institutions involved in the administration of justice in Scotland. There are three types of senator: Lords of Session (judges of the Court of Session); Lords Commissioners of Justiciary (judges of the High Court of Justiciary); and the Chairman of the Scottish Land Court. Whilst the High Court and Court of Session historically maintained separate judiciary, these are now identical, and the term ''Senator'' is almost exclusively used in referring to the judges of these courts. Senators of the college use the title ''Lord'' or ''Lady'' along with a surname or a territorial name. Note, however, that some senators have a peerage title, which would be used instead of the senatorial title. All senators of the college have the honorific, ''The Honourable'', before their titles, while those who are also privy counsellors or peers have the honorific, ''The Right Honourable''. Senators are made pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyllshire (UK Parliament Constituency)
Argyllshire was a county constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of Great Britain from 1708 to 1800 and of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom from 1801 until 1983. The constituency was named Argyll from 1950. The constituency was replaced in 1983 with Argyll and Bute. It elected one Member of Parliament (MP) using the first-past-the-post voting system. Creation The British parliamentary constituency was created in 1708 following the Acts of Union, 1707 and replaced the former Parliament of Scotland shire constituency of Argyllshire . Local government areas Until Scottish counties were abolished, for most purposes, in 1975, the constituency represented the county of Argyll, except that constituency boundaries may not have coincided at all times with county boundaries, and any parliamentary burgh within the county would have been outside the constituency. In 1975 most of the county plus the Isle of Bute became the Argyll district of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of Parliament (United Kingdom)
In the United Kingdom, a member of Parliament (MP) is an individual elected to serve in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Electoral system All 650 members of the UK House of Commons are elected using the first-past-the-post voting system in single member constituencies across the whole of the United Kingdom, where each constituency has its own single representative. Elections All MP positions become simultaneously vacant for elections held on a five-year cycle, or when a snap election is called. The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 set out that ordinary general elections are held on the first Thursday in May, every five years. The Act was repealed in 2022. With approval from Parliament, both the 2017 and 2019 general elections were held earlier than the schedule set by the Act. If a vacancy arises at another time, due to death or resignation, then a constituency vacancy may be filled by a by-election. Under the Representation of the People Act 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |