|
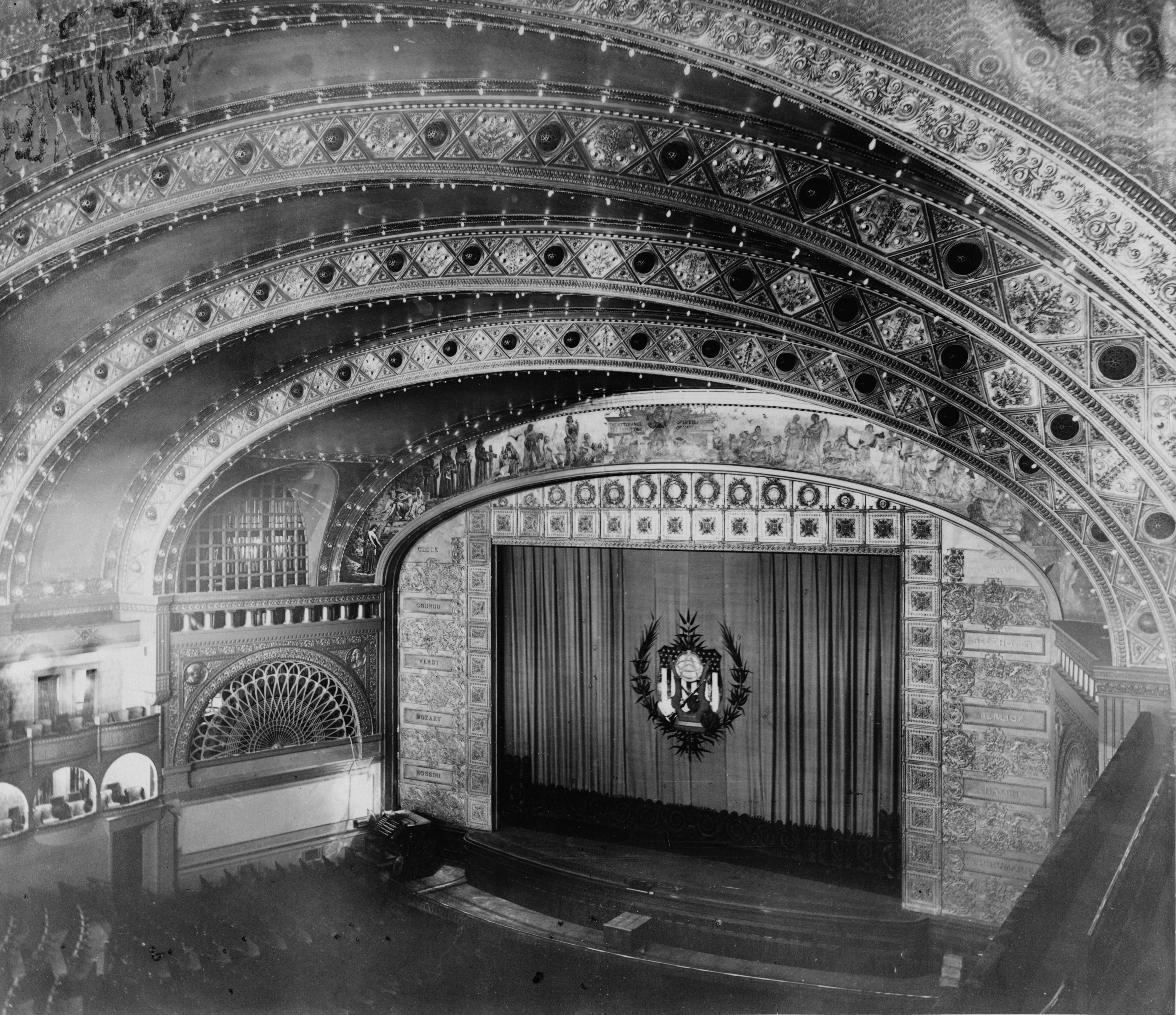
Dunamaise Arts Centre
Dunamaise Arts Centre () is an arts and cultural centre located in Portlaoise, Ireland, opened in 1999. History Maryborough Gaol was built in a Neoclassical style. It is a seven- bay, two-storey building over a concealed basement with a three-bay central breakfront, built of limestone and Portland stone. It was renovated in the 1990s, and opened in 1999 as Dunamaise Arts Centre, named for the nearby Rock of Dunamase, a medieval fortress. Facilities The theatre has 238 seats; it has a proscenium arch A proscenium ( grc-gre, προσκήνιον, ) is the metaphorical vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor ... and measures wide, deep and high. There is also an exhibition gallery, restaurant and workshop spaces. References {{Theatres in Ireland Theatres in County Laois Defunct prisons in the Republic of Ireland Buildings and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portlaoise
Portlaoise ( ), or Port Laoise (), is the county town of County Laois, Ireland. It is located in the Midland Region, Ireland, South Midlands in the province of Leinster. The 2016 census shows that the town's population increased by 9.5% to 22,050, which was well above the national average of 3.8%. It is the most populous and also the most densely populated town in the Midland Region, Ireland, Midland Region, which has a total population of 292,301 at the 2016 census. This also makes it the fastest growing of the top 20 largest towns and cities in Ireland. It was an important town in the medieval period, as the site of the Fort of Maryborough, a fort built by English settlers in the 16th century during the Plantations of Ireland#Early plantations (1556–1576), Plantation of Queen's County. Portlaoise is fringed by the Slieve Bloom Mountains, Slieve Bloom mountains to the west and north-west and the Great Heath of Maryborough to the east. It is notable for its architecture, engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Laois
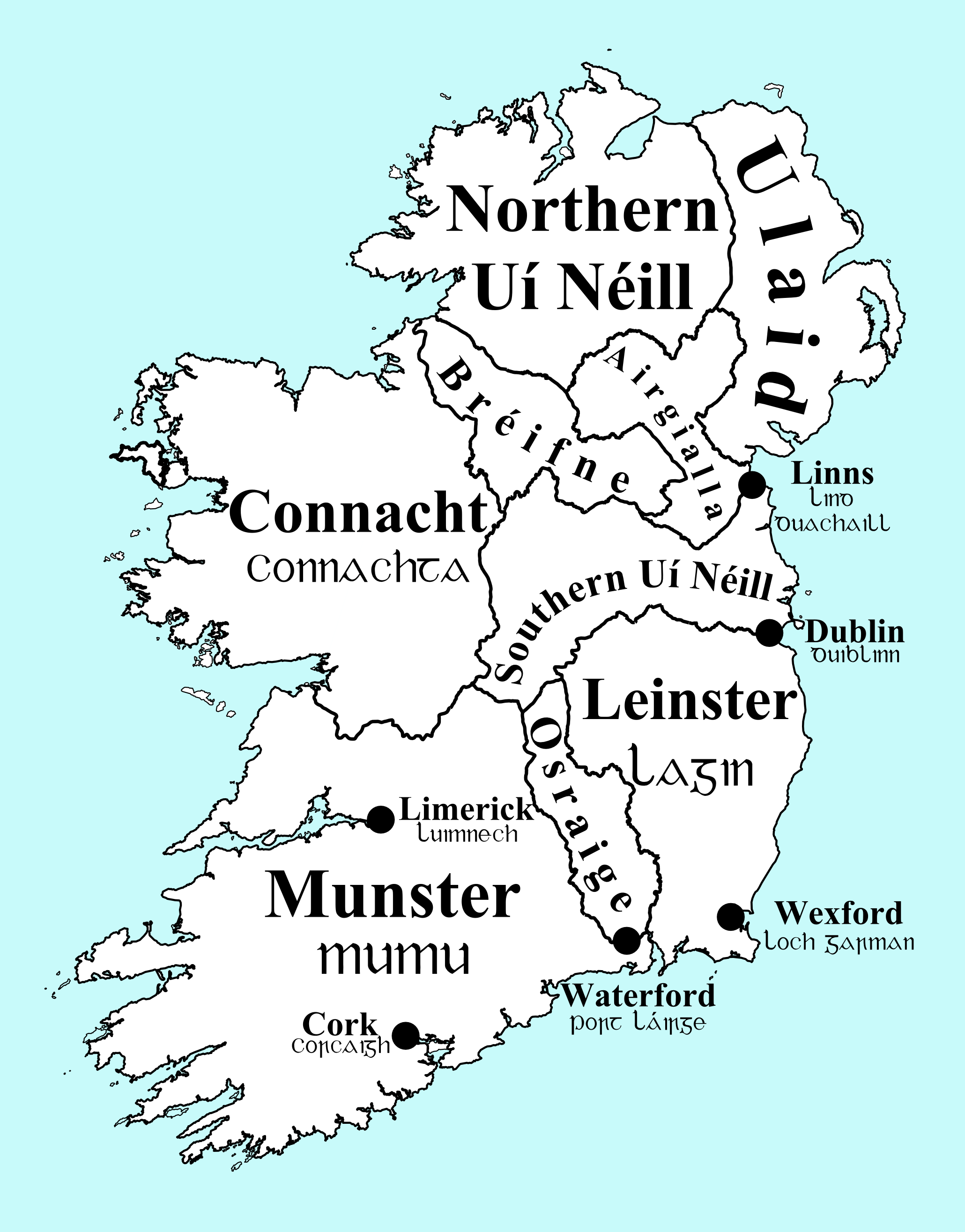
County Laois ( ; gle, Contae Laoise) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and in the province of Leinster. It was known as Queen's County from 1556 to 1922. The modern county takes its name from Loígis, a medieval kingdom. Historically, it has also been known as County Leix. Laois County Council is the local authority for the county. At the 2022 census, the population of the county was 91,657, an increase of 56% since the 2002 census. History Prehistoric The first people in Laois were bands of hunters and gatherers who passed through the county about 8,500 years ago. They hunted in the forests that covered Laois and fished in its rivers, gathering nuts and berries to supplement their diets. Next came Ireland's first farmers. These people of the Neolithic period (4000 to 2500 BC) cleared forests and planted crops. Their burial mounds remain in Clonaslee and Cuffsborough. Starting around 2500 BC, the people of the Bronze Age lived in Laois. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. Around 2.1 million of the country's population of 5.13 million people resides in the Greater Dublin Area. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the , consists of a lower house, ; an upper house, ; and an elected President () who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the (Prime Minister, literally 'Chief', a title not used in English), who is elected by the Dáil and appointed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portlaoise Railway Station
Portlaoise railway station is a station on the Dublin to Cork and also the Dublin to Limerick Intercity railway lines. It is also the terminus for the South Western Commuter also called the Portlaoise Commuter Line which forms part of the Dublin Suburban Rail network in the commuter belt for Dublin. It is the busiest county town railway station in the midlands region with up to 32 trains to Dublin (10 Non-Stop) and 30 trains from Dublin (9 Non-Stop) per day. It is situated in Portlaoise town centre, in County Laois. History Portlaoise (formerly Maryborough) railway station opened on 26 June 1847. It was designed by Sancton Wood. In March 2008, Irish Rail opened a new Traincare depot south-west of Portlaoise town centre (officially opened on 25 July 2008). The depot provides a high quality maintenance and servicing facility for the 183 intercity railcars and some facilities for outer suburban railcars serving the Dublin - Portlaoise route. Irish Rail also have their Permanent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Center
A cultural center or cultural centre is an organization, building or complex that promotes culture and arts. Cultural centers can be neighborhood community arts organizations, private facilities, government-sponsored, or activist-run. Asia * Central Cultural Center (CCC), Bangladesh * Bahman Cultural Center, Tehran, Iran * Bangkok Art and Culture Centre, Bangkok, Thailand * Beigang Cultural Center, Yunlin, Taiwan * Bentara Budaya Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia * Bentara Budaya Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia * Cultural Center of the Philippines, Philippines * Hong Kong Cultural Centre, Hong Kong, China * Japanese Cultural Center, Taipei, Taiwan * Kaohsiung Cultural Center, Kaohsiung, Taiwan * Keelung Cultural Center, Keelung, Taiwan * Ketagalan Culture Center, Taipei, Taiwan * King Abdulaziz Center for World Culture, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia * Kohima Capital Cultural Center, Kohima, Nagaland * Korean Cultural Center, Seoul, Korea * Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salem Cultural Centre, Kuwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing styles of architecture in most of Europe for the previous two centuries, Renaissance architecture and Baroque architecture, already represented partial revivals of the Classical architecture of ancient Rome and (much less) ancient Greek architecture, but the Neoclassical movement aimed to strip away the excesses of Late Baroque and return to a purer and more authentic classical style, adapted to modern purposes. The development of archaeology and published accurate records of surviving classical buildings was crucial in the emergence of Neoclassical architecture. In many countries, there was an initial wave essentially drawing on Roman architecture, followed, from about the start of the 19th century, by a second wave of Greek Revival architec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay (architecture)
In architecture, a bay is the space between architectural elements, or a recess or compartment. The term ''bay'' comes from Old French ''baie'', meaning an opening or hole."Bay" ''Online Etymology Dictionary''. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=bay&searchmode=none accessed 3/10/2014 __NOTOC__ Examples # The spaces between posts, columns, or buttresses in the length of a building, the division in the widths being called aisles. This meaning also applies to overhead vaults (between ribs), in a building using a vaulted structural system. For example, the Gothic architecture period's Chartres Cathedral has a nave (main interior space) that is '' "seven bays long." '' Similarly in timber framing a bay is the space between posts in the transverse direction of the building and aisles run longitudinally."Bay", n.3. def. 1-6 and "Bay", n.5 def 2. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press 2009 # Where there a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portland Stone
Portland stone is a limestone from the Tithonian stage of the Jurassic period quarried on the Isle of Portland, Dorset. The quarries are cut in beds of white-grey limestone separated by chert beds. It has been used extensively as a building stone throughout the British Isles, notably in major public buildings in London such as St Paul's Cathedral and Buckingham Palace. Portland Stone is also exported to many countries—being used for example in the United Nations headquarters in New York City. Geology Portland Stone formed in a marine environment, on the floor of a shallow, warm, sub-tropical sea probably near land (as evidenced by fossilized driftwood, which is not uncommon). When seawater is warmed by the sun, its capacity to hold dissolved gas is reduced; consequently, dissolved carbon dioxide (CO2) is released into the atmosphere as a gas. Calcium and bicarbonate ions within the water are then able to combine, to form calcium carbonate (CaCO3) as a precipitate. The proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Of Dunamase
Dunamase or the Rock of Dunamase ( ga, Dún Másc "fort of Másc") is a rocky outcrop in County Laois, Ireland. Rising above a plain, it has the ruins of Dunamase Castle, a defensive stronghold dating from the early Hiberno-Norman period with a view across to the Slieve Bloom Mountains. It is near the N80 road between the towns of Portlaoise and Stradbally. History Excavations in the 1990s demonstrated that the Rock was first settled in the 9th century when a hill fort or ''dún'' was constructed on the site. The first known settlement on the rock was Dun Masc, or Masc’s Fort, an early Christian settlement that was pillaged in 842 by the Vikings. In 845 the Vikings of Dublin attacked the site and the abbot of Terryglass, Aed son of Dub dá Chrích, was killed there.''Annals of Ulster'' 845.2; '' Cogad Gaedel re Gallaib'' 19. There is no clear evidence of 10th–11th century occupation. The castle was built in the second half of the 12th century. When the Normans arrive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proscenium Arch
A proscenium ( grc-gre, προσκήνιον, ) is the metaphorical vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor itself, which serves as the frame into which the audience observes from a more or less unified angle the events taking place upon the stage during a theatrical performance. The concept of the fourth wall of the theatre stage space that faces the audience is essentially the same. It can be considered as a social construct which divides the actors and their stage-world from the audience which has come to witness it. But since the curtain usually comes down just behind the proscenium arch, it has a physical reality when the curtain is down, hiding the stage from view. The same plane also includes the drop, in traditional theatres of modern times, from the stage level to the "stalls" level of the audience, which was the original meaning of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_facade_on_Piazza_dei_signori.jpg)


_(29318027412).jpg)
