|
Dukinfield Cricket Club
Dukinfield is a town in Tameside, Greater Manchester, England, on the south bank of the River Tame opposite Ashton-under-Lyne, east of Manchester. At the 2011 Census, it had a population of 19,306. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Cheshire, the town developed as a result of the Industrial Revolution when it became the site of coal mining and cotton manufacturing. History Early history The earliest evidence of human activity around Dukinfield comes from a collection of four flints from the late Neolithic/early Bronze Age. The artifacts were discovered on the site of Dukinfield Hall and have been taken as evidence of a prehistoric settlement on the site. There is no further evidence of activity in the area until the Roman period. A 3rd century bronze Roman coin, from the reign of Emperor Tetricus I was discovered in the town. Dukinfield means "Raven of the Field" and derives from the Old English ''duce'' and ''feld''. Early records show the township was inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dukinfield Town Hall
Dukinfield Town Hall is a municipal building in King Street, Dukinfield, Greater Manchester, England. The town hall, which was the headquarters of Dukinfield Borough Council, is a grade II listed building. History Shortly after it had been created in 1857, the local board of health established itself in some offices on the east side of King Street in an area designated the Market Place. Population growth associated with the increasing number of local cotton mills led to the area becoming an urban district in 1894 and a municipal borough in 1899. In this context civic leaders decided to demolish the existing offices and to erect a town hall slightly further back from where they had been. The foundation stone for the new building was laid by Mrs Gertrude Susan Nicholson of Dukinfield Lodge and of Arisaig on 23 September 1899. It was designed by John Eaton, Sons and Cantrell in the Gothic style, built by John Robinson of Ashton-under-Lyne and officially opened by the mayor, Alderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunham Massey
Dunham Massey is a civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford, Greater Manchester, England. The parish includes the villages of Sinderland Green, Dunham Woodhouses and Dunham Town, along with Dunham Massey Hall and Park, formerly the home of the last Earl of Stamford and owned by the National Trust since 1976. Dunham Massey is in the historic county of Cheshire, but since 1974 has been part of Trafford Metropolitan Borough; the nearest town is Altrincham. At the 2001 census, the parish had a population of 475. Dunham Massey's history is reflected in its 45 listed buildings. It was a regionally important place during the medieval period, and the seat of the Massey barons. The Georgian mansion with the remains of a castle on its grounds is a popular tourist attraction. There are two Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Dunham Massey: Dunham Park, located south of Dunham Town, and Brookheys Covert. History The Roman road between Chester and York passing between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
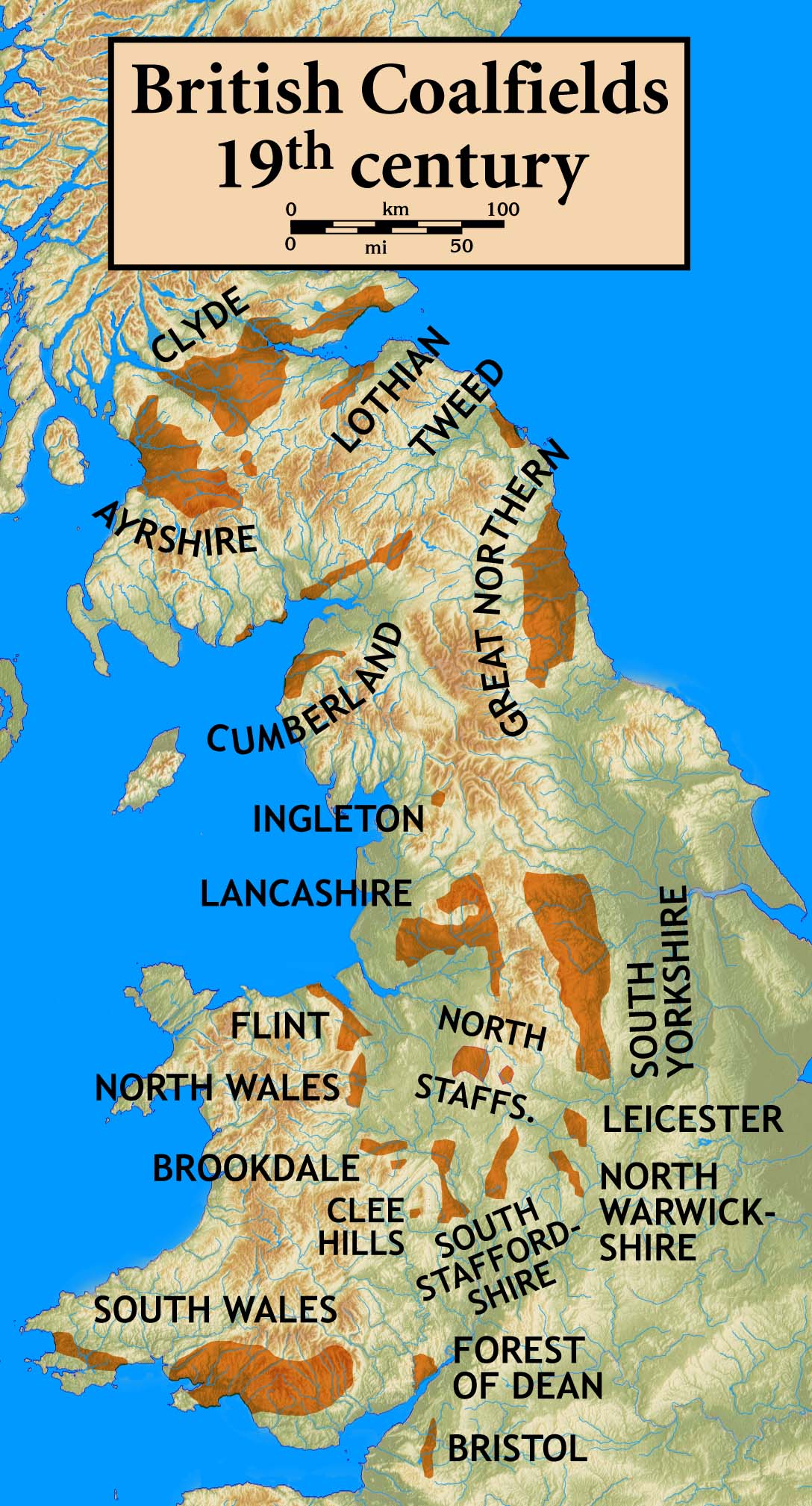
Lancashire Coalfield
The Lancashire Coalfield in North West England was an important British coalfield. Its coal seams were formed from the vegetation of tropical swampy forests in the Carboniferous period over 300 million years ago. The Romans may have been the first to use coal in Lancashire and its shallow seams and outcrops were exploited on a small scale from the Middle Ages and extensively after the start of the Industrial Revolution. The coalfield was at the forefront of innovation in coal mining, prompting the country's first canals, use of steam engines and creating conditions favourable for rapid industrialisation. The pits on the coalfield were at their most productive in 1907 when more than 26 million tons of coal were produced. By 1967 just 21 collieries remained. Parkside Colliery in Newton-le-Willows, St. Helens area, the last deep mine to be sunk on the coalfield, was closed in 1993. Geology The geology of the coalfield consists of the coal seams of the Upper, Middle and Lower Coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Measures
In lithostratigraphy, the coal measures are the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. In the United Kingdom, the Coal Measures Group consists of the Upper Coal Measures Formation, the Middle Coal Measures Formation and the Lower Coal Measures Formation. The group records the deposition of fluvio-deltaic sediments which consists mainly of clastic rocks (claystones, shales, siltstones, sandstones, conglomerates) interstratified with the beds of coal. In most places, the coal measures are underlain by coarser clastic sequences known as Millstone Grit, of Namurian age. The top of the coal measures may be marked by an unconformity, the overlying rocks being Permian or later in age. In some parts of Britain, however, the coal measures grade up into mainly coal-barren red beds of late Westphalian and possibly Stephanian age. Within the Pennine Basin these barren measures are now referred to as the Warwickshire Group, from the district where they achieve their thickest d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Mill
A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning (textiles), spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system. Although some were driven by animal power, most early mills were built in rural areas at fast-flowing rivers and streams using water wheels for power. The development of viable Watt steam engine, steam engines by Boulton and Watt from 1781 led to the growth of larger, steam-powered mills allowing them to be concentrated in urban mill towns, like Manchester, which with neighbouring Salford, Greater Manchester, Salford had more than 50 mills by 1802. The mechanisation of the spinning process in the early factories was instrumental in the growth of the machine tool industry, enabling the construction of larger cotton mills. Joint stock company, Limited companies were developed to construct mills, and the trading floors of the Manchester Royal Excha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of The Manor
Lord of the Manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England, referred to the landholder of a rural estate. The lord enjoyed manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seignory, the right to grant or draw benefit from the estate. The title continues in modern England and Wales as a legally recognised form of property that can be held independently of its historical rights. It may belong entirely to one person or be a moiety shared with other people. A title similar to such a lordship is known in French as ''Sieur'' or , in German, (Kaleagasi) in Turkish, in Norwegian and Swedish, in Welsh, in Dutch, and or in Italian. Types Historically a lord of the manor could either be a tenant-in-chief if he held a capital manor directly from the Crown, or a mesne lord if he was the vassal of another lord. The origins of the lordship of manors arose in the Anglo-Saxon system of manorialism. Following the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Astley (painter)
John Astley (24 June 1724 – 14 November 1787) was an English portrait painter and amateur architect, known for his "patronage among a vast circle of fashion" as well as a fortune acquired through marriage. Early life Born in Wem, Shropshire, England, John Astley was a son of an apothecary, Richard Astley (1671–1754), and his wife, Margaret (1685–1735). Among his siblings was a brother Richard, also a physician, whose estate he inherited. Due to his good looks, he was known as ''Beau Astley''. Some period sources also call him ''Jack Astley''. A biographer of Sir Joshua Reynolds described Astley as "a gasconading spendthrift and a beau of the flashiest order." Several jaundiced contemporary accounts of Astley's character exist, notably a lengthy observation by John Williams, (aka Anthony Pasquin), who wrote: "He thought that every advantage in civil society was compounded in women and wine: and, acting up to this principal of bliss, he gave his body to Euphrosy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manorialism
Manorialism, also known as the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fortified manor house in which the lord of the manor and his dependents lived and administered a rural estate, and a population of labourers who worked the surrounding land to support themselves and the lord. These labourers fulfilled their obligations with labour time or in-kind produce at first, and later by cash payment as commercial activity increased. Manorialism is sometimes included as part of the feudal system. Manorialism originated in the Roman villa system of the Late Roman Empire, and was widely practiced in medieval western Europe and parts of central Europe. An essential element of feudal society, manorialism was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new forms of agrarian contract. In examining the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dukinfield Baronets
The Baronetcy of Dukinfield of Dukinfield, Cheshire was created in the Baronetage of England on 16 June 1665 for Robert Dukinfield, son of Colonel Robert Dukinfield. The Dukinfield family were seated at Dukinfield, Cheshire from the early 14th century. Dukinfield Hall was demolished in about 1950. Colonel Robert Dukinfield served in the army of the Commonwealth of England during the English Civil War and was high sheriff of Cheshire in 1625 and 1648 and Governor of Chester in 1650. Despite his father's loyalties, his son Robert was raised to the Baronetcy following the English Restoration and served as High Sheriff of Cheshire in 1675. His son the 2nd Baronet married the niece of Sir Samuel Daniel who bequeathed his estate at Over Tabley, Cheshire to William, 3rd Baronet, who by Act of Parliament changed his name to Dukinfield-Daniel. On his death the 3rd Baronet left all his estates to his daughter, through whom they passed to John Astley (1724–1787). The Baronetcy passed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Model Army
The New Model Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms in that members were liable for service anywhere in the country, rather than being limited to a single area or garrison. To establish a professional officer corps, the army's leaders were prohibited from having seats in either the House of Lords or House of Commons. This was to encourage their separation from the political or religious factions among the Parliamentarians. The New Model Army was raised partly from among veteran soldiers who already had deeply held Puritan religious beliefs, and partly from conscripts who brought with them many commonly held beliefs about religion or society. Many of its common soldiers therefore held dissenting or radical views unique among English armies. Although the Army's senior officers d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Duckenfield
Lieutenant Colonel Robert Duckenfield (1619–1689) was a Parliamentarian commander during the English Civil War. Family history Robert Duckenfield came from Dukinfield in Cheshire and was born to Robert and Frances Duckenfield in 1619. The Duckenfields were a noted local family and their history in Cheshire can be traced back to the 13th century. On 28 August 1619 he was baptised in Stockport. Robert Duckenfield married Martha, the daughter of Sir Miles Fleetwood of Hesketh in Lancashire. Their son, also called Robert, born c. 1642, was raised to a baronet. Civil War During the Civil War, Duckenfield was appointed High Sheriff of Cheshire for six months in 1649. He also played a more active role in the Civil War as he defended Stockport Bridge against Prince Rupert and conducted the siege of Wythenshawe. In 1650, he was made the Governor of Chester. Most notably, he commanded the Parliamentary forces which captured the Isle of Man ) , anthem = "O Land of Our Birth" , im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



_by_Robert_Walker_and_studio.jpg)