|
Duke Zhuang I Of Qi
Duke Zhuang I of Qi (; died 731 BC) was from 794 to 731 BC the twelfth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Zhou dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Gou (呂購), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Zhuang was his posthumous title. He was the first of the two Qi rulers called Duke Zhuang. Reign Duke Zhuang succeeded his father Duke Cheng of Qi, who died in 795 BC, as ruler of Qi. He had a long reign during an era of upheaval in China. In 771 BC, the Quanrong tribes from the west attacked Haojing, capital of the Zhou dynasty, and killed King You of Zhou. Duke Xiang of the state of Qin sent his army to escort King You's son King Ping of Zhou to the new capital Luoyi, marking the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty. As a reward for Qin's protection King Ping formally granted Duke Xiang of Qin a nobility rank and elevated Qin to the status of a vassal state on par with other major states such as Qi and Jin. Although Qi was little affected by the turmoil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (state)
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a state of the Zhou dynasty-era in ancient China, variously reckoned as a march, duchy, and independent kingdom. Its capital was Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou overthrow of Shang in the 11th centuryBC. Its first marquis was Jiang Ziya, minister of King Wen and a legendary figure in Chinese culture. His family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was replaced by the Tian family in 386BC. In 221BC, Qi was the final major state annexed by Qin during its unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou conquest of Shang, Jiang Ziya, a native of Ju County served as the chief minister to King Wu. After King Wu's death, Ziya remained loyal to the Duke of Zhou during the Three Guards' failed rebellion against his regency. The Shang prince Wu Geng had joined the revolt along with the Dongyi states of Yan, Xu, and Pugu. These were suppressed by 1039 BC and Jiang w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Ping Of Zhou
King Ping of Zhou (; died 720 BC), personal name Ji Yijiu, was the thirteenth king of the Zhou dynasty and the first of the Eastern Zhou dynasty.Sima Qian. ''Records of the Grand Historian'', "Zhou Dynasty Annals". History He was the son of King You of Zhou and Queen Shen (申后). King You had exiled Queen Shen and Ji Yijiu after the king became enamoured with his concubine Bao Si and made her queen and his son Bofu his heir. As a result, Queen Shen’s father, the Marquess of Shen, teamed with the Quanrong nomads and local satellite states to overthrow King You. In the Battle of Mount Li King You and Bofu were killed, and Bao Si captured. Li Yijiu ascended the throne. At about the same time, Jī Hàn (姬翰), Duke of Guó (虢公), elevated Jī Yúchén (姬余臣) to the throne as King Xie of Zhou (周携王), and the Zhou Dynasty saw a period of two parallel kings until King Xie was killed by Marquis Wen of Jin (晋文侯) in 750 BCE. King Ping moved the Western Zhou dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Qi (state)
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim themself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Wu Of Qi
Duke Wu of Qi (; died 825 BC) was from 850 to 825 BC the eighth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Western Zhou Dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Shou (呂壽), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Wu was his posthumous title. Duke Wu succeeded his father Duke Xian of Qi, who died in 851 BC, as ruler of Qi. He reigned for 26 years and died in 825 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Duke Li of Qi. Family Sons: * Prince Wuji (; d. 816 BC), ruled as Duke Li of Qi from 824–816 BC Daughters: * Queen Xian of Zhou (), known as Queen Jiang ** Married King Xuan of Zhou (d. 782 BC) in 826 BC, and had issue (King You of Zhou King You of Zhou (; 795–771 BC), personal name Ji Gongsheng, was the twelfth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the last of Western Zhou Dynasty. He reigned from 781 to 771 BC. History In 780 BC, a major earthquake hit Guanzhong. A soothsa ...) Ancestry References {{DEFAULTSORT:Wu of Qi, Duke Monarchs of Qi (state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Li Of Qi
Duke Li of Qi (; died 816 BC) was from 824 to 816 BC the ninth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Western Zhou dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Wuji (呂無忌), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Li was his posthumous title. Duke Li succeeded his father Duke Wu of Qi, who died in 825 BC, as ruler of Qi. He was a despotic ruler, and in 816 BC the people of Qi rebelled against him and tried to make the son of Duke Hu of Qi, Duke Li's grand-uncle, the new ruler. Duke Li was killed by the rebels, but Duke Hu's son also died in the fighting. Subsequently, Duke Li's son Duke Wen ascended the throne, and executed 70 people who were responsible for Duke Li's death. Family Sons: * Prince Chi (; d. 804 BC), ruled as Duke Wen of Qi Duke Wen of Qi (; died 804 BC) was from 815 to 804 BC the tenth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Western Zhou Dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Chi (呂赤), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Wen Of Qi
Duke Wen of Qi (; died 804 BC) was from 815 to 804 BC the tenth recorded ruler of the State of Qi during the Western Zhou Dynasty of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Chi (呂赤), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜), and Duke Wen was his posthumous title. Duke Wen's father Duke Li of Qi was a despotic ruler, and in 816 BC the people of Qi rebelled and tried to make the son of Duke Hu of Qi, Duke Li's grand-uncle, the new ruler. Duke Li was killed by the rebels, but Duke Hu's son also died in the fighting. Subsequently, Duke Wen ascended the throne, and executed 70 people who were responsible for his father's death. Duke Wen reigned for 12 years and died in 804 BC. He was succeeded by his son, Duke Cheng of Qi. Family Sons: * Prince Tuo (; d. 795 BC), ruled as Duke Cheng of Qi from 803–795 BC * Prince Gao (), the grandfather of Gao Xi (), who was the progenitor of the Gao lineage Daughters: * Qi Jiang () ** Married Marquis Mu of Jin (d. 785 BC) in 808 BC, and had issue (Marqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wey (state)
Wei (; ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; Old Chinese: ''*ɢʷat-s''), commonly spelled Wey to distinguish from the contemporary larger Wei (state), Wei () state, was an State (Ancient China), ancient Chinese state that was founded in the early Western Zhou dynasty and rose to prominence during the Spring and Autumn period. Its rulers were of the surname Ji (), the same as that of the rulers of Zhou. It was located in modern northeastern Henan Province, east of Jin (Chinese state), Jin (and later Wei ), and west of Cao (state), Cao. Early history The history of Wey dates back to the beginning of the Zhou Dynasty and the Rebellion of the Three Guards. After the Duke of Zhou successfully defeated the rebellion, Shu Feng of Kang, Kang Shu, a younger brother of King Wu of Zhou was given a fief centred on Zhaoge, the capital ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuzhi (Qi)
Wuzhi (; died 685 BC), also called Gongsun Wuzhi (公孫無知, ''Gongsun'' meaning grandson of a duke), was for a few months in early 685 BC ruler of the State of Qi during the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. His personal name was Lü Wuzhi (呂無知), ancestral name Jiang ( 姜). Unlike most rulers, he was not given a posthumous title because he killed the monarch and usurped the throne. Early life Wuzhi's father Yi Zhongnian was a son of Duke Zhuang I of Qi and younger brother of Duke Xi of Qi. Yi Zhongnian died in 699 BC, but Wuzhi's uncle Duke Xi loved him and gave him the same treatment as his son, Crown Prince Zhu'er. However, the next year Duke Xi died and Zhu'er, Wuzhi's cousin, ascended the throne (posthumously known as Duke Xiang of Qi). Duke Xiang disliked Wuzhi and demoted his status. Murdering Duke Xiang In the twelfth month of 686 BC, the twelfth year of his reign, Duke Xiang injured his foot on a hunting trip. When the duke was recovering in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the Qin dynasty arose as a fief of the Western Zhou and endured for over five centuries until 221 BCE when it founded its brief empire, which lasted only until 206 BCE. It often causes confusion that the ruling family of the Qin kingdom (what is conventionally called a "dynasty") ruled for over five centuries, while the "Qin Dynasty," the conventional name for the first Chinese empire, comprises the last fourteen years of Qin's existence. The divide between these two periods occurred in 221 BCE when King Zheng of Qin declared himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor of Qin, though he had already been king of Qin since 246 BCE. Qin was a minor power for the early centuries of its existence. The streng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jin (Chinese State)
Jin (, Old Chinese: ''*''), originally known as Tang (唐), was a major state during the middle part of the Zhou dynasty, based near the centre of what was then China, on the lands attributed to the legendary Xia dynasty: the southern part of modern Shanxi. Although it grew in power during the Spring and Autumn period, its aristocratic structure saw it break apart when the duke lost power to his nobles. In 403BC, Jin was split into three successor states: Han, Zhao and Wei. The Partition of Jin marks the end of the Spring and Autumn Period and the beginning of the Warring States period. Geography Jin was located in the lower Fen River drainage basin on the Shanxi plateau. To the north were the Xirong and Beidi peoples. To the west were the Lüliang Mountains and then the Loess Plateau of northern Shaanxi. To the southwest the Fen River turns west to join the south-flowing part of the Yellow River which soon leads to the Guanzhong, an area of the Wei River Valley that wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
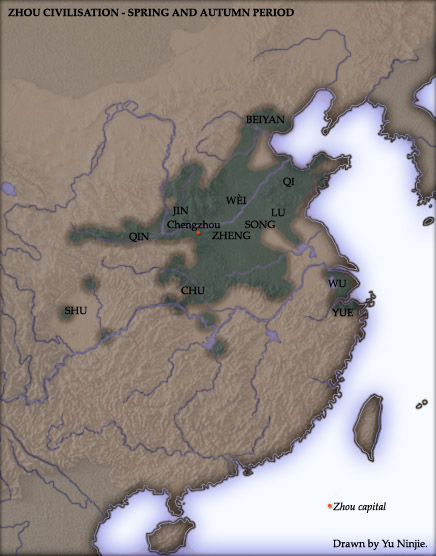
Eastern Zhou Dynasty
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |