|
Duke Of Saxe-Eisenach
Saxe-Eisenach (german: Sachsen-Eisenach) was an Ernestine duchies, Ernestine duchy ruled by the Saxon House of Wettin. The Imperial State, state intermittently existed at three different times in the Thuringian region of the Holy Roman Empire. The chief town and capital of all three duchies was Eisenach. History In the 15th century, much of what is now the States of Germany, German state of Thuringia, including the area around Eisenach, was in the hands of the Wettin dynasty, since 1423 Prince-electors of Electorate of Saxony, Saxony. In 1485, the Wettin lands were divided according to the Treaty of Leipzig, with most of the Thuringian lands going to Elector Ernest, Elector of Saxony, Ernest of Saxony and his descendants. The Ernestine Wettins also retained the title of Elector. However, when Ernest's grandson John Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, John Frederick the Magnanimous revolted against Emperor Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles V during the Schmalkaldic War, he was def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
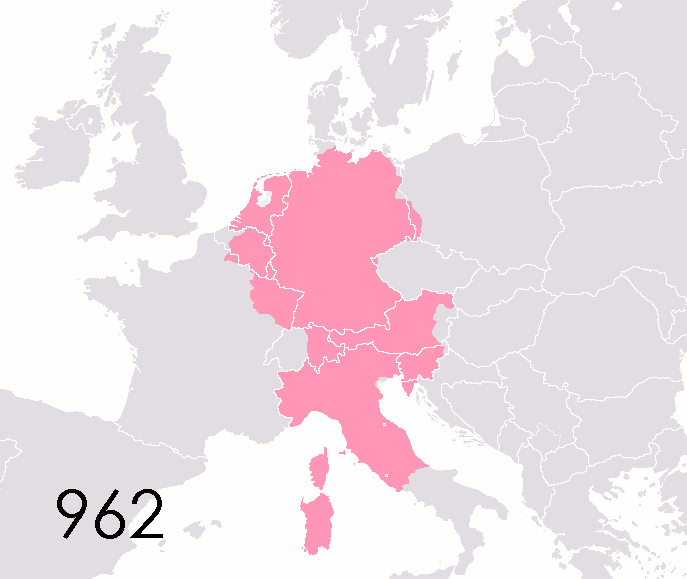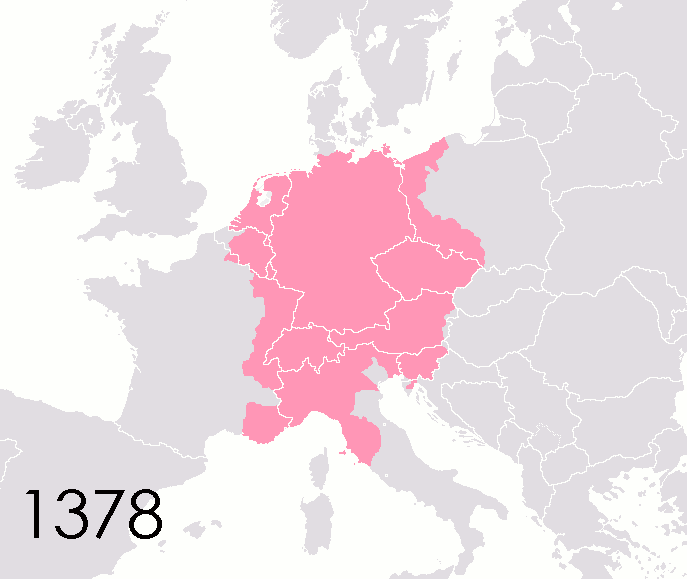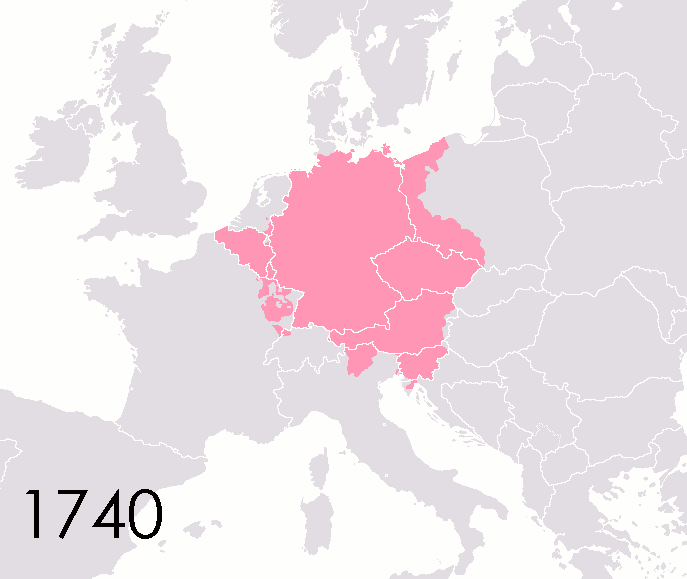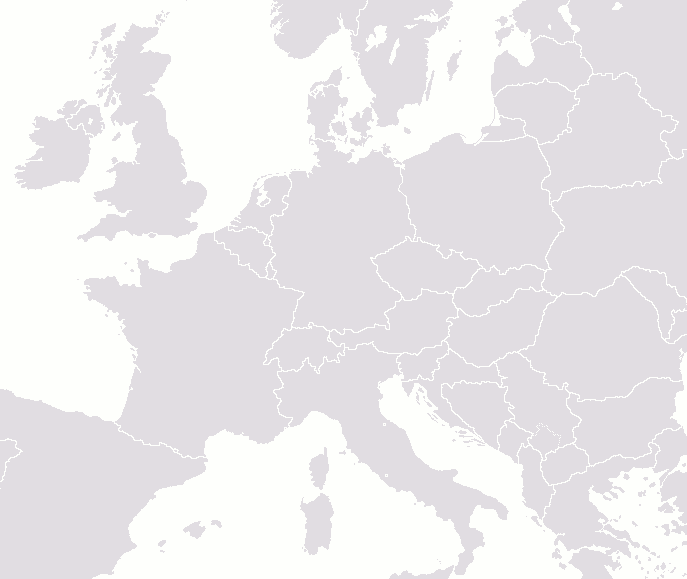
List Of States In The Holy Roman Empire
This list of states in the Holy Roman Empire includes any territory ruled by an authority that had been granted imperial immediacy, as well as many other feudal entities such as lordships, sous-fiefs and allodial fiefs. The Holy Roman Empire was a complex political entity that existed in central Europe for most of the medieval and early modern periods and was generally ruled by a German-speaking Emperor. The states that composed the Empire, while enjoying a unique form of territorial authority (called '' Landeshoheit'') that granted them many attributes of sovereignty, were never fully sovereign states in the sense that term is understood today. In the 18th century, the Holy Roman Empire consisted of approximately 1,800 such territories, the majority being tiny estates owned by the families of Imperial Knights. This page does not directly contain the list but discusses the format of the various lists and offers some background to understand the complex organisation of the Holy R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electorate Of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles IV designated the Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg an electorate, a territory whose ruler was one of the prince-electors who chose the Holy Roman emperor. After the extinction of the male Saxe-Wittenberg line of the House of Ascania in 1422, the duchy and the electorate passed to the House of Wettin. The electoral privilege was tied only to the Electoral Circle, specifically the territory of the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg. In the 1485 Treaty of Leipzig, the Wettin noble house was divided between the sons of Elector Frederick II into the Ernestine and Albertine lines, with the electoral district going to the Ernestines. In 1547, when the Ernestine elector John Frederick I was defeated in the Schmalkaldic War, the electoral district and el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John William, Duke Of Saxe-Weimar
Johann Wilhelm (11 March 1530 – 2 March 1573) was a duke of Saxe-Weimar. Life He was the second son of Johann Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, and Sibylle of Cleves. At the time of his birth, his father still carried the title Elector of Saxony, but he lost it in 1547 after his defeat and capture by the Emperor Charles V due to his support of the Protestant Reformation. Johann Frederick was released and forced to adopt the lesser title of duke of Saxony in an area substantially smaller than his former lands in Thuringia. In 1554, after the death of his father, Johann Wilhelm inherited the duchy of Saxony with his older brother, Johann Friedrich II, and his younger brother, Johann Friedrich III. The three brothers divided the duchy: Johann Friedrich II as head of the family took Eisenach and Coburg; Johann Wilhelm received Weimar; and Johann Friedrich III inherited Gotha. In 1565, however, when Johann Frederick III died without heirs, the two surviving brothers drew up a new t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Von Grumbach
Wilhelm von Grumbach (1 June 150318 April 1567) was a German adventurer, chiefly known through his connection with the so-called "Grumbach Feud" (german: Grumbachsche Händel), the last attempt of the Imperial Knights to prevail against the power of the territorial Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. Florian Geyer A member of the old Franconian noble family von Grumbach (a branch of the Wolfskeel ''Uradel'' family), Wilhelm was born in Rimpar near Würzburg, and having passed some time at the court of the Hohenzollern margrave Casimir of Bayreuth, fought alongside the princes during the German Peasants' War in 1524 and 1525. In the aftermath of the Battle of Frankenhausen, peasant leader Florian Geyer was one of the last survivors of Thomas Müntzer's army. On 9 June 1525, he was contacted in Würzburg by two servants of his brother-in-law Wilhelm von Grumbach (reportedly including Christoph Kretzen of the Grumbach-Zobel affair below), who had the stated intention of helping hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian II (31 July 1527 – 12 October 1576) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1564 until his death in 1576. A member of the Austrian House of Habsburg, he was crowned King of Bohemia in Prague on 14 May 1562 and elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) on 24 November 1562. On 8 September 1563 he was crowned King of Hungary and Croatia in the Hungarian capital Pressburg (Pozsony in Hungarian; now Bratislava, Slovakia). On 25 July 1564 he succeeded his father Ferdinand I as ruler of the Holy Roman Empire. Maximilian's rule was shaped by the confessionalization process after the 1555 Peace of Augsburg. Though a Habsburg and a Catholic, he approached the Lutheran Imperial estates with a view to overcome the denominational schism, which ultimately failed. He also was faced with the ongoing Ottoman–Habsburg wars and rising conflicts with his Habsburg Spain cousins. According to Fichtner, Maximilian failed to achieve his three major aims: rationalizing the government stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Ban
The imperial ban (german: Reichsacht) was a form of outlawry in the Holy Roman Empire. At different times, it could be declared by the Holy Roman Emperor, by the Imperial Diet, or by courts like the League of the Holy Court (''Vehmgericht'') or the ''Reichskammergericht''. People under imperial ban, known as ''Geächtete'' (from about the 17th century, colloquially also as ''Vogelfreie'', lit. "free as a bird"), lost all their rights and possessions. They were legally considered dead, and anyone was allowed to rob, injure, or kill them without legal consequences. The imperial ban automatically followed the excommunication of a person, as well as extending to anyone offering help to a person under the imperial ban. Those banned could reverse the ban by submitting to the legal authority. The ''Aberacht'', a stronger version of the imperial ban, could not be reversed. The imperial ban was sometimes imposed on whole Imperial Estates. In that case, other estates could attack and seek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Frederick II, Duke Of Saxony
John Frederick II of Saxony (8 January 1529 – 19 May 1595), was Duke of Saxony (1554–1566). Early life John Frederick II was the eldest son of John Frederick I, Elector of Saxony and Sibylle of Cleves. He was given a comprehensive education along with his younger brother Johann Wilhelm under the guidance of the legal scholar Basilius Monner. The two brothers were invited to take part in the Aulic Council, where they were able to develop their knowledge of diplomacy at a young age. Reign and military ambitions After the Battle of Mühlberg (24 April 1547) and the capture of his father, John Frederick II, along with his brother John William, succeeded their father as the regents of the lands still retained by their family. After the death of their father (1554), the brothers amicably divided the lands that were inherited from their father; even so, John Frederick II, remained as the exclusive regent for the family possessions. And even though he received Eisenach and Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitulation Of Wittenberg
{{Campaignbox Schmalkaldic War The Capitulation of Wittenberg (german: Wittenberger Kapitulation) was a treaty on 19 May 1547 by which John Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, was compelled to resign the title of elector. The Electorate of Saxony and most of his territory, including Wittenberg, passed from the elder Ernestine line to the cadet Albertine line of the House of Wettin. Wittenberg had become the focus of the Protestant Reformation. In 1517, Martin Luther had nailed his 95 Theses against Indulgences on the door of the castle church at Wittenberg, the opening act of the Reformation. In 1520 he burned the papal bull condemning him, and in 1534 the first Lutheran Bible was printed there. The Elector of Saxony was the most important patron of the Lutheran Reformation. In 1547, Emperor Charles V, with the assistance of the Duke of Alva, captured Wittenberg after the Battle of Mühlberg, where John Frederick I was taken prisoner. The Duke of Alva then presided over a court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice, Elector Of Saxony
Maurice (21 March 1521 – 9 July 1553) was Duke (1541–47) and later Elector (1547–53) of Saxony. His clever manipulation of alliances and disputes gained the Albertine branch of the Wettin dynasty extensive lands and the electoral dignity. 1521–1541: Infancy and youth Maurice was the fourth child but first son of the future Henry IV, Duke of Saxony, then a Catholic, and his Protestant wife, Catherine of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. Henry was the younger brother of George, Duke of Saxony. In December 1532, Maurice, aged 11, came to live at the castle of his godfather, Cardinal Albert of Brandenburg, Archbishop of Magdeburg and Mainz. For two years, he lived a contemplative life until his uncle Duke George demanded his return to Saxony. George began the training of the future Duke and educated him as a Catholic. But in 1536 Maurice's father became a Protestant, and when he succeeded George as Duke in 1539, he made the Duchy Protestant. Henry and Catherine took the education of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mühlberg
The Battle of Mühlberg took place near Mühlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of Protestant princes under the command of Elector John Frederick I of Saxony and Landgrave Philip I of Hesse. The battle ended the Schmalkaldic war and led to the dissolution of the Schmalkaldic League. Background The spread of the Protestant Reformation in Germany after 1517 represented a major obstacle to the universalistic projects of Charles V, the Habsburg emperor. Attempts at reconciliation between Lutherans and Catholics at the diets of Speyer of 1526 and 1529 had failed, sharpening the mutual opposition between the two opposing sides. The Reformation offered to most independent German states the pretext to affirm their autonomy not only on the religious level, but also on the political one. For some of these smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmalkaldic War
The Schmalkaldic War (german: link=no, Schmalkaldischer Krieg) was the short period of violence from 1546 until 1547 between the forces of Emperor Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire (simultaneously King Charles I of Spain), commanded by the Duke of Alba and the Duke of Saxony, and the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League within the domains of the Holy Roman Empire. Background In the course of the Lutheran Reformation numerous Imperial States had adopted the new confession, against the opposition of the ruling Catholic House of Habsburg, who recognised these conversions as a quest for increasing autonomy to the detriment of the central Imperial authority. At the 1521 Diet of Worms Emperor Charles V had Martin Luther banned and the proliferation of his writings prohibited. The edicts of the Diet condemned Luther and officially banned citizens of the Holy Roman Empire from defending or propagating his ideas, subjecting advocates of Lutheranism to forfeiture of all property, half of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain (Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon) from 1516 to 1556, and Lord of the Netherlands as titular Duke of Burgundy from 1506 to 1555. He was heir to and then head of the rising House of Habsburg during the first half of the 16th century, his dominions in Europe included the Holy Roman Empire, extending from Kingdom of Germany, Germany to Kingdom of Italy (Holy Roman Empire), northern Italy with direct rule over the Austrian hereditary lands and the Burgundian Low Countries, and Habsburg Spain, Spain with its southern Italy, southern Italian possessions of Kingdom of Naples, Naples, Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily, and Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia. He oversaw both the continuation of the long-lasting Spanish colonization of the Americas and the short-live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |