|
Dublin Mountains
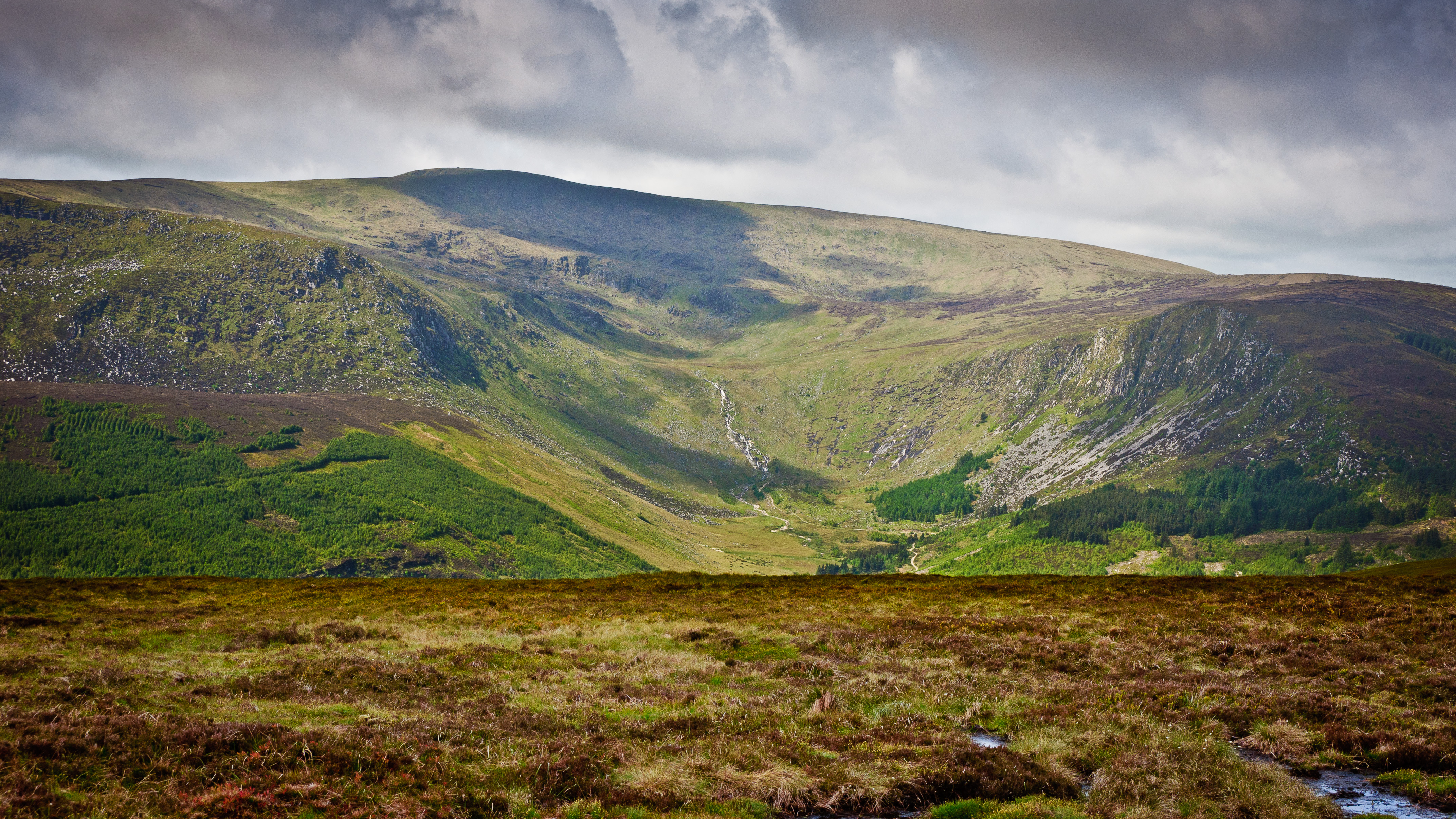
The Wicklow Mountains (, archaic: ''Cualu'') form the largest continuous upland area in the Republic of Ireland. They occupy the whole centre of County Wicklow and stretch outside its borders into the counties of Dublin, Wexford and Carlow. Where the mountains extend into County Dublin, they are known locally as the Dublin Mountains (''Sléibhte Bhaile Átha Cliath''). The highest peak is Lugnaquilla at . The mountains are primarily composed of granite surrounded by an envelope of mica-schist and much older rocks such as quartzite. They were pushed up during the Caledonian orogeny at the start of the Devonian period and form part of the Leinster Chain, the largest continuous area of granite in Ireland and Britain. The mountains owe much of their present topography to the effects of the last ice age, which deepened the valleys and created corrie and ribbon lakes. Copper and lead have been the main metals mined in the mountains and a brief gold rush occurred in the 18th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonelagee
Tonelagee () at , is the 25th–highest peak in Ireland on the Arderin scale, and the 33rd–highest peak on the Vandeleur-Lynam scale.Mountainviews, (September 2013), "A Guide to Ireland's Mountain Summits: The Vandeleur-Lynams & the Arderins", Collins Books, Cork, Tonelagee is situated in the central sector of the Wicklow Mountains range, and sits on the main "central spine" of the range that runs from Kippure in the north, to Lugnaquillia in the south; and in particular, the continuous "central boggy ridge" that runs from the Sally Gap in the north, via Mullaghcleevaun, to Tonelagee. Tonelagee is the third highest peak in Wicklow after Lugnaquilla and Mullaghcleevaun. To the north is the subsidiary summit of Stoney Top , and to the east is another subsidiary summit of Tonelagee NE Top ; between these three summits is the deep "heart-shaped" corrie lake of Lough Ouler. Naming Irish academic Paul Tempan, notes Tonelagee is sometimes spelled Tonelegee and its Irish name o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaism
In language, an archaism (from the grc, ἀρχαϊκός, ''archaïkós'', 'old-fashioned, antiquated', ultimately , ''archaîos'', 'from the beginning, ancient') is a word, a sense of a word, or a style of speech or writing that belongs to a historical epoch long beyond living memory, but that has survived in a few practical settings or affairs. Lexical archaisms are single archaic words or expressions used regularly in an affair (e.g. religion or law) or freely; literary archaism is the survival of archaic language in a traditional literary text such as a nursery rhyme or the deliberate use of a style characteristic of an earlier age—for example, in his 1960 novel '' The Sot-Weed Factor'', John Barth writes in an 18th-century style. Archaic words or expressions may have distinctive emotional connotations—some can be humorous (''forsooth''), some highly formal (''What say you?''), and some solemn (''With thee do I plight my troth''). A distinction between archaic and obsole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Avoca
The Avoca ( ga, Abhainn Abhóca) is a river in County Wicklow, Ireland. It is contained completely within the county. Its length is 35 miles (56.3 km). The Avoca starts life as two rivers, the Avonmore () and the Avonbeg (). These join at a spot called the ''Meeting of the Waters'' (''Cumar an dá Uisce'') in the ''Vale of Avoca'', which is considered a local beauty spot, and was celebrated by Thomas Moore in his song of the same name. The village of Avoca is situated on the river. The Avoca flows into the Irish Sea at Arklow where it widens into a large estuary, giving Arklow its Irish language name ''an t-Inbhear Mór'' (the big inlet). The catchment area of the Avoca is 652 km2. The long term average flow rate of the Avoca is 20.2 cubic metres per second (m3/s) Name The Avoca was originally called Abhainn Mhór / Abhainn Dé (great river/God's river); the present name was derived from ''Oboka'' (), the name of a river in Ptolemy's ''Geography'', which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Slaney
The River Slaney () is a large river in the southeast of Ireland. It rises on Lugnaquilla Mountain in the western Wicklow Mountains and flows west and then south through counties Wicklow, Carlow and Wexford for 117.5 km (73 mi), before entering St George's Channel in the Irish Sea at Wexford town. The estuary of the Slaney is wide and shallow and is known as Wexford Harbour. The catchment area of the River Slaney is 1,762 km2. The long term average flow rate of the River Slaney is 37.4m3/s Towns that the Slaney runs through include Stratford-on-Slaney, Baltinglass, Tullow, Bunclody, Enniscorthy and Wexford. The river is crossed by 32 road bridges and one railway bridge. Wildlife Varied and plentiful wildlife can be found in the environs of the river. In Wicklow, herds of deer can be seen, as well as swans, dippers, wild ducks, herons and kingfishers. At dusk, bats, owls and otters may be seen, while the mudflats of the estuary are favoured by black-headed gul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Dargle
The River Dargle () is a river that flows from the Wicklow Mountains in Ireland to the Irish Sea. It forms Powerscourt Waterfall, receives the Glencree and Glencullen Rivers, and later the Glenmunder Stream / County Brook, and the Swan River at Bray, and reaches the sea at Bray Harbour. Course The Dargle rises in the Wicklow Mountains, Ireland, on the southern slopes of Tonduff . It flows down the Glensoulan hanging valley, to fall over the Powerscourt Waterfall. The Dargle then flows through the Glencree valley where it is fed by the River Glencree, before flowing east for a further . It receives the Glencullen River, and later the Glenmunder Stream, also known as the County Brook or Ballyman Stream. A final small tributary, the Swan River, joins opposite the People's Park, Little Bray. The final section reaches the Irish Sea at Bray Harbour. Name The river's name in Irish refers to the tint of red in the rocks at its source. Historical events Battle of Bloody Bank In Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Liffey
The River Liffey (Irish: ''An Life'', historically ''An Ruirthe(a)ch'') is a river in eastern Ireland that ultimately flows through the centre of Dublin to its mouth within Dublin Bay. Its major tributaries include the River Dodder, the River Poddle and the River Camac. The river supplies much of Dublin's water and supports a range of recreational activities. Name Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (2nd century AD) described a river, perhaps the Liffey, which he labelled Οβοκα (''Oboka''). Ultimately this led to the name of the River Avoca in County Wicklow. The Liffey was previously named ''An Ruirthech'', meaning "fast (or strong) runner". The word ''Liphe'' (or ''Life'') referred originally to the name of the plain through which the river ran, but eventually came to refer to the river itself. The word may derive from the same root as Welsh ''llif'' (flow, stream), namely Proto-Indo-European ''lē̆i-4'', but Gearóid Mac Eoin has more recently proposed that it may derive from a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
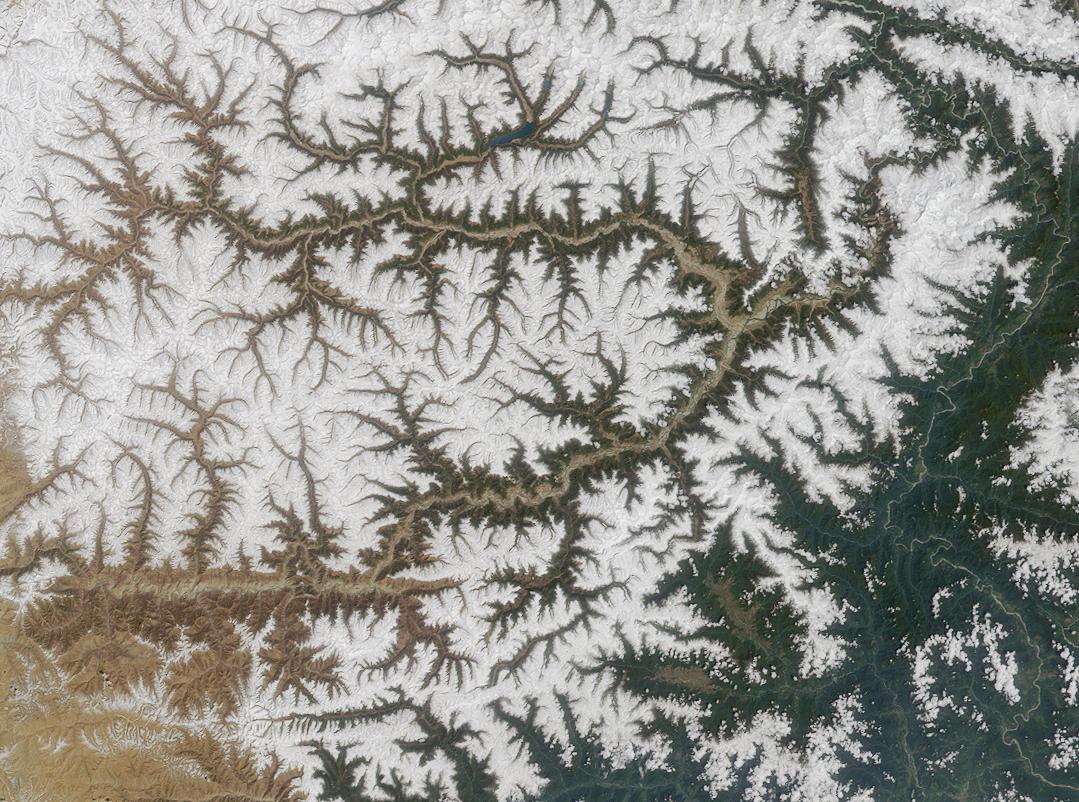
Drainage System (geomorphology)
In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins (and sub-basins). This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available. Drainage patterns Per the lie of channels, drainage systems can fall into one of several categories, known as drainage patterns. These depend on the topography and geology of the land. All forms of transitions can occur between parallel, dendritic, and trellis patterns. Accordant versus discordant drainage patterns A drai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Rush
A gold rush or gold fever is a discovery of gold—sometimes accompanied by other precious metals and rare-earth minerals—that brings an onrush of miners seeking their fortune. Major gold rushes took place in the 19th century in Australia, New Zealand, Brazil, Chile, South Africa, the United States, and Canada while smaller gold rushes took place elsewhere. In the 19th century, the wealth that resulted was distributed widely because of reduced migration costs and low barriers to entry. While gold mining itself proved unprofitable for most diggers and mine owners, some people made large fortunes, and merchants and transportation facilities made large profits. The resulting increase in the world's gold supply stimulated global trade and investment. Historians have written extensively about the mass migration, trade, colonization, and environmental history associated with gold rushes. Gold rushes were typically marked by a general buoyant feeling of a "free-for-all" in income mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
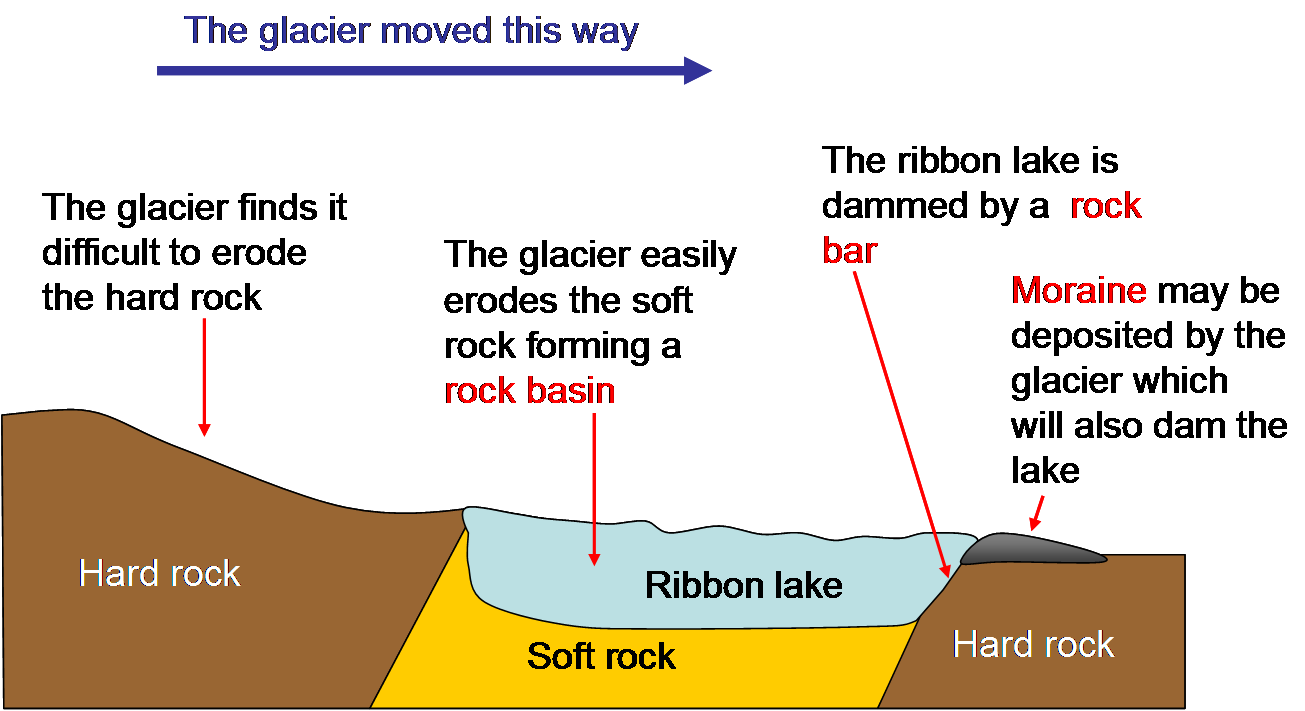
Ribbon Lake
A ribbon lake is a long and deep, finger-shaped lake, usually found in a glacial trough. As such, a ribbon lake is one of a number of glacial landscapes, including arêtes, corries, rock lips, rock basins and terminal moraines. Such a lake's formation begins when a glacier moves over an area containing alternate bands of hard and soft bedrock. The sharp-edged boulders that are picked up by the glacier and carried at the bottom of the glacier erode the softer rock more quickly by abrasion, thus creating a hollow called a rock basin. On either side of the rock basin, the more resistant rock is eroded less and these outcrops of harder rock are known as rock bars, which act as dams between which rainwater may accumulate after the retreat of the ice age, filling up the rock basin and creating a ribbon lake. A ribbon lake may also form behind a terminal or recessional moraine, both of which also act as dams, enabling water to accumulate behind them. A ribbon lake may also occur if a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirque
A (; from the Latin word ') is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from Scottish Gaelic , meaning a pot or cauldron) and (; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform arising from fluvial erosion. The concave shape of a glacial cirque is open on the downhill side, while the cupped section is generally steep. Cliff-like slopes, down which ice and glaciated debris combine and converge, form the three or more higher sides. The floor of the cirque ends up bowl-shaped, as it is the complex convergence zone of combining ice flows from multiple directions and their accompanying rock burdens. Hence, it experiences somewhat greater erosion forces and is most often overdeepened below the level of the cirque's low-side outlet (stage) and its down-slope (backstage) valley. If the cirque is subject to seasonal melting, the floor of the cirque most often forms a tarn (small lake) behind a dam, which marks the down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describe this entire period up to the present as an "ice age", in popular culture this term usually refers to the most recent glacial period, or to the Pleistocene epoch in general. Since Earth still has polar ice sheets, geologists consider the Quaternary glaciation to be ongoing, though currently in an interglacial period. During the Quaternary glaciation, ice sheets appeared, expanding during glacial periods and contracting during interglacial periods. Since the end of the last glacial period, only the Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets have survived, with other sheets formed during glacial periods, such as the Laurentide Ice Sheet, having completely melted. The major effects of the Quaternary glaciation have been the continental erosion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |