|
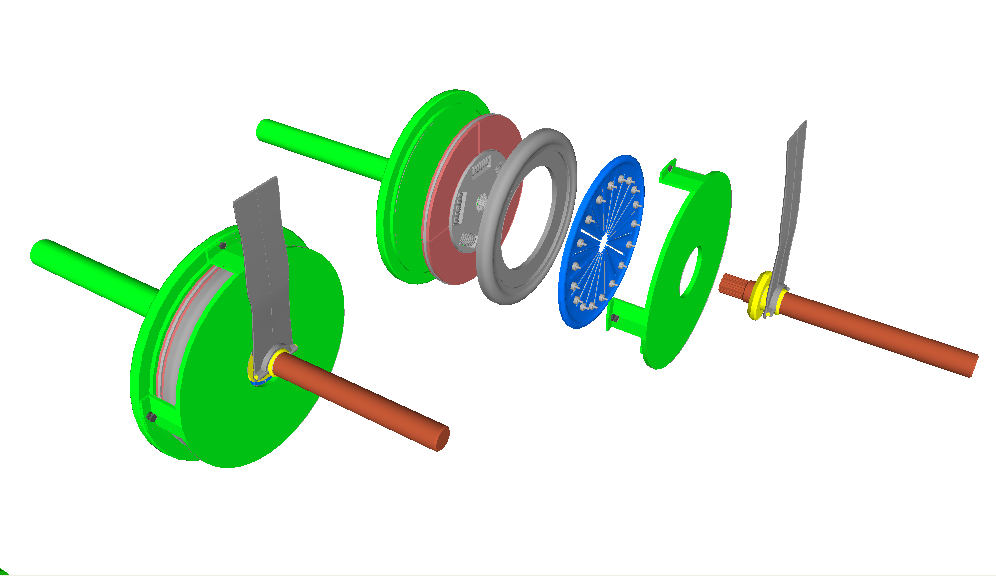
Dual Mass Flywheel
A dual-mass flywheel (DMF or DMFW) is a rotating mechanical device that is used to provide continuous energy ( rotational energy) in systems where the energy source is not continuous, the same way as a conventional flywheel acts, but damping any violent variation of torque or revolutions that could cause an unwanted vibration. The vibration reduction is achieved by accumulating stored energy in the two flywheel half masses over a period of time but damped by arc springs, doing that at a rate that is compatible with the energy source, and then releasing that energy at a much higher rate over a relatively short time. A compact dual-mass flywheel often includes the whole clutch, including the pressure plate and the friction disc. History Dual-mass flywheels were developed to address the escalation of torque and power, especially at low revs. The growing concern for the environment and the adoption of more stringent regulations have marked the development of more efficient n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Spring Characteristic Curve (two-stage)
ARC may refer to: Business * Aircraft Radio Corporation, a major avionics manufacturer from the 1920s to the '50s * Airlines Reporting Corporation, an airline-owned company that provides ticket distribution, reporting, and settlement services * Airport Regions Conference, a European organization of major airports * Amalgamated Roadstone Corporation, a British stone quarrying company * American Record Company (1904–1908, re-activated 1979), one of two United States record labels by this name * American Record Corporation (1929–1938), a United States record label also known as American Record Company * ARC (American Recording Company) (1978-present), a vanity label for Earth, Wind & Fire * ARC Document Solutions, a company based in California, formerly American Reprographics Company * Amey Roadstone Construction, a former British construction company * Aqaba Railway Corporation, a freight railway in Jordan * ARC/Architectural Resources Cambridge, Inc., Cambridge, Massachus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flywheels
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, assuming the flywheel's moment of inertia is constant (i.e., a flywheel with fixed mass and second moment of area revolving about some fixed axis) then the stored (rotational) energy is directly associated with the square of its rotational speed. Since a flywheel serves to store mechanical energy for later use, it is natural to consider it as a kinetic energy analogue of an electrical inductor. Once suitably abstracted, this shared principle of energy storage is described in the generalized concept of an accumulator. As with other types of accumulators, a flywheel inherently smooths sufficiently small deviations in the power output of a system, thereby effectively playing the role of a low-pass filter with respect to the mechanical velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Moments Of Inertia
Moment of inertia, denoted by , measures the extent to which an object resists rotational acceleration about a particular axis, it is the rotational analogue to mass (which determines an object's resistance to ''linear'' acceleration). The moments of inertia of a mass have units of dimension ML2(ass× engthsup>2). It should not be confused with the second moment of area, which is used in beam calculations. The mass moment of inertia is often also known as the rotational inertia, and sometimes as the angular mass. For simple objects with geometric symmetry, one can often determine the moment of inertia in an exact closed-form expression. Typically this occurs when the mass density is constant, but in some cases the density can vary throughout the object as well. In general, it may not be straightforward to symbolically express the moment of inertia of shapes with more complicated mass distributions and lacking symmetry. When calculating moments of inertia, it is useful to rememb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Balancer
A harmonic damper is a device fitted to the free (accessory drive) end of the crankshaft of an internal combustion engine to counter torsional and resonance vibrations from the crankshaft. This device must be interference fit to the crankshaft in order to operate in an effective manner. An interference fit ensures the device moves in perfect step with the crankshaft. It is essential on engines with long crankshafts (such as straight-six or straight-eight engines) and V8 engines with cross plane cranks, or V6 and straight-three engines with uneven firing order. Harmonics and torsional vibrations can greatly reduce crankshaft life, or cause instantaneous failure if the crankshaft runs at or through an amplified resonance. Dampers are designed with a specific weight (mass) and diameter, which are dependent on the damping material/method used, to reduce mechanical Q factor, or damp, crankshaft resonances. A harmonic balancer (sometimes called crankshaft damper, torsional damper, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flywheel Energy Storage
Flywheel energy storage (FES) works by accelerating a rotor (flywheel) to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy. When energy is extracted from the system, the flywheel's rotational speed is reduced as a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy; adding energy to the system correspondingly results in an increase in the speed of the flywheel. Most FES systems use electricity to accelerate and decelerate the flywheel, but devices that directly use mechanical energy are being developed.Torotrak Toroidal variable drive CVT , retrieved June 7, 2007. Advanced FES systems have rotors made of high strength carbon-fiber composites, suspended by |
Flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, assuming the flywheel's moment of inertia is constant (i.e., a flywheel with fixed mass and second moment of area revolving about some fixed axis) then the stored (rotational) energy is directly associated with the square of its rotational speed. Since a flywheel serves to store mechanical energy for later use, it is natural to consider it as a kinetic energy analogue of an electrical inductor. Once suitably abstracted, this shared principle of energy storage is described in the generalized concept of an accumulator. As with other types of accumulators, a flywheel inherently smooths sufficiently small deviations in the power output of a system, thereby effectively playing the role of a low-pass filter with respect to the mechanical velocity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). In these devices, one shaft is typically attached to an engine or other power unit (the driving member), while the other shaft (the driven member) provides output power for work. Typically the motions involved are rotary, but linear clutches also exist. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission, and briefly disconnects, or separates the engine from the transmission system. This disconnects the drive wheels whenever the clutch pedal is depressed, allowing the driver to smoothly change gears. In a torque-controlled drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor, and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so they may be locked together and spin at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrifugal Pendulum Absorber
A centrifugal pendulum absorber is a type of Tuned mass damper. It reduces the amplitude of a Torsional vibration in drive trains that use a combustion engine. History The centrifugal pendulum absorber was first patented in 1937 by R. Sarazin and a different version by R. Chilton in 1938. Generally, both Sarazin and Chilton are credited with the invention. Sarazin's work was used during World War II by Pratt & Whitney for aircraft engines with increased power output. The power increase caused an increase in torsional vibrations which threatened the durability. This resulted in the Pratt & Whitney R-2800 engine that used pendulum weights attached to the crank shaft. The use of centrifugal pendulum absorbers in land vehicles did not start until later. Although internal combustion engines had always caused torsional vibrations in the drive train, the vibration amplitude was generally not high enough to affect durability or driver comfort. One application existed in tuned racing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
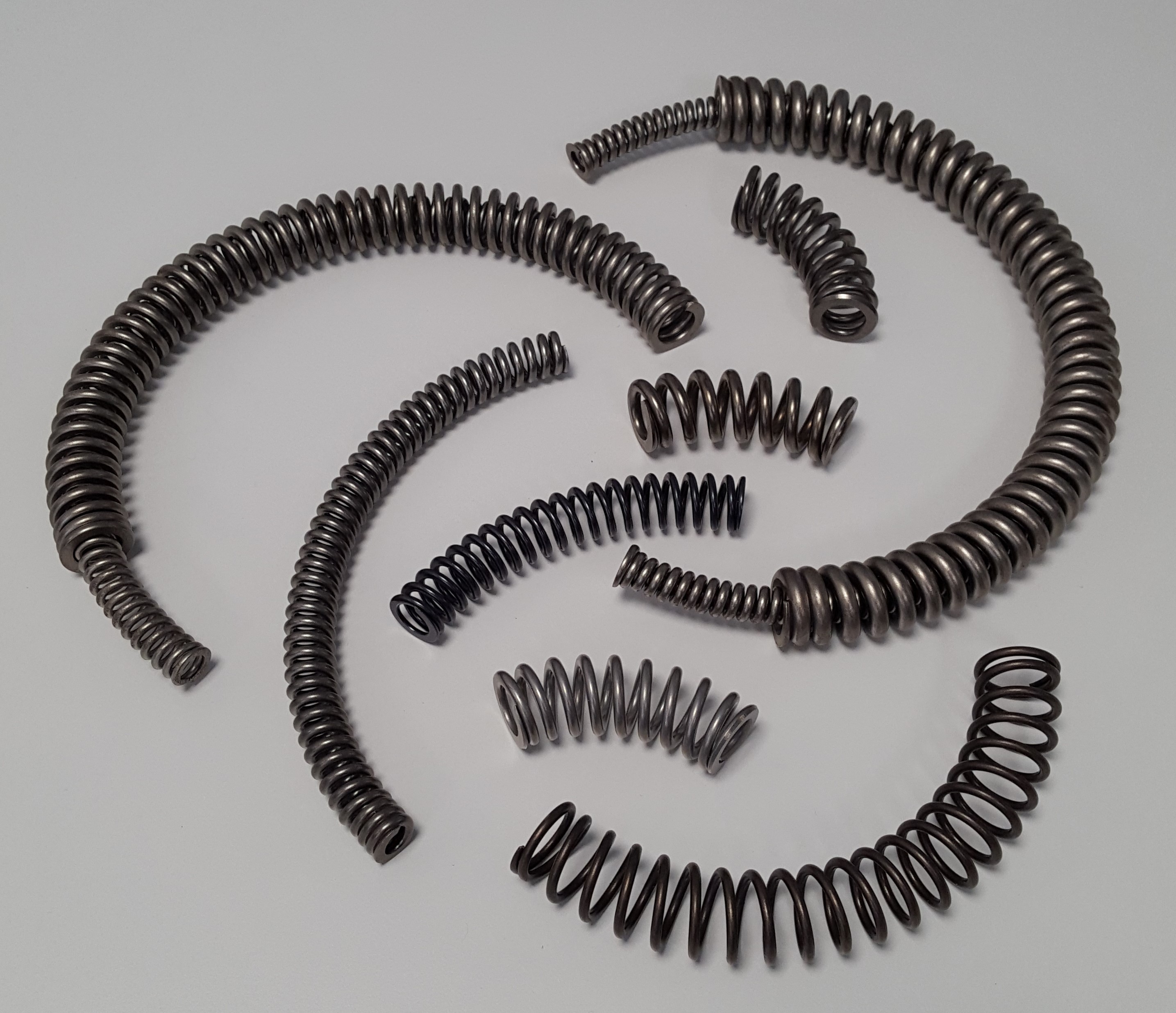
Arc Spring
The arc spring (also known as - bow spring, curved spring, circular spring or "banana" spring) is a special form of coil spring which was originally developed for use in the dual-mass flywheel of internal combustion engine drive trains. The term "arc spring" is used to describe pre-curved or arc-shaped helical compression springs. They have an arc-shaped coil axis. Function Like other technical springs, arc springs are based on the fundamental principle of storing mechanical work in the form of potential energy and the ability to release this energy again. The force is applied through the ends of the spring. A torque M=F\cdot r can be transmitted around an axis via the force F directed along this helical axis and the lever arm to the system center point r. The wire of the arc spring is mainly subjected to torsional stress. Support An arc spring requires suitable support to transmit torque. The support is usually provided from the outside in the form of an arcuate channe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotational Energy
Rotational energy or angular kinetic energy is kinetic energy due to the rotation of an object and is part of its total kinetic energy. Looking at rotational energy separately around an object's axis of rotation, the following dependence on the object's moment of inertia is observed: :E_\mathrm = \tfrac I \omega^2 where : \omega \ is the angular velocity : I \ is the moment of inertia around the axis of rotation : E \ is the kinetic energy The mechanical work required for or applied during rotation is the torque times the rotation angle. The instantaneous power of an angularly accelerating body is the torque times the angular velocity. For free-floating (unattached) objects, the axis of rotation is commonly around its center of mass. Note the close relationship between the result for rotational energy and the energy held by linear (or translational) motion: :E_\mathrm = \tfrac m v^2 In the rotating system, the moment of inertia, ''I'', takes the role of the mass, ''m' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DMF
DMF may refer to: Science and technology Chemistry * Dimethylformamide, a common solvent * Dimethyl fumarate, a small molecule anti-inflammatory human medicine * 2,5-Dimethylfuran, a liquid biofuel Computing * Distribution Media Format, the computer floppy disk format * DivX Media Format, the media container format * Death Master File, a document listing deaths in the US Medicine * Decay-missing-filled index for assessing dental caries prevalence as well as dental treatment needs among populations * Drug Master File, a document in the pharmaceutical industry Other technology * Digital microfluidics, a fluid handling technique * Dual-mass flywheel, a rotating mechanical device Other uses * Danish Musicians' Union, a Danish trade union * Defensive midfielder A midfielder is an outfield position in association football. Midfielders may play an exclusively defensive role, breaking up attacks, and are in that case known as defensive midfielders. As central midfielders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)