|
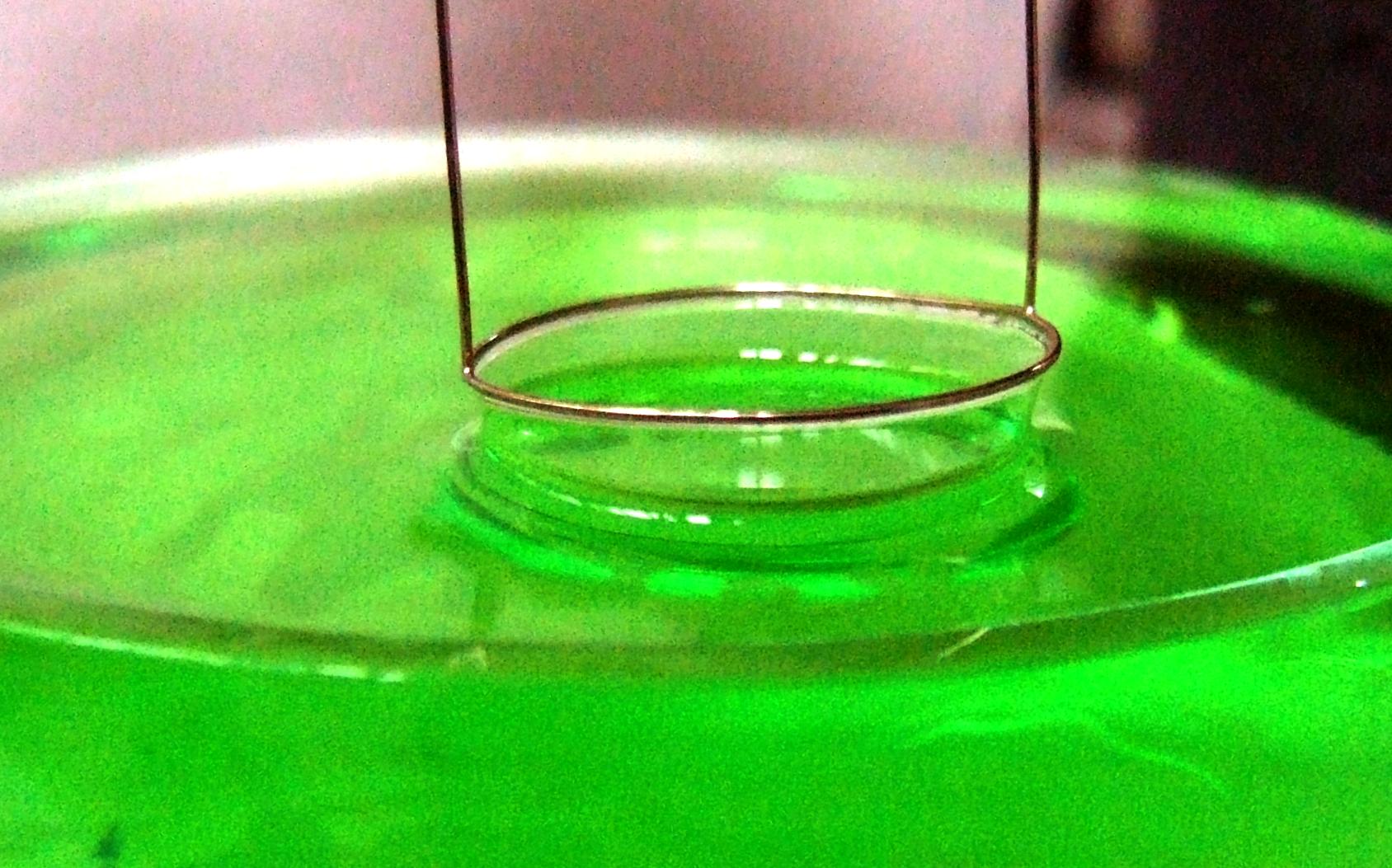
Du Noüy–Padday Method
The du Noüy–Padday method is a minimized version of the du Noüy ring method replacing the large platinum ring with a thin rod that is used to measure equilibrium surface tension or dynamic surface tension at an air–liquid interface. In this method, the rod is oriented perpendicular to the interface, and the force exerted on it is measured. Based on the work of Padday,Padday, J. F., Pitt, A. R., Pashley, R. M.,1974, "Menisci at a free liquid surface: surface tension from the maximum pull on a rod",J. Chem. Soc., Far. Trans. I, 71(10), 1919–1931 (1974) this method finds wide use in the preparation and monitoring of Langmuir–Blodgett films, ink & coating development, pharmaceutical screening, and academic research. Detailed description The du Noüy Padday rod consists of a rod usually on the order of a few millimeters square making a small ring. The rod is often made from a composite metal material that may be roughened to ensure complete wetting at the interface. The rod is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
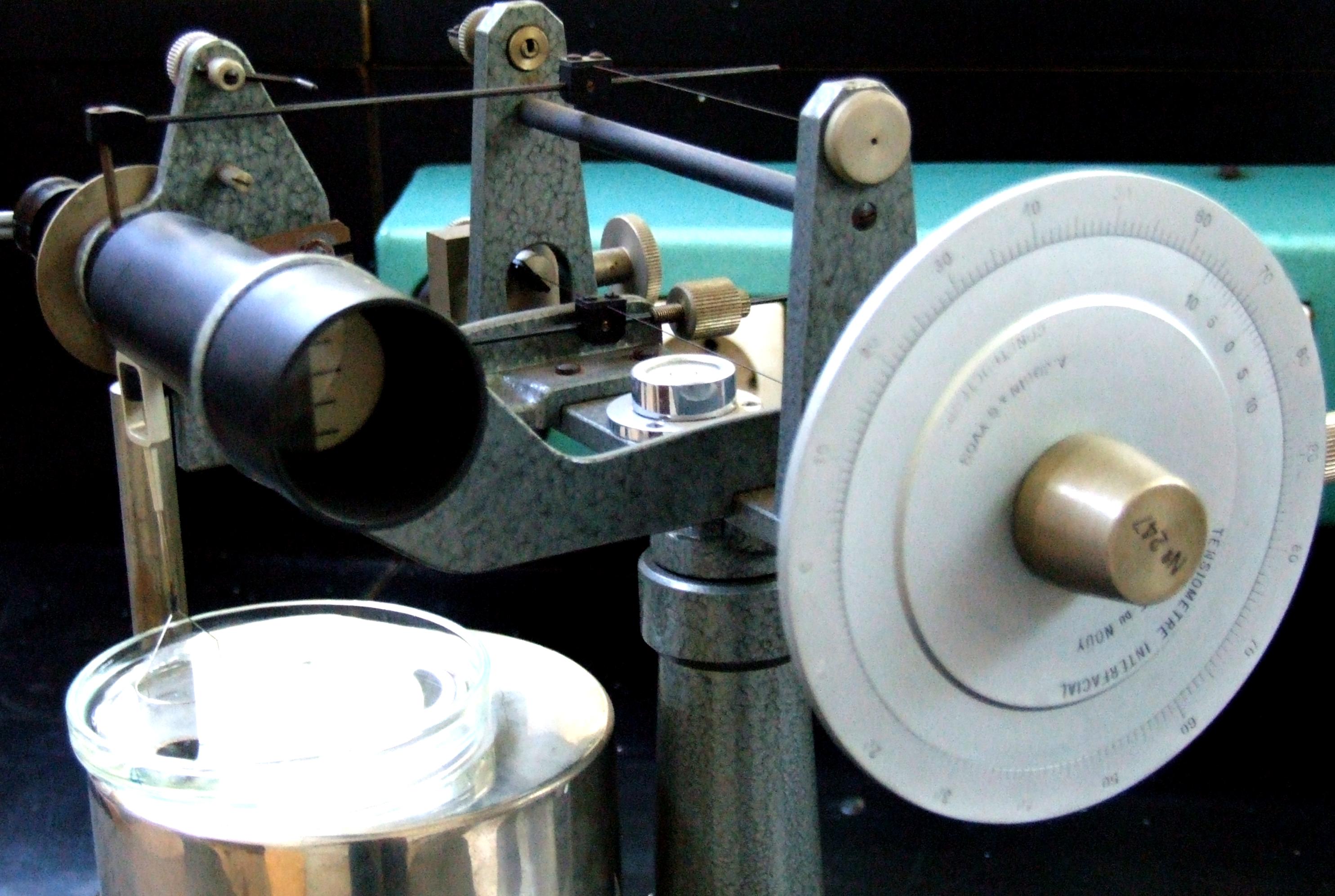
Du Noüy Ring Method
In surface science, the du Noüy ring method is a technique for measuring the surface tension of a liquid. The method involves slowly lifting a ring, often made of platinum, from the surface of a liquid. The force, , required to raise the ring from the liquid's surface is measured and related to the liquid's surface tension, : :F= w_\text + 2\pi \cdot (r_i + r_a) \cdot \gamma where is the radius of the inner ring of the liquid film pulled and is the radius of the outer ring of the liquid film. is the weight of the ring minus the buoyant force due to the part of the ring below the liquid surface. When the ring's thickness is much smaller than its diameter, this equation can be simplified to: :F= w_\text + 4\pi R \gamma where is the average of the inner and outer radius of the ring, i.e. \tfrac. This technique was proposed by the French physicist Pierre Lecomte du Noüy (1883–1947) in a paper published in 1925. The measurement is performed with a force tensiometer, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langmuir–Blodgett Film
A Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) film is a nanostructured system formed when Langmuir films—or Langmuir monolayers (LM)—are transferred from the liquid-gas interface to solid supports during the vertical passage of the support through the monolayers. LB films can contain one or more monolayers of an organic material, deposited from the surface of a liquid onto a solid by immersing (or emersing) the solid substrate into (or from) the liquid. A monolayer is adsorbed homogeneously with each immersion or emersion step, thus films with very accurate thickness can be formed. This thickness is accurate because the thickness of each monolayer is known and can therefore be added to find the total thickness of a Langmuir–Blodgett film. The monolayers are assembled vertically and are usually composed either of amphiphilic molecules (see chemical polarity) with a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail (example: fatty acids) or nowadays commonly of nanoparticles. Langmuir–Blodgett films are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. This happens in presence of a gaseous phase or another liquid phase not miscible with the first one. The degree of wetting (wettability) is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces. Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of two materials. Wetting and the surface forces that control wetting are also responsible for other related effects, including capillary effects. There are two types of wetting: non-reactive wetting and reactive wetting. Wetting deals with three phases of matter: gas, liquid, and solid. It is now a center of attention in nanotechnology and nanoscience studies due to the advent of many nanomaterials in the past two decades (e.g. graphene, Carbon nano tube, carbon nanotube, boron nitride nanomesh). Explanation Adhesive forces between a liquid and solid cause a liq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Brain Barrier
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in vertebrate blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-throughput Screening
High-throughput screening (HTS) is a method for scientific experimentation especially used in drug discovery and relevant to the fields of biology, materials science and chemistry. Using robotics, data processing/control software, liquid handling devices, and sensitive detectors, high-throughput screening allows a researcher to quickly conduct millions of chemical, genetic, or pharmacological tests. Through this process one can quickly recognize active compounds, antibodies, or genes that modulate a particular biomolecular pathway. The results of these experiments provide starting points for drug design and for understanding the noninteraction or role of a particular location. Assay plate preparation The key labware or testing vessel of HTS is the microtiter plate, which is a small container, usually disposable and made of plastic, that features a grid of small, open divots called ''wells''. In general, microplates for HTS have either 96, 192, 384, 1536, 3456 or 6144 wells. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipidosis
Phospholipidosis is a lysosomal storage disorder characterized by the excess accumulation of phospholipids in tissues. Certain cases may be triggered by medications. The traditional method to evaluate drug-induced phospholipidosis (DIPL) is visual confirmation of myeloid bodies in tissues by electron microscopy An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. As the wavelength of an electron can be up to 100,000 times shorter than that of visible light photons, electron microscopes have a .... Electron microscopy has limited utility to monitor DIPL in humans because of the invasive nature of acquiring patient tissue biopsy samples. A qualified biomarker of DIPL in the blood or urine is needed to provide a more routine, non-invasive, and cost effective means to monitor DIPL in the clinic. References Clinical pharmacology {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tensiometer (surface Tension)
In surface science, a tensiometer is a measuring instrument used to measure the surface tension () of liquids or surfaces. Tensiometers are used in research and development laboratories to determine the surface tension of liquids like coatings, lacquers or adhesives. A further application field of tensiometers is the monitoring of industrial production processes like parts cleaning or electroplating. Types Goniometer/Tensiometer Surface scientists commonly use an optical goniometer/tensiometer to measure the surface tension and interfacial tension of a liquid using the pendant or sessile drop methods. A drop is produced and captured using a CCD camera. The drop profile is subsequently extracted, and sophisticated software routines then fit the theoretical Young-Laplace equation to the experimental drop profile. The surface tension can then be calculated from the fitted parameters. Unlike other methods, this technique requires only a small amount of liquid making it suitabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessile Drop Technique
image:Contact angle.svg, 400px, Fig 1: An illustration of the sessile drop technique with a liquid droplet partially wetting a solid substrate. is the contact angle, and represent the solid–gas, gas–liquid, and liquid–solid interfaces, respectively. In materials science, the sessile drop technique is a method used for the characterization of solid surface energy, surface energies, and in some cases, aspects of liquid surface energies. The main premise of the method is that by placing a droplet of liquid with a known surface energy and contact angle, the surface energy of the solid substrate can be calculated. The liquid used for such experiments is referred to as the probe liquid, and the use of several different probe liquids is required. Probe liquid The surface energy is measured in units of Joules per area, which is equivalent in the case of liquids to surface tension, measured in Newtons per meter. The overall surface tension/energy of a liquid can be acquired th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelmy Plate
A Wilhelmy plate is a thin plate that is used to measure equilibrium surface or interfacial tension at an air–liquid or liquid–liquid interface. In this method, the plate is oriented perpendicular to the interface, and the force exerted on it is measured. Based on the work of Ludwig Wilhelmy, this method finds wide use in the preparation and monitoring of Langmuir films. Detailed description The Wilhelmy plate consists of a thin plate usually on the order of a few square centimeters in area. The plate is often made from filter paper, glass or platinum which may be roughened to ensure complete wetting. In fact, the results of the experiment do not depend on the material used, as long as the material is wetted by the liquid. The plate is cleaned thoroughly and attached to a balance with a thin metal wire. The force on the plate due to wetting is measured using a tensiometer or microbalance and used to calculate the surface tension (\gamma) using the Wilhelmy equation: : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Science
Surface science is the study of physical and chemical phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, including solid–liquid interfaces, solid– gas interfaces, solid– vacuum interfaces, and liquid– gas interfaces. It includes the fields of '' surface chemistry'' and ''surface physics''. Some related practical applications are classed as surface engineering. The science encompasses concepts such as heterogeneous catalysis, semiconductor device fabrication, fuel cells, self-assembled monolayers, and adhesives. Surface science is closely related to interface and colloid science. Interfacial chemistry and physics are common subjects for both. The methods are different. In addition, interface and colloid science studies macroscopic phenomena that occur in heterogeneous systems due to peculiarities of interfaces. History The field of surface chemistry started with heterogeneous catalysis pioneered by Paul Sabatier on hydrogenation and Fritz Haber on the Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |