|
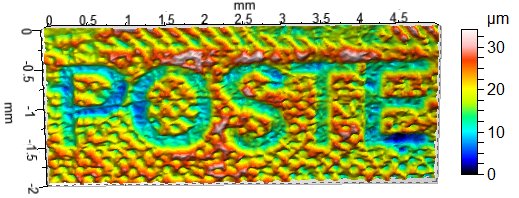
Drypoint
Drypoint is a printmaking technique of the intaglio (printmaking), intaglio family, in which an image is incised into a plate (or "matrix") with a hard-pointed "needle" of sharp metal or diamond point. In principle, the method is practically identical to engraving. The difference is in the use of tools, and that the raised ridge along the furrow is not scraped or filed away as in engraving. Traditionally the plate was copper, but now cellulose acetate, acetate, zinc, or plexiglas are also commonly used. Like etching, drypoint is easier to master than engraving for an artist trained in drawing because the technique of using the needle is closer to using a pencil than the Burin (engraving), engraver's burin. The term is also used for inkless scratched inscriptions, such as glosses in manuscripts. Lines and burrs The lines produced by printing a drypoint are formed by the Burr (metal), burr thrown up at the edge of the incised lines, in addition to the depressions formed in the sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Cassatt
Mary Stevenson Cassatt (; May 22, 1844June 14, 1926) was an American painter and printmaker. She was born in Allegheny, Pennsylvania (now part of Pittsburgh's North Side), but lived much of her adult life in France, where she befriended Edgar Degas and exhibited with the Impressionists. Cassatt often created images of the social and private lives of women, with particular emphasis on the intimate bonds between mothers and children. She was described by Gustave Geffroy as one of "les trois grandes dames" (the three great ladies) of Impressionism alongside Marie Bracquemond and Berthe Morisot. In 1879, Diego Martelli compared her to Degas, as they both sought to depict movement, light, and design in the most modern sense. Early life Cassatt was born in Allegheny City, Pennsylvania, which is now part of Pittsburgh. She was born into an upper-middle-class family: Her father, Robert Simpson Cassat (later Cassatt), was a successful stockbroker and land speculator. The ancestral n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed technique, rather than a photographic reproduction of a visual artwork which would be printed using an electronic machine ( a printer); however, there is some cross-over between traditional and digital printmaking, including risograph. Except in the case of monotyping, all printmaking processes have the capacity to produce identical multiples of the same artwork, which is called a print. Each print produced is considered an "original" work of art, and is correctly referred to as an "impression", not a "copy" (that means a different print copying the first, common in early printmaking). However, impressions can vary considerably, whether intentionally or not. Master printmakers are technicians who are capable of printing identical "impressions" by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Duerer, was a German painter, printmaker, and theorist of the German Renaissance. Born in Nuremberg, Dürer established his reputation and influence across Europe in his twenties due to his high-quality woodcut prints. He was in contact with the major Italian artists of his time, including Raphael, Giovanni Bellini, and Leonardo da Vinci, and from 1512 was patronized by Emperor Maximilian I. Dürer's vast body of work includes engravings, his preferred technique in his later prints, altarpieces, portraits and self-portraits, watercolours and books. The woodcuts series are more Gothic than the rest of his work. His well-known engravings include the three '' Meisterstiche'' (master prints) ''Knight, Death and the Devil'' (1513), '' Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio (printmaking)
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally, copper or in recent times zinc sheets, called plates, are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. Process In intaglio printing, the lines to be printed are cut into a metal (e.g. copper) plate by means either of a cutting tool called a burin, held in the hand – in which case the process is called ''engraving''; or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the history of art and the most important in Dutch art history.Gombrich, p. 420. Unlike most Dutch masters of the 17th century, Rembrandt's works depict a wide range of style and subject matter, from portraits and self-portraits to landscapes, genre scenes, allegorical and historical scenes, biblical and mythological themes and animal studies. His contributions to art came in a period of great wealth and cultural achievement that historians call the Dutch Golden Age, when Dutch art (especially Dutch painting), whilst antithetical to the Baroque style that dominated Europe, was prolific and innovative. This era gave rise to important new genres. Like many artists of the Dutch Golden Age, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rembrandt Harmenszoon Van Rijn
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally considered one of the greatest visual artists in the history of art The history of art focuses on objects made by humans for any number of spiritual, narrative, philosophical, symbolic, conceptual, documentary, decorative, and even functional and other purposes, but with a primary emphasis on its aesthetic vis ... and the most important in Dutch art history.Gombrich, p. 420. Unlike most Dutch masters of the 17th century, :Works by Rembrandt, Rembrandt's works depict a wide range of style and subject matter, from portrait painting, portraits and self-portraits to landscapes, genre scenes, allegorical and historical scenes, biblical and mythological themes and animal studies. His contributions to art came in a period of great wealth and cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio (printmaking)
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally, copper or in recent times zinc sheets, called plates, are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. Process In intaglio printing, the lines to be printed are cut into a metal (e.g. copper) plate by means either of a cutting tool called a burin, held in the hand – in which case the process is called ''engraving''; or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a Burin (engraving), burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or Glass engraving, glass are engraved, or may provide an Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing images on paper as prints or illustrations; these images are also called "engravings". Engraving is one of the oldest and most important techniques in printmaking. Wood engraving is a form of relief printing and is not covered in this article, same with rock engravings like petroglyphs. Engraving was a historically important method of producing images on paper in artistic printmaking, in mapmaking, and also for commercial reproductions and illustrations for books and magazines. It has long been replaced by various photographic processes in its commercial applications and, partly because of the difficulty of learning th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Canadian Encyclopedia
''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' (TCE; french: L'Encyclopédie canadienne) is the national encyclopedia of Canada, published online by the Toronto-based historical organization Historica Canada, with the support of Canadian Heritage. Available for free online in both English and French, ''The Canadian Encyclopedia'' includes more than 19,500 articles in both languages on numerous subjects including history, popular culture, events, people, places, politics, arts, First Nations, sports and science. The website also provides access to the ''Encyclopedia of Music in Canada'', the ''Canadian Encyclopedia Junior Edition'', ''Maclean's'' magazine articles, and ''Timelines of Canadian History''. , over 700,000 volumes of the print version of ''TCE'' have been sold and over 6 million people visit ''TCE'''s website yearly. History Background While attempts had been made to compile encyclopedic material on aspects of Canada, ''Canada: An Encyclopaedia of the Country'' (1898–1900), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Brown Milne
David Milne (January 8, 1882 – December 26, 1953) was a Canadian painter, printmaker, and writer. Biography David Milne was born near Paisley in 1882. He was the last of 10 children born to Scottish immigrant parents. His early education was in Paisley, followed by high school in Walkerton; he performed well in school and soon after graduation began teaching in a country school near Paisley. During 1902 and 1903 he studied art through correspondence, eventually deciding to move to New York City in 1903 at the age of 21. In New York, he spent two years (and a third year of night school) studying at the Art Students League. He had five paintings exhibited in the Armory Show of 1913, and he was also represented by the N. E. Montross Gallery (same as 'The Eight' or Ashcan School artists). In 1912, he married Frances May (known as Patsy) and later they moved to Boston Corners, a small hamlet where Milne painted with oils and watercolours. Milne left Boston Corners in 1917 for b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatint
Aquatint is an intaglio printmaking technique, a variant of etching that produces areas of tone rather than lines. For this reason it has mostly been used in conjunction with etching, to give both lines and shaded tone. It has also been used historically to print in colour, both by printing with multiple plates in different colours, and by making monochrome prints that were then hand-coloured with watercolour. It has been in regular use since the later 18th century, and was most widely used between about 1770 and 1830, when it was used both for artistic prints and decorative ones. After about 1830 it lost ground to lithography and other techniques. There have been periodic revivals among artists since then. An aquatint plate wears out relatively quickly, and is less easily reworked than other intaglio plates. Many of Goya's plates were reprinted too often posthumously, giving very poor impressions. Among the most famous prints using the aquatint technique are the major serie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann-Paul
René Georges Hermann-Paul (27 December 1864 – 23 June 1940) was a French artist. He was born in Paris and died in Saintes-Maries-de-la-Mer. He was a well-known illustrator whose work appeared in numerous newspapers and periodicals. His fine art was displayed in gallery exhibitions alongside Vuillard, Matisse and Toulouse-Lautrec. Early works were noted for their satiric characterizations of the foibles of French society. His points were made with simple caricature. His illustrations relied on blotches of pure black with minimum outline to define his animated marionettes. His exhibition pieces were carried by large splashes of color and those same fine lines of black. Hermann-Paul worked in Ripolin enamel paint, watercolors, woodcuts, lithographs, drypoint engraving, oils, and ink. Recent efforts to catalog the work of Hermann-Paul reveal an artist of considerable scope. On the eve of the First World War, he made quite an impression as part of M. Druet's "First Group." As noted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Portrait_of_Artist's_Wife%2C_drypoint%2C_ca_1905%2C_11.5x7.7_cm.jpg)