|
Droid Razr M
The Droid Razr M (Motorola XT905/XT906/XT907) is an Android-based, 4G LTE-capable smartphone designed by Motorola as a smaller successor to the Droid Razr. It was advertised as "The full screen phone" with thin edges, though it lacked a robust resolution. It came with a light skin of Android (operating system) for Verizon Wireless (XT907), SoftBank Mobile (XT902), and Telstra as well as an unbranded retail version for the Australian market (both XT905). The Electrify M (XT901) for U.S. Cellular is a CDMA handheld with a different housing, but otherwise same specification as the Razr M. History The lower-end Droid Razr M was announced alongside the Droid Razr HD and Razr Maxx HD on 5 September 2012. The Razr HD and M models ship with Android 4.0 (Ice Cream Sandwich). The Android 4.1 (Jelly Bean) upgrade for the Razr M started rolling out on Nov 9, 2012 and the upgrade to Android 4.4 (KitKat) on May 12, 2014. RAZR i The RAZR i (XT890) is an almost identical edition exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Droid Razr
The Verizon Droid Razr (GSM/UMTS version: Motorola Razr; both versions styled RAZR) is an Android-based, 4G LTE-capable smartphone designed by Motorola that launched on Verizon Wireless on November 11, 2011. It was announced on October 18, 2011 in New York City. At launch, the Razr was the thinnest smartphone in the world at only 7.1 mm thick on most of the device (it does, however, have a "bump" on top that is approximately 11.1 mm thick.) and includes a super active-matrix organic light emitting diode (AMOLED) advanced PenTile display, covered in a Gorilla glass screen and a Kevlar back plate. It is powered by an OMAP 4430 SoC with dual 1.2 GHz ARM Cortex-A9 processor cores. Its 8-megapixel rear-facing camera can record 1080p HD videos. It comes with 1 GB of RAM and runs Android version 4.1.2. The Razr Maxx is a variant with a higher capacity battery at 3300 mAh an 85% increase in capacity over the 1780 mAh battery in the original RAZR. Due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A Random access, random-access memory device allows data items to be read (computer), read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older Magnetic tape data storage, magnetic tapes and drum memory), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. RAM contains multiplexer, multiplexing and demultiplexing circuitry, to connect the data lines to the addressed storage for reading or writing the entry. Usually more than one bit of storage is accessed by the same address, and RAM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android (operating System)
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorilla Glass
Gorilla Glass is a brand of chemically strengthened glass developed and manufactured by Corning, now in its seventh generation. Designed to be thin, light and damage-resistant, the glass gains its surface strength, ability to contain flaws, and crack-resistance by being immersed in a hot, potassium-salt, ion-exchange bath. As a brand, Gorilla Glass is specific to Corning, but close equivalents exist, including AGC Inc.'s Dragontrail and Schott AG's Xensation. The alkali-aluminosilicate sheet glass is used primarily as cover glass for portable electronic devices, including mobile phones, smartwatches, portable media players, portable computer displays, and television screens. It is manufactured in Harrodsburg, Kentucky; in Asan, South Korea; and in Taiwan. In October 2017, some five billion devices globally contained Gorilla Glass. While dominating its market, Gorilla Glass faces varying competition from rivals such as Dragontrail and synthetic sapphire. Background and develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Field Communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used to bootstrap more-capable wireless connections. Like other "proximity card" technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two so-called antennas present on NFC-enabled devices—for example a smartphone and a printer—communicating in one or both directions, using a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band using the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 424 kbit/s. The standards were provided by the NFC Forum. The forum was responsible for promoting the technology and setting standards and certifies device compliance. Secure communications are available by applying encryption algorithms as is done for credit cards and if they fit the crite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola
Motorola, Inc. () was an American Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications company based in Schaumburg, Illinois, United States. After having lost $4.3 billion from 2007 to 2009, the company split into two independent public companies, Motorola Mobility and Motorola Solutions on January 4, 2011. Motorola Solutions is the legal successor to Motorola, Inc., as the reorganization was structured with Motorola Mobility being spun off. Motorola Mobility was acquired by Lenovo in 2014. Motorola designed and sold wireless network equipment such as cellular transmission base stations and signal amplifiers. Motorola's home and broadcast network products included set-top boxes, digital video recorders, and network equipment used to enable video broadcasting, computer telephony, and high-definition television. Its business and government customers consisted mainly of wireless voice and broadband systems (used to build private networks), and, public safety communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision. Satellite navigation devices supporting both GPS and GLONASS have more satellites available, meaning positions can be fixed more quickly and accurately, especially in built-up areas where buildings may obscure the view to some satellites. GLONASS supplementation of GPS systems also improves positioning in high latitudes (north or south). Development of GLONASS began in the Soviet Union in 1976. Beginning on 12 October 1982, numerous rocket launches added satellites to the system, unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frame Rate
Frame rate (expressed in or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images (frames) are captured or displayed. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also be called the , and be expressed in hertz. Frame rate in electronic camera specifications may refer to the maximal possible rate, where, in practice, other settings (such as exposure time) may reduce the frequency to a lower number. Human vision The temporal sensitivity and resolution of human vision varies depending on the type and characteristics of visual stimulus, and it differs between individuals. The human visual system can process 10 to 12 images per second and perceive them individually, while higher rates are perceived as motion. Modulated light (such as a computer display) is perceived as stable by the majority of participants in studies when the rate is higher than 50 Hz. This perception of modulated light as steady is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
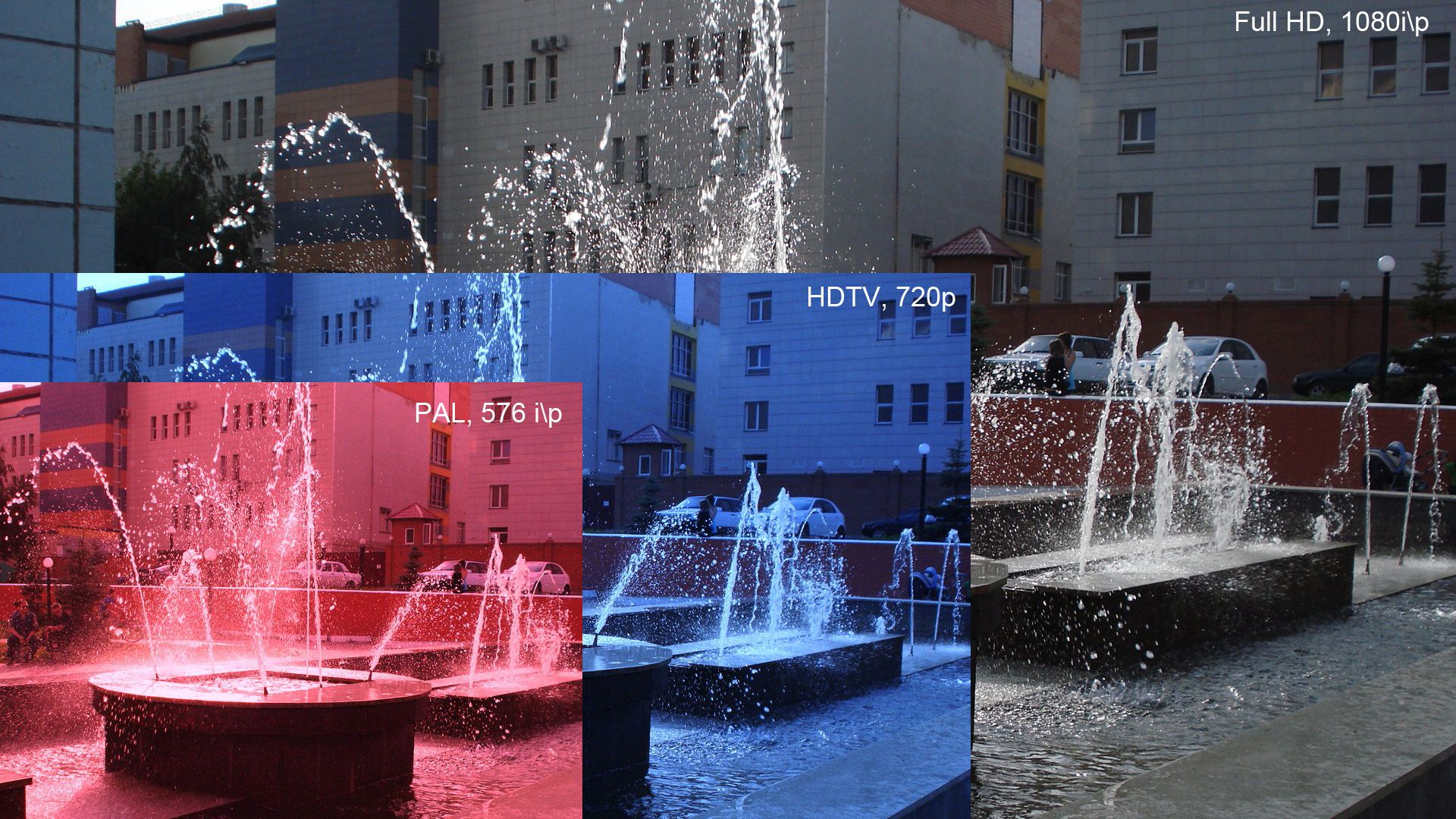
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-definition Video
High-definition video (HD video) is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for ''high-definition'', generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical scan lines (North America) or 576 vertical lines (Europe) is considered high-definition. 480 scan lines is generally the minimum even though the majority of systems greatly exceed that. Images of standard resolution captured at rates faster than normal (60 frames/second North America, 50 fps Europe), by a high-speed camera may be considered high-definition in some contexts. Some television series shot on high-definition video are made to look as if they have been shot on film, a technique which is often known as filmizing. History The first electronic scanning format, 405 lines, was the first ''high definition'' television system, since the mechanical systems it replaced had far fewer. From 1939, Europe and the US tried 605 and 441 lines until, in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megapixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as red, green, and blue, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet other contexts (like MRI) it may refer to a set of component intensities for a spatial position. Etymology The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exmor
Exmor is the name of a technology Sony implemented on some of their CMOS image sensors. It performs on-chip analog/digital signal conversion and two-step noise reduction in parallel on each column of the CMOS sensor. Exmor RS is the world's first stacked CMOS image sensor and was announced by Sony on 20 August 2012. Subsequently, Sony announced the first 3-layer stacked CMOS sensor, which added a DRAM cell array in the middle. History In October 2015, Sony Semiconductor Solutions was established as a wholly owned group company to reinforce the CMOS image sensor business and integrate the semiconductor-related business operations of Sony Group. Following the incorporation, all the Exmor sensors are designed and manufactured by the company. On May 14, 2020, the Intelligent Vision Sensor was announced with an introduction that reads: "the first image sensor in the world to be equipped with AI processing functionality". The new sensor distinguishes itself from the previous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)