|
Drift-barrier Hypothesis
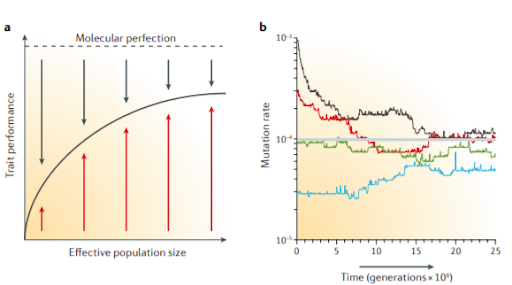
The drift-barrier hypothesis is an ecological hypothesis formulated by Michael Lynch in 2010. It suggests that the perfection of the performance of a trait, in a specific environment, by natural selection will hit a hypothetical barrier. The closer a trait comes to perfection, the smaller the fitness advantages become. Once this barrier is reached, the effects of further beneficial mutations are unlikely to be large enough to overcome the power of random genetic drift. Selection generally favors lower mutation rates due to the associated load of deleterious mutations that come with a high mutation rate. Description Every population contains a certain amount of genetic variation, coding for different functional traits. When the environment in which the population lives changes, some of these traits turn out to be more advantageous for this new situation than others. Through natural selection and random genetic drift, the traits with a negative effect on population fitness disapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Lynch (geneticist)
Michael Lynch (born 1951) is the Director of the Biodesign Institute for Mechanisms of Evolution at Arizona State University, Tempe, Arizona. Biography He held a Distinguished Professorship of Evolution, Population Genetics and Genomics at Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana. Besides over 250 papers, especially in population genetics, he has written a two volume textbook with Bruce Walsh. Alongside this textbook he has also published two other books. He promotes neutral theories to explain genomic architecture based on the effects of population sizes in different lineages; he presented this point of view in his 2007 book "The Origins of Genome Architecture". In 2009, he was elected to the National Academy of Sciences (Evolutionary Biology). Lynch was a Biology undergraduate at St. Bonaventure University and received a B.S. in Biology in 1973. He obtained his PhD from the University of Minnesota (Ecology and Behavioral Biology) in 1977. Honors and awards *2013: President of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drift Barrier Hypothesis
Drift or Drifts may refer to: Geography * Drift or ford (crossing) of a river * Drift, Kentucky, unincorporated community in the United States * In Cornwall, England: ** Drift, Cornwall, village ** Drift Reservoir, associated with the village Science, technology, and physics * Directional Recoil Identification from Tracks, a dark matter experiment * Drift (video gaming), a typical game controller malfunction * Drift pin, metalworking tool for localizing hammer blows and for aligning holes * Drift (geology), deposited material of glacial origin * Drift, linear term of a stochastic process * Drift (motorsport), the controlled sliding of a vehicle through a sharp turn, either via over-steering with sudden sharp braking, or counter-steering with a sudden "clutch kick" acceleration * Incremental changes: ** Drift (linguistics), a type of language change ** Genetic drift, change in allele frequency ** Drift (telecommunication), long-term change in an attribute of a system or eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, but other mechanisms, such as genetic drift, contribute to it, as well. Among individuals within a population Genetic variation can be identified at many levels. Identifying genetic variation is possible from observations of phenotypic variation in either quantitative traits (traits that vary continuously and are coded for by many genes (e.g., leg length in dogs)) or discrete traits (traits that fall into discrete categories and are coded for by one or a few genes (e.g., white, pink, or red petal color in certain flowers)). Genetic variation can also be identified by examining variation at the level of enzymes using the process of protein electrophoresis. Polymorphic genes have more than one allele at each locus. Half of the genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Ecology
Functional ecology is a branch of ecology that focuses on the roles, or functions, that species play in the community or ecosystem in which they occur. In this approach, physiological, anatomical, and life history characteristics of the species are emphasized. The term "function" is used to emphasize certain physiological processes rather than discrete properties, describe an organism's role in a trophic system, or illustrate the effects of natural selective processes on an organism." Towards A Definition Of Functional Ecology On JSTOR ". Jstor.org. N. p., 2017. Web. 2 May 2017. This sub-discipline of ecology represents the crossroads between ecological patterns and the processes and mechanisms that underlie them. It focuses on traits represented in large number of species and can be measured in two ways – the first being screening, which involves measuring a trait across a number of species, and the second being empiricism, which provides quantitative relationships for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend to survive and reproduce more than individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable. In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Motoo Kimura rekindled the debate with his neutral theory of molecular evolution, which claims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness (biology)
Fitness (often denoted w or ω in population genetics models) is the quantitative representation of individual reproductive success. It is also equal to the average contribution to the gene pool of the next generation, made by the same individuals of the specified genotype or phenotype. Fitness can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment or time. The fitness of a genotype is manifested through its phenotype, which is also affected by the developmental environment. The fitness of a given phenotype can also be different in different selective environments. With asexual reproduction, it is sufficient to assign fitnesses to genotypes. With sexual reproduction, recombination scrambles alleles into different genotypes every generation; in this case, fitness values can be assigned to alleles by averaging over possible genetic backgrounds. Natural selection tends to make alleles with higher fitness more common over time, resulting in Dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Pool
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species. Description A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survive bouts of intense selection. Meanwhile, low genetic diversity (see inbreeding and population bottlenecks) can cause reduced biological fitness and an increased chance of extinction, although as explained by genetic drift new genetic variants, that may cause an increase in the fitness of organisms, are more likely to fix in the population if it is rather small. When all individuals in a population are identical with regard to a particular phenotypic trait, the population is said to be 'monomorphic'. When the individuals show several variants of a particular trait they are said to be polymorphic. History The Russian geneticist Alexander Sergeevich Serebrovsky first formulated the concept in the 1920s as ''genofond'' (gene fund), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
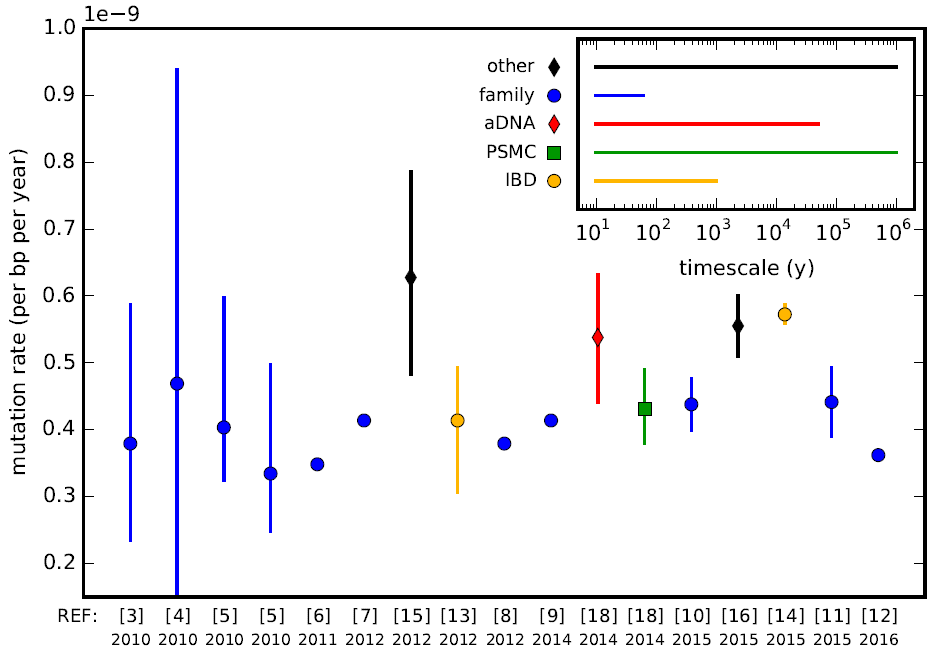
Mutation Rate
In genetics, the mutation rate is the frequency of new mutations in a single gene or organism over time. Mutation rates are not constant and are not limited to a single type of mutation; there are many different types of mutations. Mutation rates are given for specific classes of mutations. Point mutations are a class of mutations which are changes to a single base. Missense mutation, Missense and Nonsense mutations are two subtypes of point mutations. The rate of these types of substitutions can be further subdivided into a mutation spectrum which describes the influence of the genetic context on the mutation rate. There are several natural units of time for each of these rates, with rates being characterized either as mutations per base pair per cell division, per gene per generation, or per genome per generation. The mutation rate of an organism is an evolved characteristic and is strongly influenced by the genetics of each organism, in addition to strong influence from the envi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the population during that process. Thirdly, it is a phenotypic trait or adaptive trait, with a functional role in each individual organism, that is maintained and has evolved through natural selection. Historically, adaptation has been described from the time of the ancient Greek philosophers such as Empedocles and Aristotle. In 18th and 19th century natural theology, adaptation was taken as evidence for the existence of a deity. Charles Darwin proposed instead that it was explained by natural selection. Adaptation is related to biological fitness, which governs the rate of evolution as measured by change in allele frequencies. Often, two or more species co-adapt and co-evolve as they develop adaptations that interlock with those of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixation (population Genetics)
In population genetics, fixation is the change in a gene pool from a situation where there exists at least two variants of a particular gene (allele) in a given population to a situation where only one of the alleles remains. In the absence of mutation or heterozygote advantage, any allele must eventually be lost completely from the population or fixed (permanently established at 100% frequency in the population). Whether a gene will ultimately be lost or fixed is dependent on selection coefficients and chance fluctuations in allelic proportions. Fixation can refer to a gene in general or particular nucleotide position in the DNA chain ( locus). In the process of substitution, a previously non-existent allele arises by mutation and undergoes fixation by spreading through the population by random genetic drift or positive selection. Once the frequency of the allele is at 100%, i.e. being the only gene variant present in any member, it is said to be "fixed" in the population. Simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directional Selection
In population genetics, directional selection, is a mode of negative natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype. Under directional selection, the advantageous allele increases as a consequence of differences in survival and reproduction among different phenotypes. The increases are independent of the dominance of the allele, and even if the allele is recessive, it will eventually become fixed. Directional selection was first described by Charles Darwin in the book ''On the Origin of Species'' as a form of natural selection. Other types of natural selection include stabilizing and disruptive selection. Each type of selection contains the same principles, but is slightly different. Disruptive selection favors both extreme phenotypes, different from one extreme in directional selection. Stabilizing selection favors the middle phenotype, causing the dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |