|
Drawplate
A draw plate is type of die consisting of a hardened steel plate with one or more holes through which wire is drawn to make it thinner. A typical plate will have twenty to thirty holes so a wide range of diameters can be drawn. With a mandrel, a draw plate can be used to draw tubes of metal. Plates are available in many different sizes and shapes for drawing different shapes of wire, including round, square, oval, half-round and hexagonal. The plate has rows of holes drilled through it which are slightly wider at the back. Drawing wire When drawing, the plate is held securely in a vise or other fixture. Annealed wire is filed at one end to give it an initial taper. The tapered end is inserted into a hole with a final diameter just smaller than its current width. Special pliers, called draw tongs are used to hold the tip of the wire and pull it through, sometimes with the aid of grease or wax as a lubricant. Small diameter wire may be drawn manually, while very thick wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draw Plates-two
Draw, drawing, draws, or drawn may refer to: Common uses * Draw (terrain), a terrain feature formed by two parallel ridges or spurs with low ground in between them * Drawing (manufacturing), a process where metal, glass, or plastic or anything else is stretched ** Wire drawing *Drawing, the result or the act of making an image with a writing utensil * To select or wield: ** A part of many card games, to "draw" a card ** A part of a lottery, to "draw" a lottery number ** The act of wielding a weapon by removing from a sheath, to "draw" a knife or sword ** The act of wielding a weapon by removing from a holster, to "draw" a pistol ** Venipuncture People * Stefanie Draws (born 1989), German footballer Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Draw'', the debut album of Matthew Jay * ''Drawn'' (album), a 1998 album by Regina Velasquez Other arts, entertainment, and media * ''Draw!'', a 1984 comedy-western film * ''Drawn'' (series), game series Computing and technology * Dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die (manufacturing)
A die is a specialized machine tool used in manufacturing industries to cut and/or form material to a desired shape or profile. Stamping dies are used with a press, as opposed to drawing dies (used in the manufacture of wire) and casting dies (used in molding) which are not. Like molds, dies are generally customized to the item they are used to create. Products made with dies range from simple paper clips to complex pieces used in advanced technology. Continuous-feed laser cutting may displace the analogous die-based process in the automotive industry, among others. Die stamping Blanking and piercing are two die cutting operations, and bending is an example of a die forming operation. Die forming Forming operations work by deforming materials like sheet metal or plastic using force (compression, tension, or both) and rely on the material's mechanical properties. Forming dies are typically made by tool and die makers and put into production after mounting into a press. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardened Steel
The term hardened steel is often used for a medium or high carbon steel that has been given heat treatment and then quenching followed by tempering. The quenching results in the formation of metastable martensite, the fraction of which is reduced to the desired amount during tempering. This is the most common state for finished articles such as tools and machine parts. In contrast, the same steel composition in annealed state is softer, as required for forming and machining. Depending on the temperature and composition of the steel, it can be hardened or softened. To make steel harder, it must be heated to very high temperatures. The final result of exactly how hard the steel becomes depends on the amount of carbon present in the metal. Only steel that is high in carbon can be hardened and tempered. If a metal does not contain the necessary quantity of carbon, then its crystalline structure cannot be broken, and therefore the physical makeup of the steel cannot be altered. Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Drawing
Wire drawing is a metalworking process used to reduce the cross-section of a wire by pulling the wire through a single, or series of, drawing die(s). There are many applications for wire drawing, including electrical wiring, cables, tension-loaded structural components, springs, paper clips, spokes for wheels, and stringed musical instruments. Although similar in process, drawing is different from extrusion, because in drawing the wire is pulled, rather than pushed, through the die. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process, but it may be performed at elevated temperatures for large wires to reduce forces. Process The wire drawing process is quite simple in concept. The wire is prepared by shrinking the beginning of it, by hammering, filing, rolling or swaging, so that it will fit through the die; the wire is then pulled through the die. As the wire is pulled through the die, its volume remains the same, so as the diameter de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandrel
A mandrel, mandril, or arbor is a gently tapered cylinder against which material can be forged or shaped (e.g., a ring mandrel - also called a triblet - used by jewelers to increase the diameter of a wedding ring), or a flanged or tapered or threaded bar that grips a workpiece to be machined in a lathe. A flanged mandrel is a parallel bar of a specific diameter with an integral flange towards one end, and threaded at the opposite end. Work is gripped between the flange and a nut on the thread. A tapered mandrel (often called a plain mandrel) has a taper of approximately 0.005 inches per foot and is designed to hold work by being driven into an accurate hole on the work, gripping the work by friction. A threaded mandrel may have a male or female thread, and work which has an identical thread is screwed onto the mandrel. On a lathe, mandrels are commonly mounted between centres and driven by a lathe dog (typically the flanged or tapered mandrels), but may also be gripped in a ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annealing (metallurgy)
In metallurgy and materials science, annealing is a heat treatment that alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it more workable. It involves heating a material above its recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature for an appropriate amount of time and then cooling. In annealing, atoms migrate in the crystal lattice and the number of dislocations decreases, leading to a change in ductility and hardness. As the material cools it recrystallizes. For many alloys, including carbon steel, the crystal grain size and phase composition, which ultimately determine the material properties, are dependent on the heating rate and cooling rate. Hot working or cold working after the annealing process alters the metal structure, so further heat treatments may be used to achieve the properties required. With knowledge of the composition and phase diagram, heat treatment can be used to ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
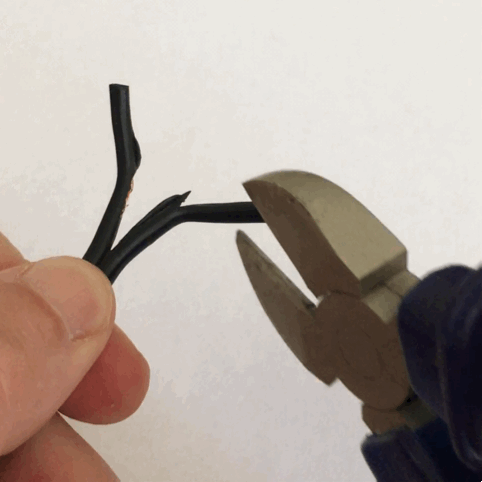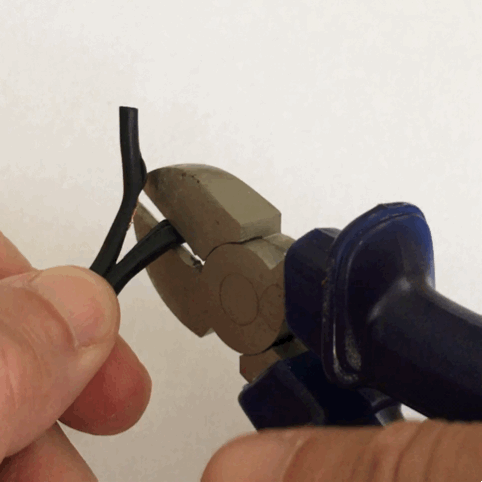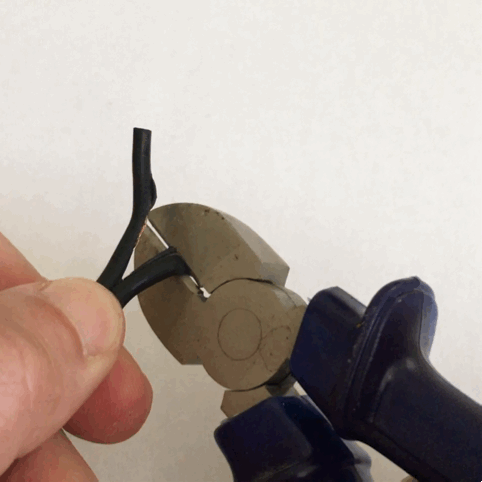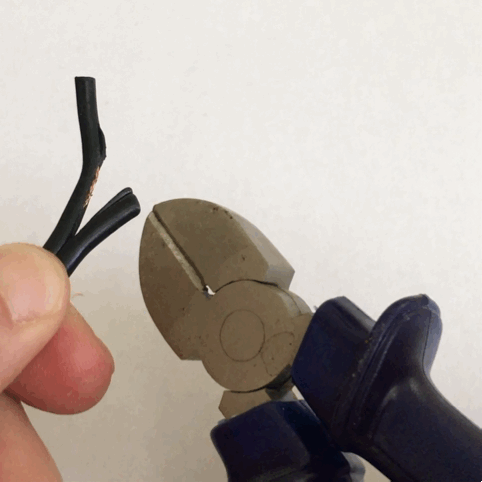
Pliers
Pliers are a hand tool used to hold objects firmly, possibly developed from tongs used to handle hot metal in Bronze Age Europe. They are also useful for bending and physically compressing a wide range of materials. Generally, pliers consist of a pair of metal first-class levers joined at a fulcrum positioned closer to one end of the levers, creating short ''jaws'' on one side of the fulcrum, and longer handles on the other side. This arrangement creates a mechanical advantage, allowing the force of the grip strength to be amplified and focused on an object with precision. The jaws can also be used to manipulate objects too small or unwieldy to be manipulated with the fingers. Diagonal pliers, also called side cutters, are a similarly-shaped tool used for cutting rather than holding, having a pair of stout blades, similar to scissors except that the cutting surfaces meet parallel to each other rather than overlapping. Ordinary (holding/squeezing) pliers may incorporate a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongs
Tongs are a type of tool used to grip and lift objects instead of holding them directly with hands. There are many forms of tongs adapted to their specific use. The first pair of tongs belongs to the Egyptians. Tongs likely started off as basic wooden tongs and then over time progressed to bronze bars as early as 3000BC. Over time they progressed to what we now know as modern-day tongs. An Egyptian wall painting from 1450 BCE shows a crucible supported between two metal bars. The same painting shows someone holding a small object over a fire with a tong-like instrument. Bronze loops capable of handling heavy crucibles also happened to appear at this time. # Tongs that have long arms terminating in small flat circular ends of tongs and are pivoted at a joint close to the handle used to handle delicate objects. Common fire-tongs, used for picking up pieces of coal and placing them on a fire without burning fingers or getting them dirty are of this type. Tongs for grilling, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking (oils and fats in use in frying pans, in baking to prevent food sticking), bioapplications on humans (e.g. lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better and efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of years. Calcium soaps have been identified on the axles of chariots dated to 1400 BC. Building stones were slid on oil-impregrated lumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Hardening
In materials science, work hardening, also known as strain hardening, is the strengthening of a metal or polymer by plastic deformation. Work hardening may be desirable, undesirable, or inconsequential, depending on the context. This strengthening occurs because of dislocation movements and dislocation generation within the crystal structure of the material. Many non-brittle metals with a reasonably high melting point as well as several polymers can be strengthened in this fashion. Alloys not amenable to heat treatment, including low-carbon steel, are often work-hardened. Some materials cannot be work-hardened at low temperatures, such as indium, however others can be strengthened only via work hardening, such as pure copper and aluminum. Undesirable work hardening An example of undesirable work hardening is during machining when early passes of a cutter inadvertently work-harden the workpiece surface, causing damage to the cutter during the later passes. Certain alloys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tube Drawing
Tube drawing is a process to size a tube by shrinking a large diameter tube into a smaller one, by drawing the tube through a die. This process produces high-quality tubing with precise dimensions, good surface finish, and the added strength of cold working.Degarmo, p. 433. For this reason this process is established for many materials, mainly metalworking but also glass. Because it is so versatile, tube drawing is suitable for both large- and small-scale production. The large-scale production of glass typically uses a one step process where glass is directly drawn into a tube from a melting tank. There are five types of tube drawing: tube sinking, mandrel drawing, stationary mandrel, moving mandrel, and floating mandrel. A mandrel is used in many of the types to prevent buckling or wrinkling in the workpiece. Processes Tube sinking Tube sinking, also known as ''free tube drawing'', reduces the diameter of the tube without a mandrel inside the tube. The inner diameter is determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |