|
Drascombe Lugger Onkahye Boomkin
The word Drascombe is a trademark that was first registered by John Watkinson who applied it to a series of sailing boats which he designed and built in the period 1965–79 and sold in the United Kingdom (UK). They comprised the Coaster, Cruiser Longboat, Dabber, Drifter, Driver, Gig, Launch, Longboat, Lugger, Peterboat, Scaffie, Scaith and Skiff, together with a few other one-offs. They have wide and deep cockpits, adaptable boomless rigs and high bulwarks. The word drascombe is also used as a generic term for any boat built to a design by John Watkinson. These include both 'the Drascombe range' build by Churchouse Boats Churchouse Boats ltd . Accessed 28 August 2009. and the 'Original Devon' range produced by Honnor Marine, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drascombe Lugger Roamer Starboard Tack
The word Drascombe is a trademark that was first registered by John Watkinson who applied it to a series of sailing boats which he designed and built in the period 1965–79 and sold in the United Kingdom (UK). They comprised the Coaster, Cruiser Longboat, Dabber, Drifter, Driver, Gig, Launch, Longboat, Drascombe Lugger, Lugger, Peterboat, Scaffie, Scaith and Skiff, together with a few other one-offs. They have wide and deep cockpits, adaptable boomless rigs and high bulwarks. The word drascombe is also used as a generic term for any boat built to a design by John Watkinson. These include both 'the Drascombe range' build by Churchouse Boats Churchouse Boats ltd . Accessed 28 August 2009. and the 'Original Devon' range produced by Honnor Marine, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foresail
A foresail is one of a few different types of sail set on the foremost mast (''foremast'') of a sailing vessel: * A fore-and-aft sail set on the foremast of a schooner or similar vessel. * The lowest square sail on the foremast of a full-rigged ship or other vessel which is square-rigged. Sails set forward of the mainmast, such as jibs and staysails, are sometimes referred to as foresails, although "headsails" is a more common term, headsail can also specifically refer to the sail on a forestay that connects directly to the head of the mast. History Foresails set on foremasts between midships and bow were the first type of sail to appear after the mainsail which had been the sole standard rig on sailing vessels for millennia, down to classical antiquity. The earliest foresail, or two-masted ship, has been identified on an Etruscan pyxis from Caere, Italy, dating to the mid-7th century BC: a warship with a furled mainsail is engaging an enemy vessel, deploying a foresai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galley (kitchen)
The galley is the compartment of a ship, train, or aircraft where food is cooked and prepared. It can also refer to a land-based kitchen on a naval base, or, from a kitchen design point of view, to a straight design of the kitchen layout. Ship's cooking area A galley is the cooking area aboard a vessel, usually laid out in an efficient typical style with longitudinal units and overhead cabinets. This makes the best use of the usually limited space aboard ships. It also caters for the rolling and heaving nature of ships, making them more resistant to the effects of the movement of the ship. For this reason galley stoves are often gimballed, so that the liquid in pans does not spill out. They are also commonly equipped with bars, preventing the cook from falling against the hot stove. A small cooking area on deck was called a caboose or ''camboose'', originating from the nl, kombuis, which is still in use today. In English it is a defunct term used only for a cooking area that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeboard (nautical)
In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relative to the ship's load line, regardless of deck arrangements, is the mandated and regulated meaning. In yachts, a low freeboard is often found on racing boats, for increased speed (by reducing weight and therefore drag). A higher freeboard will give more room in the cabin, but will increase weight and drag, compromising speed. A higher freeboard, such as used on ocean liners, also helps weather waves and so reduce the likelihood of being washed over by full water waves. A low-freeboard vessel is susceptible to taking in water in rough seas. Freighter ships and warships use high freeboard designs to increase internal volume, which also allows them to satisfy International Maritime Organization (IMO) damage stability regulations, due to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowsprit
The bowsprit of a sailing vessel is a spar extending forward from the vessel's prow. The bowsprit is typically held down by a bobstay that counteracts the forces from the forestays. The word ''bowsprit'' is thought to originate from the Middle Low German word ''bōchsprēt'' – ''bōch'' meaning "bow" and ''sprēt'' meaning "pole". It is sometimes used to hold up the figurehead In politics, a figurehead is a person who ''de jure'' (in name or by law) appears to hold an important and often supremely powerful title or office, yet ''de facto'' (in reality) exercises little to no actual power. This usually means that they .... References References * {{Sailing ship elements Sailboat components ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
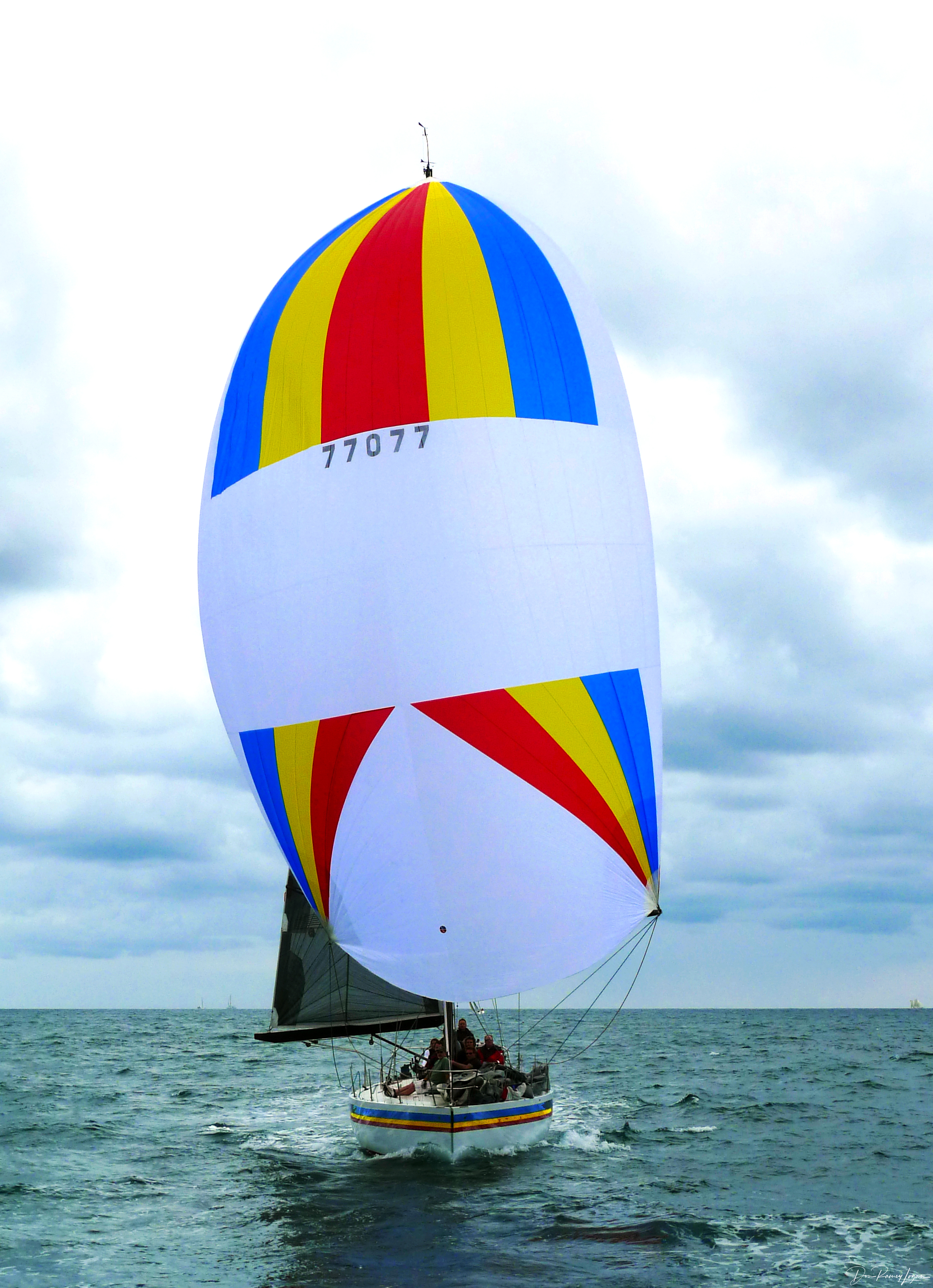
Cruising Chute
A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach (wind at 90° to the course) to downwind (course in the same direction as the wind). Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and are often brightly colored. They may be designed to perform best as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams. They are attached at only three points and said to be ''flown''. Nomenclature Informal names for a spinnaker are ''kite'' or ''chute'' (owing to their resemblance to a parachute in both construction and appearance). Boats may have more than one spinnaker, differentiated by a letter to indicate symmetric (S) or asymmetric (A) and a number to indicate size (with higher numbers indicating smaller size), e.g. ''A1'' would be a large asymmetric sail and ''S3'' would be a smaller symmetric sail. Operation A spinnaker is used for sailing with the direction of the wind. Symmetrical s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N18 With Drascombe
{{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ...
N18 may refer to: Roads * N18 road (Belgium), a National Road of Belgium * Route nationale 18, in France * N18 road (Ireland) * A18 motorway (Netherlands) * N18 (South Africa) * Nebraska Highway 18, in the United States Other uses * BMW N18, an automobile engine * Chronic kidney disease * , a submarine of the Royal Navy * London Buses route N18 * Nissan Almera (N18), a Japanese automobile * Nitrogen-18, an isotope of nitrogen * Tinak Airport, on Arno Atoll, Marshall Islands * N18, a postcode district in the N postcode area N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''en'' (pronounced ), plural ''ens''. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
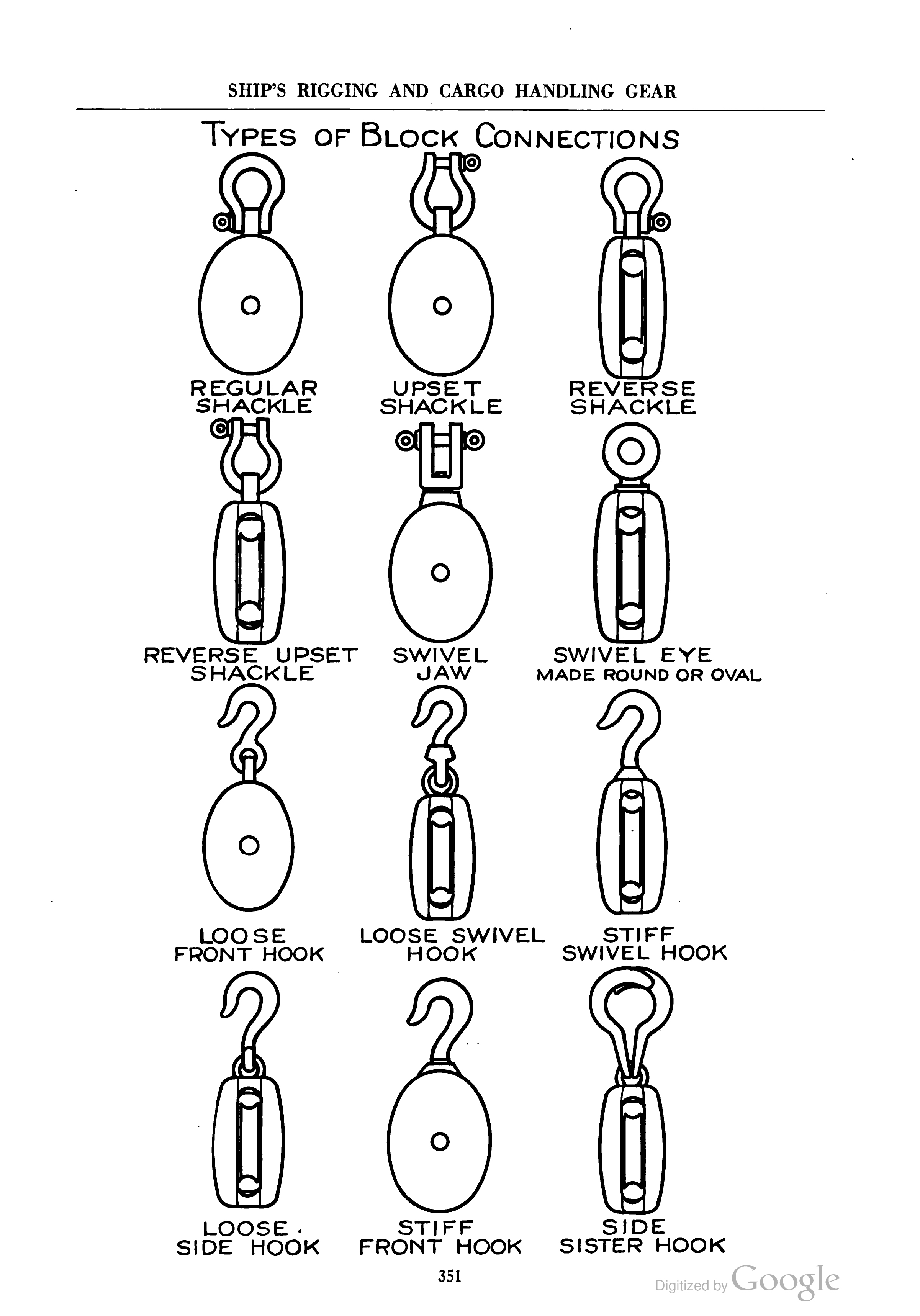
Block (sailing)
In sailing, a block is a single or multiple pulley. One or a number of ''sheaves'' are enclosed in an assembly between ''cheeks'' or ''chocks''. In use, a block is fixed to the end of a line, to a spar (sailing), spar, or to a surface. A line (rope) is ''reeved'' through the sheaves, and maybe through one or more matching blocks at some far end, to make up a Block and tackle, tackle. The ''purchase'' of a tackle refers to its mechanical advantage. In general the more sheaves in the blocks that make up a tackle, the higher its mechanical advantage. The matter is slightly complicated by the fact that every tackle has a ''working end'' where the final run of rope leaves the last sheave. More mechanical advantage can be obtained if this end is attached to the moving load rather than the fixed end of the tackle. There are various types of blocks that are used in sailing. Some blocks are used to increase mechanical advantage and others are used simply to change the direction of a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centreboard
A centreboard or centerboard (US) is a retractable hull appendage which pivots out of a slot in the hull of a sailboat, known as a ''centreboard trunk'' (UK) or ''centerboard case'' (US). The retractability allows the centreboard to be raised to operate in shallow waters, to move the centre of lateral resistance (offsetting changes to the sailplan that move the centre of effort aft), to reduce drag when the full area of the centreboard is not needed, or when removing the boat from the water, as when trailering. A centreboard which consists of solely a pivoting metal plate is called a centerplate. A daggerboard is similar but slides vertically rather than pivoting. The analog in a scow is a bilgeboard: these are fitted in pairs and used one at a time. General History Lt. John Schank (c. 1740 – 6 February 1823) was an officer of the British Royal Navy and is credited with the invention of the centerboard. Schank, however, gave credit for the idea to British Brigadier General ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, aircraft, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (generally aircraft, air or watercraft, water). On an aircraft the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull (watercraft), hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yaw (rotation), yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or after end. Often rudders are shaped so as to minimize Drag (physics), hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may be used to link rudders to steering wheels. In typical air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)