|
Dr. Nim
Dr. Nim is a toy invented by John Thomas Godfrey and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the mid-1960s. It consists of a marble-powered plastic computer capable of playing the game of Nim. The machine selects its moves through the action of the marbles falling through the levers of the machine. Game play and construction Dr. Nim is an early computer game. The "game board" is based on the mechanical Digi-Comp II digital computer. It has memory switches that hold bits of data. The unit is programmed by lobed levers that affect and are affected by marbles that are released from the top of the game. Three of the levers set the start position. The fourth lever is the 'equaliser' option; if set, the player can win if they play perfectly. A fifth lever acts as a switch to indicate whose turn it is. The player takes a turn by pressing a button to release one marble at a time, to a maximum of three, then flips the switch and presses the button again to start the machine's turn. After the machi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as Computer program, programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the Computer hardware, hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of Programmable logic controller, industrial and Consumer electronics, consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
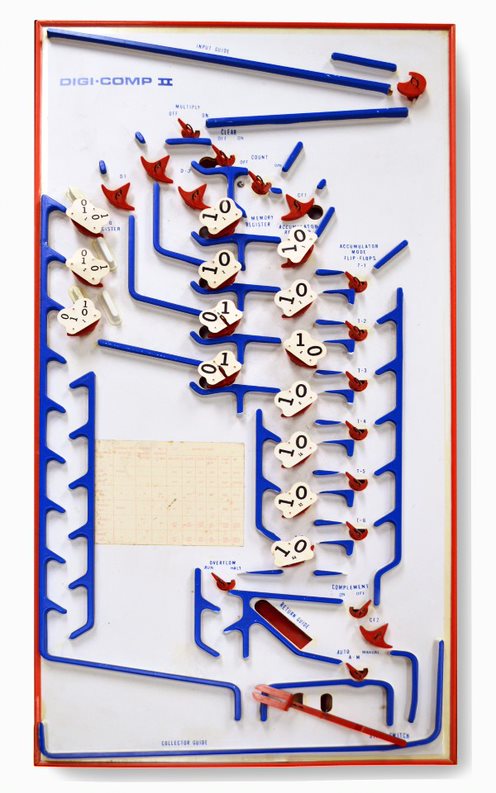
Digi-Comp II
The Digi-Comp II was a toy computer invented by John "Jack" Thomas Godfrey (1924–2009) in 1965 and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the late 1960s that used marbles rolling down a ramp to perform basic calculations. A two-level masonite platform with blue plastic guides served as the medium for a supply of marbles that rolled down an inclined plane moving plastic cams as they went. The red plastic cams played the part of flip-flops in an electronic computer - as a marble passed one of the cams, it would flip the cam around - in one position, the cam would allow the marble to pass in one direction, in the other position, it would cause the marble to drop through a hole and roll to the bottom of the ramp. The Digi-Comp II platform measures . The Digi-Comp II was not programmable, unlike the Digi-Comp I, an earlier offering in the E.S.R. product line that used an assortment of plastic slides, tubes, and bent metal wires to solve simple logic problems. Computational power Compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matt Parker
Matthew Thomas Parker (born 22 December 1980) is an Australian recreational mathematician, author, comedian, YouTube personality and science communicator based in the United Kingdom. His book ''Humble Pi'' was the first maths book in the UK to be a Sunday Times No. 1 bestseller. Parker was the Public Engagement in Mathematics Fellow at Queen Mary University of London. He is a former maths teacher and has helped popularise maths via his tours and videos. Early life and education Matt Parker was born in Perth, Australia, and grew up in the northern suburb of Duncraig. He began showing an interest in maths and science from a young age, and at one point was part of his school's titration team. Parker went to the University of Western Australia and started off studying mechanical engineering before he "realized the very real risk of being employable at the end of it." He switched into physics and later mathematics. His love of maths led him to want a job in the subject. While a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Computers
A mechanical computer is a computer built from mechanical components such as levers and gears rather than electronic components. The most common examples are adding machines and mechanical counters, which use the turning of gears to increment output displays. More complex examples could carry out multiplication and division—Friden used a moving head which paused at each column—and even differential analysis. One model, the Ascota 170 accounting machine sold in the 1960s calculated square roots. Mechanical computers can be either analog, using smooth mechanisms such as curved plates or slide rules for computations; or digital, which use gears. Mechanical computers reached their zenith during World War II, when they formed the basis of complex bombsights including the Norden, as well as the similar devices for ship computations such as the US Torpedo Data Computer or British Admiralty Fire Control Table. Noteworthy are mechanical flight instruments for early spacecraft, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |