|
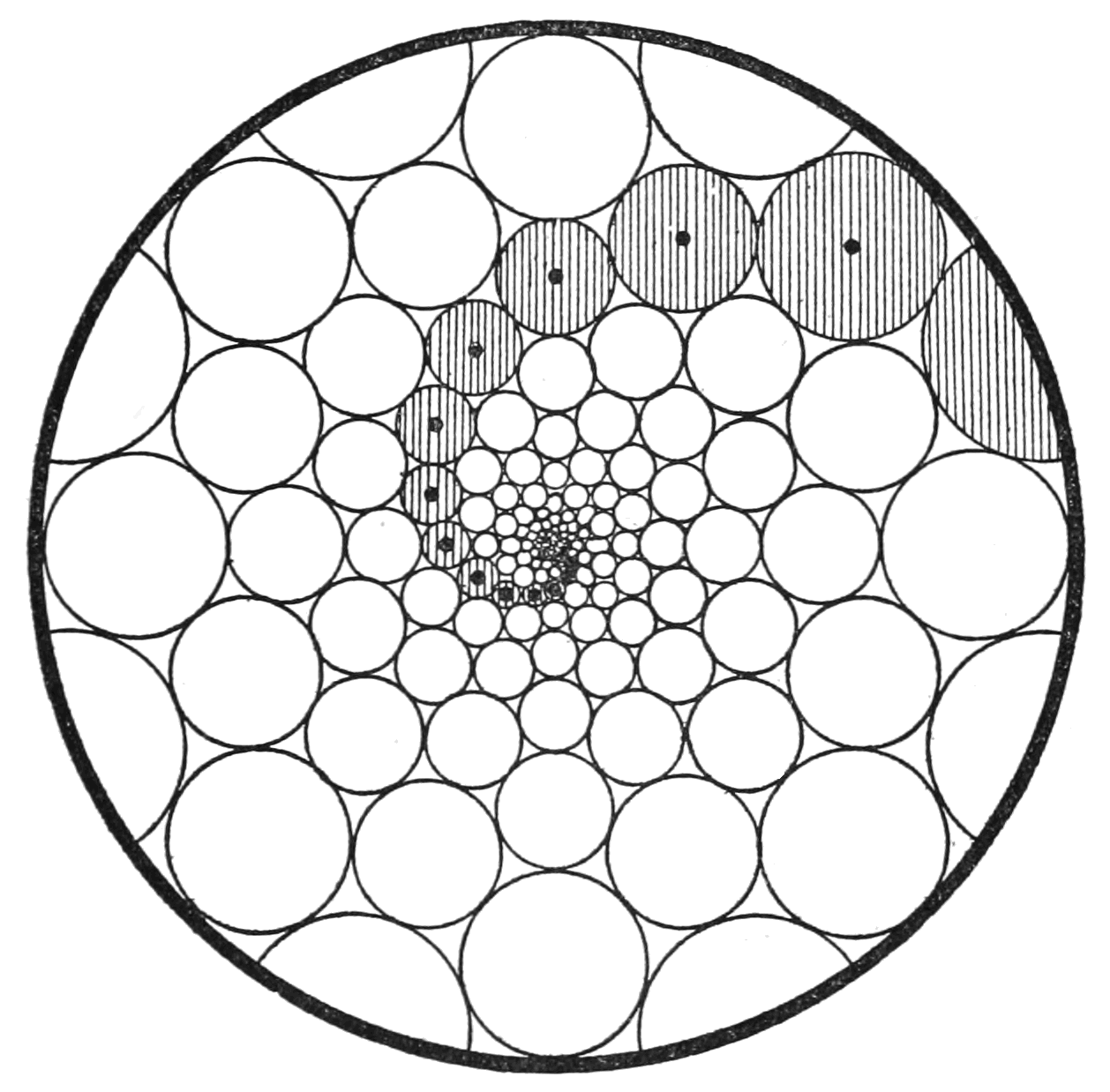
Doyle Spiral
In the mathematics of circle packing, a Doyle spiral is a pattern of non-crossing circles in the plane in which each circle is surrounded by a ring of six tangent circles. These patterns contain spiral arms formed by circles linked through opposite points of tangency, with their centers on logarithmic spirals of three different shapes. Doyle spirals are named after mathematician Peter G. Doyle, who made an important contribution to their mathematical construction in the late 1980s or However, their study in phyllotaxis (the mathematics of plant growth) dates back to the early Definition A Doyle spiral is defined to be a certain type of circle packing, consisting of infinitely many circles in the plane, with no two circles having overlapping interiors. In a Doyle spiral, each circle is enclosed by a ring of six other circles. The six surrounding circles are tangent to the central circle and to their two neighbors in the Properties Radii As Doyle the only way to pack circl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSM V79 D459 Logarithmic Spiral In Flower Growth Configuration
PSM, an acronym, may refer to: Organizations * Sepaktakraw Association of Malaysia ( ms, Persatuan Sepaktakraw Malaysia; PSM), a national governing body in Malaysia. * Pakistan School Muscat, a Pakistani co-educational institute in Oman * Palestine Solidarity Movement, a student organization in the United States * Panhellenic Socialist Movement, a centre-left party in Greece * Parti Sosialis Malaysia, a socialist political party in Malaysia * PlayStation: The Official Magazine, a magazine originally known as PlayStation Magazine or PSM * Ponce School of Medicine, a post-graduate medical school located in Ponce, Puerto Rico * Power Systems Mfg, a subsidiary of Alstom, specializing in aftermarket gas turbine servicing for power generating industry. * ''Poznańska Spółdzielnia Mieszkaniowa'', a housing cooperative administering most of the Piątkowo district of Poznań, Poland * PSM3, a UK video game magazine specializing in Sony consoles * PSM Makassar, a football club tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0, where the Greek letter phi ( or \phi) denotes the golden ratio. The constant \varphi satisfies the quadratic equation \varphi^2 = \varphi + 1 and is an irrational number with a value of The golden ratio was called the extreme and mean ratio by Euclid, and the divine proportion by Luca Pacioli, and also goes by several other names. Mathematicians have studied the golden ratio's properties since antiquity. It is the ratio of a regular pentagon's diagonal to its side and thus appears in the construction of the dodecahedron and icosahedron. A golden rectangle—that is, a rectangle with an aspect ratio of \varphi—may be cut into a square and a smaller rectangle with the same aspect ratio. The golden ratio has been used to analyze the proportions of natural object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cone
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex. A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines connecting a common point, the apex, to all of the points on a base that is in a plane that does not contain the apex. Depending on the author, the base may be restricted to be a circle, any one-dimensional quadratic form in the plane, any closed one-dimensional figure, or any of the above plus all the enclosed points. If the enclosed points are included in the base, the cone is a solid object; otherwise it is a two-dimensional object in three-dimensional space. In the case of a solid object, the boundary formed by these lines or partial lines is called the ''lateral surface''; if the lateral surface is unbounded, it is a conical surface. In the case of line segments, the cone does not extend beyond the base, while in the case of half-lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in ball and sphere)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term cylinder could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the ''right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through a fixed plane curve in a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold Emch
Arnold F. Emch (24 March 1871 – 1959) was an American mathematician, known for his work on the inscribed square problem. Emch received his Ph.D. in 1895 at the University of Kansas under the supervision of Henry Byron Newson. In the late 1890s until 1905 he was an assistant professor of graphic mathematics in the school of engineering at the Kansas State Agricultural College (now Kansas State University). In 1905 Emch became a professor of mathematics at the Kantonsschule in Solothurn, Switzerland. In 1908 Emch gave a lecture at the International Congress of Mathematicians in Rome. From 1911 to 1939 he was a professor at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (U of I, Illinois, University of Illinois, or UIUC) is a public land-grant research university in Illinois in the twin cities of Champaign and Urbana. It is the flagship institution of the University .... His wife was Hilda Walters Emch (1875–1962) and they had two so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibonacci Numbers
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted , form a sequence, the Fibonacci sequence, in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors start the sequence from 1 and 1 or sometimes (as did Fibonacci) from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the first few values in the sequence are: :0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144. The Fibonacci numbers were first described in Indian mathematics, as early as 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of Sanskrit poetry formed from syllables of two lengths. They are named after the Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, later known as Fibonacci, who introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics in his 1202 book ''Liber Abaci''. Fibonacci numbers appear unexpectedly often in mathematics, so much so that there is an entire journal dedicated to their study, the ''Fibonacci Quarterly''. Applications of Fibonacci numbers include co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parastichy
Parastichy, in phyllotaxy, is the spiral pattern of particular plant organs on some plants, such as areoles on cacti stems, florets in sunflower heads and scales in pine cones. These spirals involve the insertion of a single primordium. See also * Embryology * * Gerrit van Iterson * * Phyllotaxis In botany, phyllotaxis () or phyllotaxy is the arrangement of leaf, leaves on a plant stem. Phyllotactic spirals form a distinctive class of patterns in nature. Leaf arrangement The basic leaf#Arrangement on the stem, arrangements of leaves ... References External links Smith College Spiral Lattices & Parastichy Interactive Parastichies Explorer Plant morphology {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerrit Van Iterson
''This page was created from the Dutch Wikipedia with the aid of automatic translation'' Gerrit van Iterson Jr (Roermond, August 19, 1878 – Wassenaar, January 4, 1972) was a Dutch botanist and professor who developed a mathematical approach to plant growth (phyllotaxis). Biography Gerrit van Iterson studied in the Department of Chemical Engineering at the Polytechnic in Delft from 1897 to 1901. He studied chemistry under H. Behrens and microbiology under Martinus Willem Beijerinck. He got a PhD in 1907 with a thesis on phyllotaxis, where he fielded a mathematical theory for leaf growth (''Mathematical und Studien über microscopic anatomical Blattstellungen, etc.''). He also created a diagram that came to be called the van Iterson Diagram, based on his studies of how spheres can be arranged in a regular cylindrical pattern called a 'rhombic lattice'. Smith College's "About Phyllotaxis" page notes that the van Iterson Diagram of plant growth is related to a tiling of the hyperb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibonacci Number
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted , form a sequence, the Fibonacci sequence, in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors start the sequence from 1 and 1 or sometimes (as did Fibonacci) from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the first few values in the sequence are: :0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144. The Fibonacci numbers were first described in Indian mathematics, as early as 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of Sanskrit poetry formed from syllables of two lengths. They are named after the Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, later known as Fibonacci, who introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics in his 1202 book ''Liber Abaci''. Fibonacci numbers appear unexpectedly often in mathematics, so much so that there is an entire journal dedicated to their study, the ''Fibonacci Quarterly''. Applications of Fibonacci numbers include co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space of dimension n is the unique simply connected, n-dimensional Riemannian manifold of constant sectional curvature equal to -1. It is homogeneous, and satisfies the stronger property of being a symmetric space. There are many ways to construct it as an open subset of \mathbb R^n with an explicitly written Riemannian metric; such constructions are referred to as models. Hyperbolic 2-space, H2, which was the first instance studied, is also called the hyperbolic plane. It is also sometimes referred to as Lobachevsky space or Bolyai–Lobachevsky space after the names of the author who first published on the topic of hyperbolic geometry. Sometimes the qualificative "real" is added to differentiate it from complex hyperbolic spaces, quaternionic hyperbolic spaces and the octononic hyperbolic plane which are the other symmetric spaces of negative curvature. Hyperbolic space serves as the prototype of a Gromov hyperbolic space which is a far-reachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleinian Group
In mathematics, a Kleinian group is a discrete subgroup of the group (mathematics), group of orientation-preserving Isometry, isometries of hyperbolic 3-space . The latter, identifiable with PSL(2,C), , is the quotient group of the 2 by 2 complex number, complex matrix (mathematics), matrices of determinant 1 by their center (group theory), center, which consists of the identity matrix and its product by . has a natural representation as orientation-preserving conformal transformations of the Riemann sphere, and as orientation-preserving conformal transformations of the open unit ball in . The group of Möbius transformation, Möbius transformations is also related as the non-orientation-preserving isometry group of , . So, a Kleinian group can be regarded as a discrete subgroup group action, acting on one of these spaces. History The theory of general Kleinian groups was founded by and , who named them after Felix Klein. The special case of Schottky groups had been studied a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwarzian Derivative
In mathematics, the Schwarzian derivative is an operator similar to the derivative which is invariant under Möbius transformations. Thus, it occurs in the theory of the complex projective line, and in particular, in the theory of modular forms and hypergeometric functions. It plays an important role in the theory of univalent functions, conformal mapping and Teichmüller spaces. It is named after the German mathematician Hermann Schwarz. Definition The Schwarzian derivative of a holomorphic function of one complex variable is defined by : (Sf)(z) = \left( \frac\right)' - \frac\left(\right)^2 = \frac-\frac\left(\right)^2. The same formula also defines the Schwarzian derivative of a function of one real variable. The alternative notation :\ = (Sf)(z) is frequently used. Properties The Schwarzian derivative of any Möbius transformation : g(z) = \frac is zero. Conversely, the Möbius transformations are the only functions with this property. Thus, the Schwarzian der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |