|
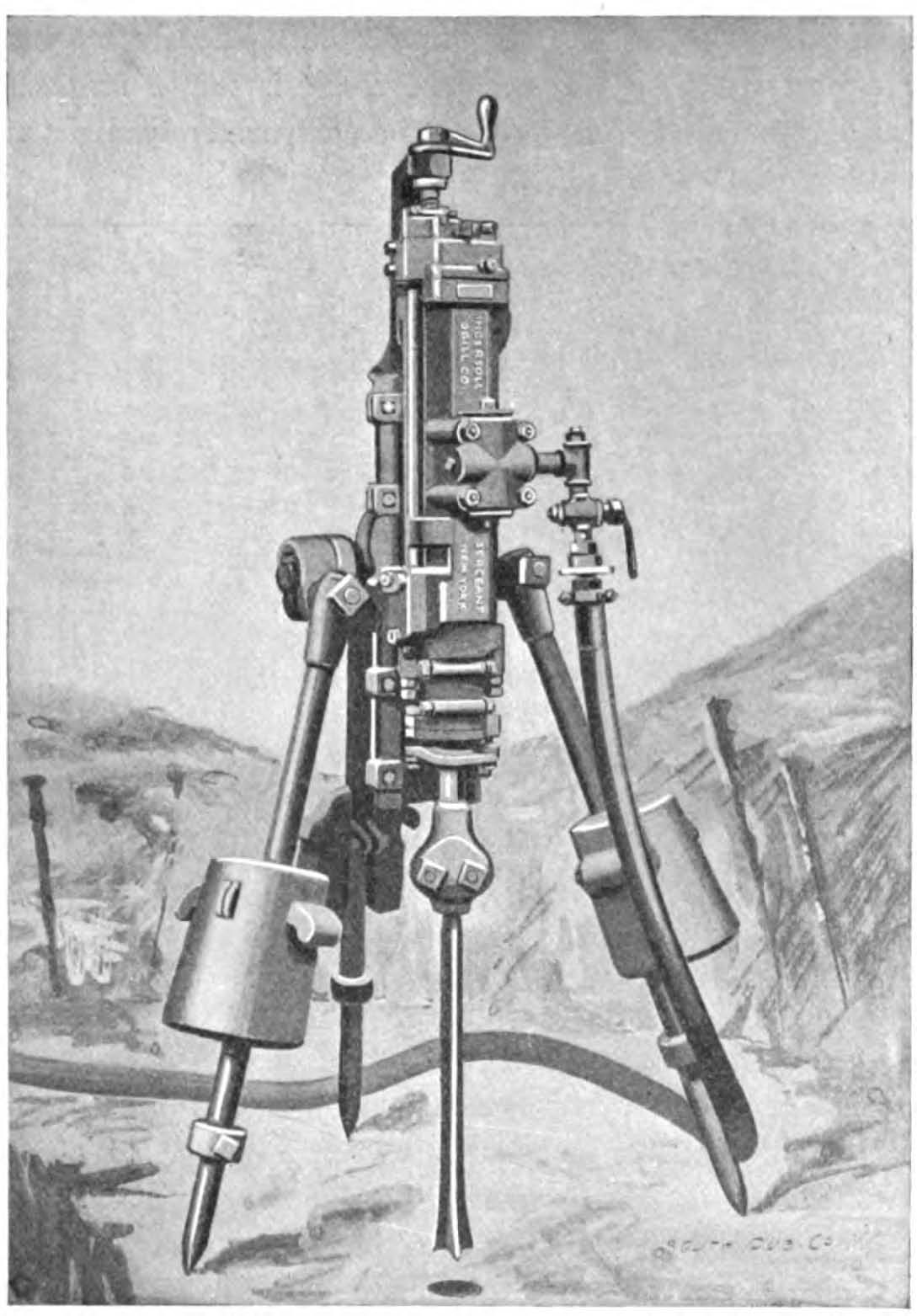
Down-the-hole Drill
A down-the-hole drill, usually called DTH by most professionals, is basically a jackhammer screwed on the bottom of a drill string. The fast hammer action breaks hard rock into small cuttings and dust that are evacuated by a fluid (air, water or drilling mud). The DTH hammer is one of the fastest ways to drill hard rock. The system is thought to have been invented independently by Stenuick Frères in Belgium and Ingersoll Rand in the USA in the mid-1950s. Origin of the name DTH is short for “down-the-hole”. Since the DTH method was originally developed to drill large-diameter holes downwards in surface-drilling applications, its name originated from the fact that the percussion mechanism followed the bit down into the hole. Applications were later found for the DTH method underground, where the direction of drilling is generally upwards instead of downwards. Technical details In ''DTH'' drilling, the percussion mechanism – commonly called the hammer – is located direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackhammer
A jackhammer (pneumatic drill or demolition hammer in British English) is a pneumatic or electro-mechanical tool that combines a hammer directly with a chisel. It was invented by William Mcreavy, who then sold the patent to Charles Brady King. Hand-held jackhammers are generally powered by compressed air, but some are also powered by electric motors. Larger jackhammers, such as rig-mounted hammers used on construction machinery, are usually hydraulically powered. These tools are typically used to break up rock, pavement, and concrete. A jackhammer operates by driving an ''internal'' hammer up and down. The hammer is first driven down to strike the chisel and then back up to return the hammer to the original position to repeat the cycle. The effectiveness of the jackhammer is dependent on how much force is applied to the tool. It is generally used like a hammer to break the hard surface or rock in construction works and it is not considered under earth moving equipment, along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill String
A drill string on a drilling rig is a column, or string, of drill pipe that transmits drilling fluid (via the mud pumps) and torque (via the kelly drive or top drive) to the Well drilling#Drill bits in mechanical drilling, drill bit. The term is loosely applied to the assembled collection of the smuggler pool, drill collars, tools and drill bit. The drill string is hollow so that drilling fluid can be pumped down through it and circulated back up the Annulus (oil well), annulus (the void between the drill string and the casing/open hole). Drill string components The drill string is typically made up of three sections: * Bottom hole assembly (BHA) * Transition pipe, which is often heavyweight drill pipe (HWDP) * Drill pipe Bottom hole assembly (BHA) The Bottom Hole Assembly (BHA) is made up of: a drill bit#Well drilling bits, drill bit, which is used to break up the rock Geologic formation, formations; drill collars, which are heavy, thick-walled tubes used to apply we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Fluid
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also called drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Often used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. One of the functions of drilling mud is to carry cuttings out of the hole. The three main categories of drilling fluids are: water-based muds (WBs), which can be dispersed and non-dispersed; non-aqueous muds, usually called oil-based muds (OBs); and gaseous drilling fluid, in which a wide range of gases can be used. Along with their formatives, these are used along with appropriate polymer and clay additives for drilling various oil and gas formations. The main functions of drilling fluids include providing hydrostatic pressure to prevent formation fluids from entering into the well bore, keeping the drill bit cool and clean during drilling, carrying out drill cuttings, and suspending t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of . Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven. Belgium is a sovereign state and a federal constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system. Its institutional organization is complex and is structured on both regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingersoll Rand
Ingersoll Rand is an American multinational company that provides flow creation and industrial products. The company was formed in February 2020 through the spinoff of the industrial segment of Ingersoll-Randplc (now known as Trane Technologies) and its merger with Gardner Denver. Its products are sold under more than 40 brands across all major global markets. Based in Davidson, North Carolina, Ingersoll Rand operates in two segments: Industrial Technologies and Services and Precision and Science Technologies. History History of Ingersoll Rand Simon Ingersoll founded Ingersoll Rock Drill Company in 1871 in New York, and in 1888, it combined with Sergeant Drill to form Ingersoll Sergeant Drill Company. The Ingersoll Sergeant Drill Company introduced the world's first direct-connected, electronic motor-driven compressor. Also in 1871, brothers Addison Rand and Jasper Rand, Jr. established Rand Drill Company with its main manufacturing plant in Tarrytown, New York. Rand drills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatic Tool
A pneumatic tool, air tool, air-powered tool or pneumatic-powered tool is a type of power tool, driven by compressed air supplied by an air compressor. Pneumatic tools can also be driven by compressed carbon dioxide () stored in small cylinders allowing for portability. Most pneumatic tools convert the compressed air to work using a pneumatic motor. Compared to electric power tool equivalents, pneumatic tools are safer to run and maintain, without risk of sparks, short-circuiting or electrocution, and have a higher power to weight ratio, allowing a smaller, lighter tool to accomplish the same task. Furthermore, they are less likely to self-destruct in case the tool is jammed or overloaded. General grade pneumatic tools with a short life span are commonly less expensive and considered “disposable tools” in tooling industries, while industrial grade pneumatic tools with long life span are more expensive. In general, pneumatic tools are cheaper than the equivalent electric-powere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes through sintering for use in industrial machinery, cutting tools, chisels, abrasives, armor-piercing shells and jewelry. Tungsten carbide is approximately twice as stiff as steel, with a Young's modulus of approximately 530–700 GPa, and is double the density of steel—nearly midway between that of lead and gold. It is comparable with corundum (α-) in hardness and can be polished and finished only with abrasives of superior hardness such as cubic boron nitride and diamond powder, wheels and compounds. Naming Historically referred to as Wolfram, ''Wolf Rahm'', wolframite ore was then later carburized and cemented with a binder creating a composite now called "tungsten carbide". Tungsten is Swedish for "heavy stone". Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Copiapó Mining Accident
The 2010 Copiapó mining accident, also known then as the "Chilean mining accident", began on 5 August 2010, with a cave-in at the San José copper–gold mine, located in the Atacama Desert north of the regional capital of Copiapó, in northern Chile. Thirty-three men, trapped underground and from the mine's entrance via spiraling underground ramps, were rescued after 69 days. After the state-owned mining company, Codelco, took over rescue efforts from the mine's owners, exploratory boreholes were drilled. Seventeen days after the accident, a note was found taped to a drill bit pulled back to the surface: "Estamos bien en el refugio los 33" ("We are well in the shelter, the 33 of us"). Three separate drilling rig teams; nearly every Chilean government ministry; the United States' space agency, NASA; and a dozen corporations from around the world cooperated in completing the rescue. On 13 October 2010 the men were winched to the surface one at a time, in a specially built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Foundation
A deep foundation is a type of foundation that transfers building loads to the earth farther down from the surface than a shallow foundation does to a subsurface layer or a range of depths. A pile or piling is a vertical structural element of a deep foundation, driven or drilled deep into the ground at the building site. There are many reasons that a geotechnical engineer would recommend a deep foundation over a shallow foundation, such as for a skyscraper. Some of the common reasons are very large design loads, a poor soil at shallow depth, or site constraints like property lines. There are different terms used to describe different types of deep foundations including the pile (which is analogous to a pole), the pier (which is analogous to a column), drilled shafts, and caissons. Piles are generally driven into the ground in situ; other deep foundations are typically put in place using excavation and drilling. The naming conventions may vary between engineering discip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Wells
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve that is then mounted with an extraction device such as a pumpjack which allows extraction from the reserve. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in hard to reach areas, e.g., when creating offshore oil platforms. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century, but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs during the 20th century. Wells are frequently sold or exchanged between different oil and gas companies as an asset – in large part because during falls in price of oil and gas, a well may be unproductive, but if price ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

