|
Double Check
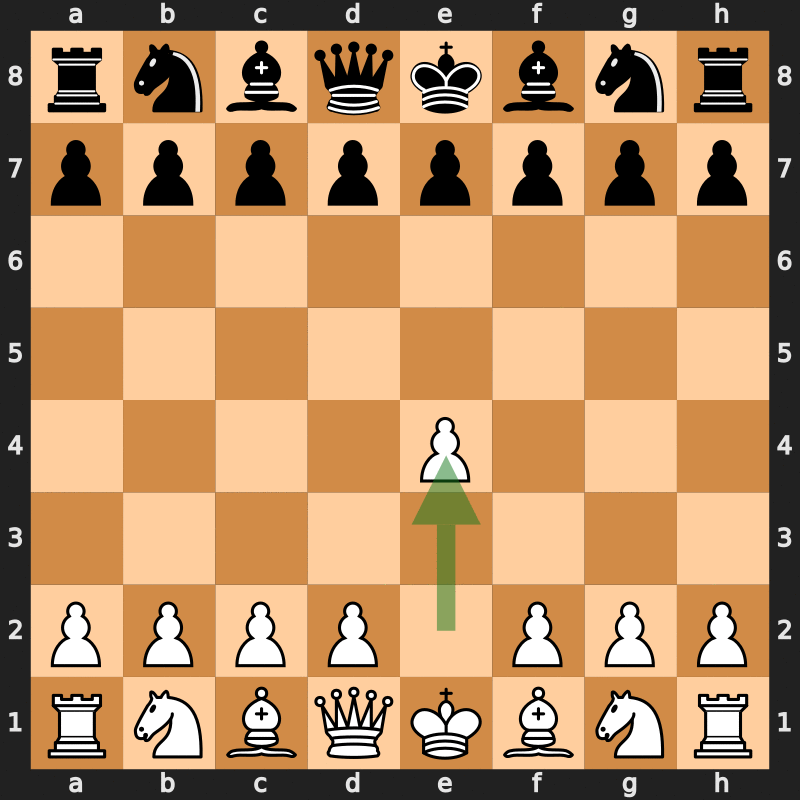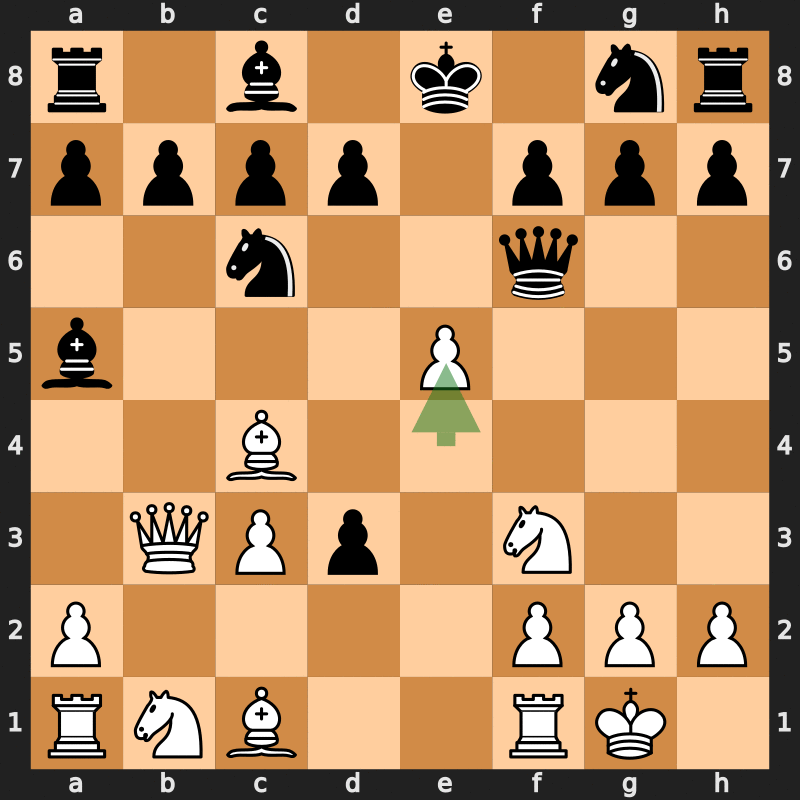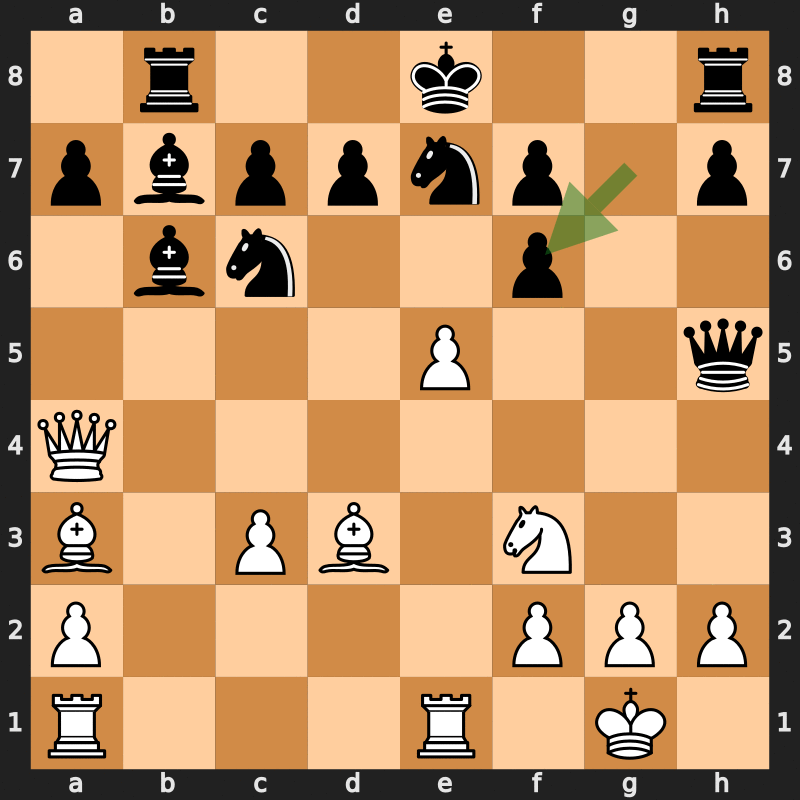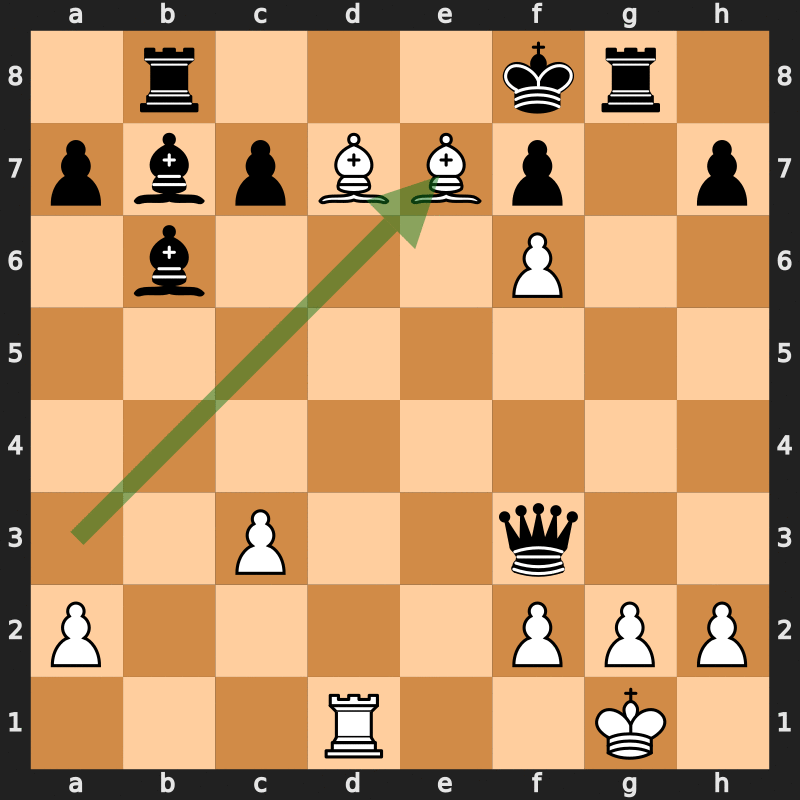
In chess and other related games, a double check is a check delivered by two pieces simultaneously. In chess notation, it is almost always represented the same way as a single check ("+"), but it is sometimes symbolized by "++" (however, "++" is also sometimes used to denote checkmate). This article uses "++" for double check and "#" for checkmate. Chess The most common form of double check involves one piece moving to deliver check and revealing a discovered check at the same time from a piece it had been blocking. The only possible reply to a double check is a king move, as it is impossible to block or capture both checking pieces at once (though the king move may capture one of these pieces). In exceptional circumstances, it is possible for the moved piece in a double check to not give check. The only way for this to happen in orthodox chess is by way of an '' en passant'' capture. In the position shown, Black has just played 1...g7–g5. White replies 2.hxg6++. The res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Sacrifice
In chess, a queen sacrifice is a move that sacrifices a queen in return for some compensation, such as a tactical or positional advantage. Queen sacrifice: real versus sham In his book ''The Art of Sacrifice in Chess'', Rudolf Spielmann distinguishes between ''real'' and ''sham'' sacrifices. A sham sacrifice leads to a and immediate benefit for the sacrificer, usually in the form of a quick checkmate (or perpetual check or stalemate if seeking a draw), or the recouping of the sacrificed after a forced . Since any amount of material can be sacrificed as long as checkmate will be achieved, the queen is not above being sacrificed as part of a combination. Possible reasons for a sham queen sacrifice include: * a forced checkmate after the opponent takes the queen; * more than adequate material compensation (say, a rook (chess), rook and two knight (chess), knights) after a forced continuation; * clearing the way for a pawn (chess), pawn's Promotion (chess), promotion to a rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Terminology
This glossary of chess explains commonly used terms in chess, in alphabetical order. Some of these terms have their own pages, like '' fork'' and '' pin''. For a list of unorthodox chess pieces, see Fairy chess piece; for a list of terms specific to chess problems, see Glossary of chess problems; for a list of named opening lines, see List of chess openings; for a list of chess-related games, see List of chess variants. A B , "lightning"] A #fast chess, fast form of chess with a very short time limit, usually three or five minutes per player for the entire game. With the advent of electronic chess clocks A chess clock consists of two adjacent clocks with buttons to stop one clock while starting the other, so that the two clocks never run simultaneously. Chess clocks are used in chess and other two-player games w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janggi
''Janggi'' (including romanizations ''changgi'' and ''jangki''), sometimes called Korean chess, is a strategy board game popular on the Korean Peninsula. The game was derived from xiangqi (Chinese chess), and is very similar to it, including the starting position of some of the pieces, and the 9×10 gameboard, but without the xiangqi "river" dividing the board horizontally in the middle. Janggi is played on a board nine lines wide by ten lines long. The game is sometimes fast paced due to the jumping cannons and the long-range elephants, but professional games most often last over 150 moves and so are typically slower than those of Western chess. In 2009, the first world janggi tournament was held in Harbin, Heilongjiang, China. Rules Board The board is composed of 90 intersections of 9 vertical files and 10 horizontal rows. The board has nearly the same layout as that used in xiangqi, except the janggi board has no "river" in the central row. The pieces consist of disks ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiangqi
''Xiangqi'' (; ), also called Chinese chess or elephant chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is the most popular board game in China. ''Xiangqi'' is in the same family of games as ''shogi'', ''janggi'', Western chess, '' chaturanga'', and Indian chess. Besides China and areas with significant ethnic Chinese communities, this game is also a popular pastime in Vietnam, where it is known as , literally 'general chess'. The game represents a battle between two armies, with the primary object being to checkmate the enemy's general (king). Distinctive features of xiangqi include the cannon (''pao''), which must jump to capture; a rule prohibiting the generals from facing each other directly; areas on the board called the ''river'' and ''palace'', which restrict the movement of some pieces but enhance that of others; and the placement of the pieces on the intersections of the board lines, rather than within the squares. Board Xiangqi is played on a board nine line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairy Chess Piece
A fairy chess piece, variant chess piece, unorthodox chess piece, or heterodox chess piece is a chess piece not used in conventional chess but incorporated into certain chess variants and some chess problems. Compared to conventional pieces, fairy pieces vary mostly in the way they move, but they may also follow special rules for capturing, promotions, etc. Because of the distributed and uncoordinated nature of unorthodox chess development, the same piece can have different names, and different pieces can have the same name in various contexts. Most are symbolised as inverted or rotated icons of the standard pieces in diagrams, and the meanings of these "wildcards" must be defined in each context separately. Pieces invented for use in chess variants rather than problems sometimes instead have special icons designed for them, but with some exceptions (the princess, empress, and occasionally amazon), many of these are not used beyond the individual games for which they were invente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess Variant
A chess variant is a game related to, derived from, or inspired by chess. Such variants can differ from chess in many different ways. "International" or "Western" chess itself is one of a family of games which have related origins and could be considered variants of each other. Chess developed from ''chaturanga'', from which other members of this family, such as '' shatranj'', Tamerlane chess, ''shogi'', and '' xiangqi'' also evolved. Many chess variants are designed to be played with the equipment of regular chess. Most variants have a similar public-domain status as their parent game, but some have been made into commercial proprietary games. Just as in traditional chess, chess variants can be played over the board, by correspondence, or by computer. Some internet chess servers facilitate the play of some variants in addition to orthodox chess. In the context of chess problems, chess variants are called heterodox chess or fairy chess. Fairy chess variants tend to be crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nightrider (chess)
The nightrider, alternatively spelled knightrider and also known as the knightmare or unicorn (though the latter term sometimes refers to the bishop+nightrider compound), is a fairy chess piece that can move any number of steps as a knight in the same direction. The nightrider is often represented by an altered version of the knight's icon. at '''' In this article, the nightrider is represented by an inverted knight and notated as ''N''; the knight is abbreviated as ''S'' for the German name ''Springer''. The night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasshopper (chess Piece)
The grasshopper is a fairy chess piece that moves along , , and (as a queen) but only by hopping over another piece. The piece to be hopped may be any distance away, but the grasshopper must land on the square immediately behind it in the same direction. If there is no piece to hop over, it cannot move. If the square beyond a piece is occupied by a piece of the opposite color, the grasshopper can capture that piece. The grasshopper may jump over pieces of either color; the piece being jumped over is unaffected. The grasshopper was introduced by T. R. Dawson in 1913 in problems published in the ''Cheltenham Examiner'' newspaper. It is one of the most popular fairy pieces used in chess problems. In this article, the grasshopper is shown as an inverted queen with notation ''G''. Movement In the diagram to the right, the white grasshopper on d4 can move to the squares marked with crosses (b2, d1, d7, and h8) or capture the black pawn on a7. It cannot move to g4, as there are two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Dufresne
Jean Dufresne (14 February 1829 – 13 April 1893) was a German chess player and chess composer. He was a student of Adolf Anderssen, to whom he lost the " Evergreen game" in 1852. Life Dufresne was born and died in Berlin. The son of a wealthy Jewish businessman, he attended law school but was forced to abandon his studies when his father ran into financial difficulties. He subsequently became a journalist. Dufresne was an unsuccessful novelist under the anagrammatic pseudonym E. S. Freund, but wrote several chess books, one of which, ''Kleines Lehrbuch des Schachspiels'' (1881, known in Germany as ''Der Kleine Dufresne'') ran to many editions and taught several generations of players. In a letter to Paul Dirac at the end of 1929, Werner Heisenberg deemed Dufresne's handbook "the best book about theory of Chess". He also wrote a popular book on Paul Morphy Paul Charles Morphy (June 22, 1837 – July 10, 1884) was an American chess player. He is considered to have bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Anderssen
Karl Ernst Adolf Anderssen (July 6, 1818 – March 13, 1879)"Anderssen, Adolf" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 385. was a German chess master. He won the great international tournaments of 1851 and 1862, but lost matches to Paul Morphy in 1858, and to Wilhelm Steinitz in 1866. Accordingly, he is generally regarded as having been the world's leading chess player from 1851 to 1858, and leading active player from 1862 to 1866, although the title of World Chess Champion did not yet exist. Anderssen became the most successful tournament player in Europe, winning over half the events he entered, including the very strong Baden-Baden 1870 chess tournament. He achieved most of these successes when he was over the age of 50. Anderssen is famous today for his brilliant sacrificial attacking play, particularly in the " Immortal Game" (1851) and the " Evergreen Game" (1852). He was an important figure in the dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evergreen Game
The Evergreen Game is a famous chess game won by Adolf Anderssen against Jean Dufresne in 1852. This was probably an . At the time, there was no formal title of "World Champion", but the German mathematics professor Anderssen was widely considered the best player in the world after winning the first major international chess tournament in London in 1851. Though not in the same class as Anderssen, Dufresne, a popular author of chess books, was also a strong player. It is usually assumed that the game was played in Berlin, where Dufresne lived and Anderssen often visited, but no details of the game's circumstances were given in the original publication in the September and October 1852 issues of ''Deutsche Schachzeitung''. Winter, Edward''Anderssen v Dufresne: The Evergreen Game''/ref> Anderssen, Adolf''Gespielte Partieen 450, Zwischen Anderssen und Dufresne'' ''Deutsche Schachzeitung'', September 1852 pages 338–39 & ''Schluss der Partie 450'', Oct 1852 page 383 Beginning with H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |