|
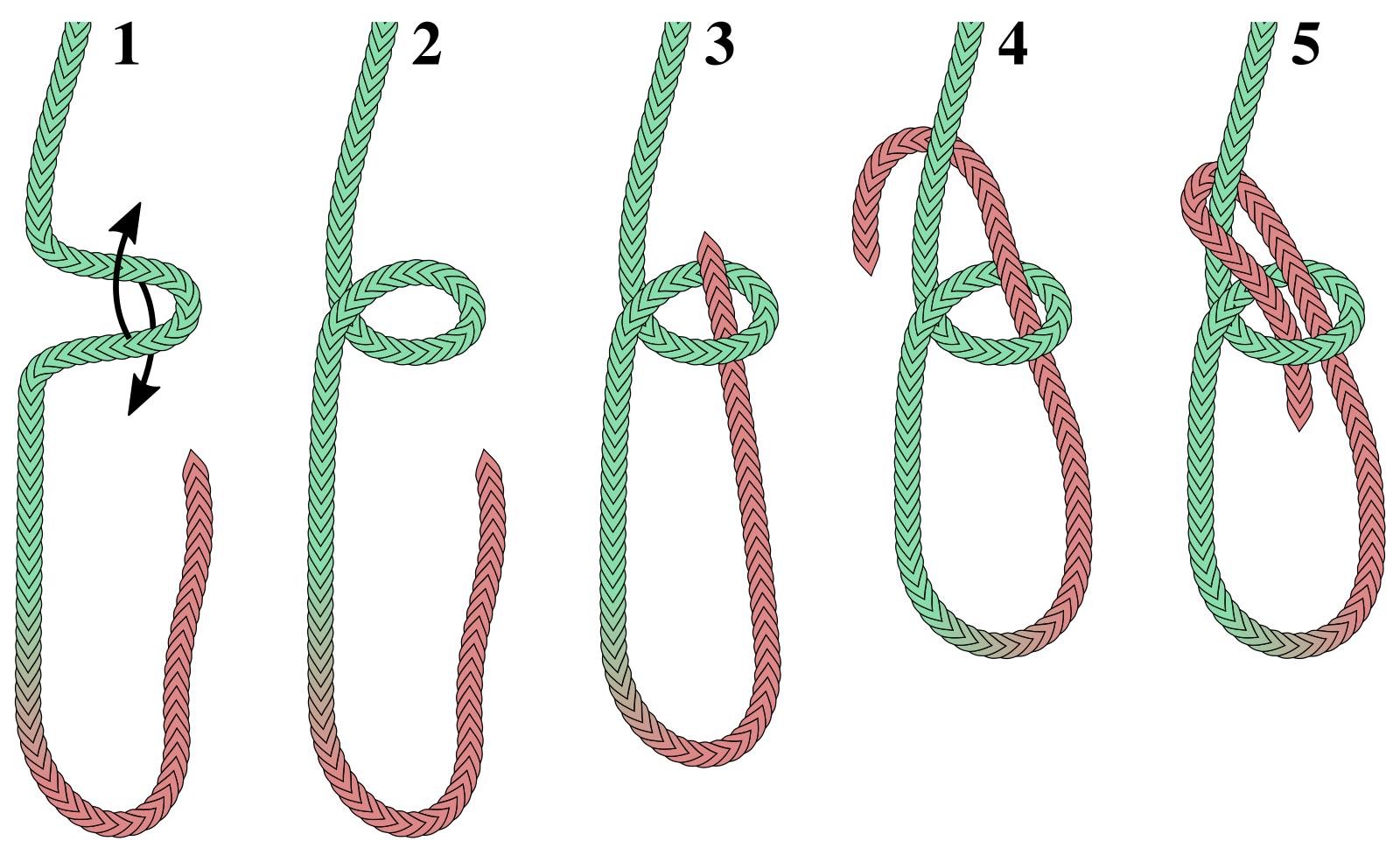
Double Bowline
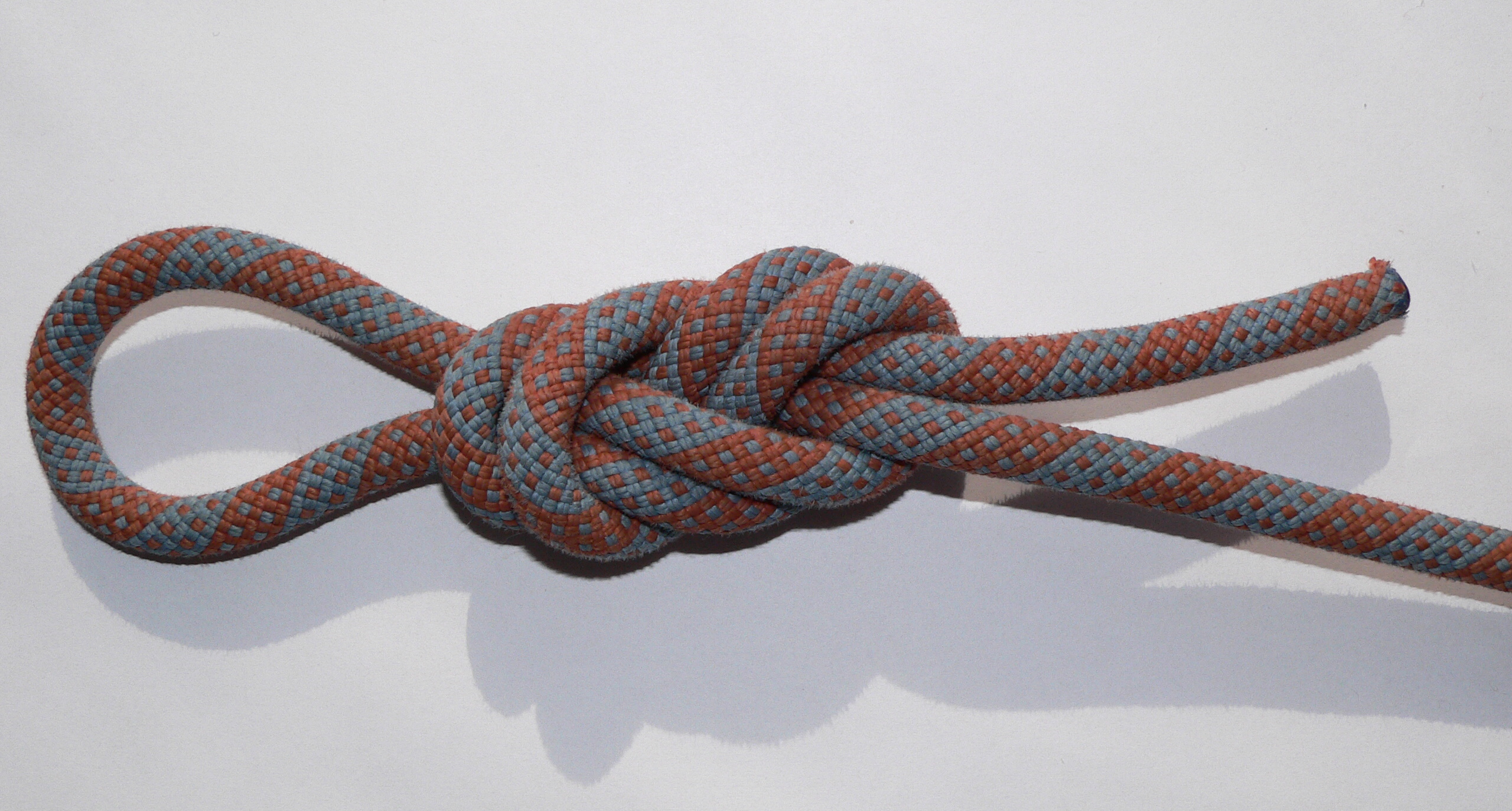
A double bowline (or round turn bowline) is a type of loop knot. Instead of the single turn of the regular bowline, the double bowline uses a round turn. This forms a more secure loop than a standard bowline. Naming Though called "double bowline" by Clifford Ashley, this name is also reasonably descriptive of a different knot: the bowline on a bight. Because of this ambiguity some sources differentiate by using one of the alternate names above. And at least one other source uses the name "double bowline" for a mid-line loop knot made by tying a basic bowline with a bight of rope instead of the end. Tying First, learn to tie the bowline by laying the working end on the standing part and twisting to form a loop (the "hole" that the rabbit comes out of). Wrap the loop once more around the working end. Then pass the working end behind the standing part and back down through the double loop. Uses The double bowline is one of the typical tie-in knots used in climbing, along with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowline
The bowline ( or ) is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as ''King of the knots'' because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend and the clove hitch, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots. The common bowline shares some structural similarity with the sheet bend. Virtually all end-to-end joining knots (i.e., bends) have a corresponding loop knot. Although the bowline is generally considered a reliable knot, its main deficiencies are a tendency to work loose when not under load (or under cyclic loading), to slip when pulled sideways, and the bight portion of the knot to capsize in certain circumstances. To address these shortcomings, a number of more secure variations of the bowline have been developed for use in safety-critical applications, or by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ashley Book Of Knots
''The Ashley Book of Knots'' is an encyclopedia of knots written and illustrated by the American sailor and artist Clifford W. Ashley. First published in 1944, it was the culmination of over 11 years of work. The book contains 3,857 numbered entries (the final number, "3854", is added to by three "1/2" #s (794.5, 1034.5, & 2585.5) and, in later editions of the book, #1425a for Hunter's Bend; and one number has no entry) and approximately 7,000 illustrations. The entries include knot instructions, uses, and some histories, categorized by type or function. It remains one of the most important and comprehensive books on knots. Use as a reference Due to its scope and wide availability, ''The Ashley Book of Knots'' has become a significant reference work in the field of knotting. The numbers Ashley assigned to each knot can be used to unambiguously identify them. This helps to identify knots despite local colloquialisms or identification changes. Citations to Ashley numbers are usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
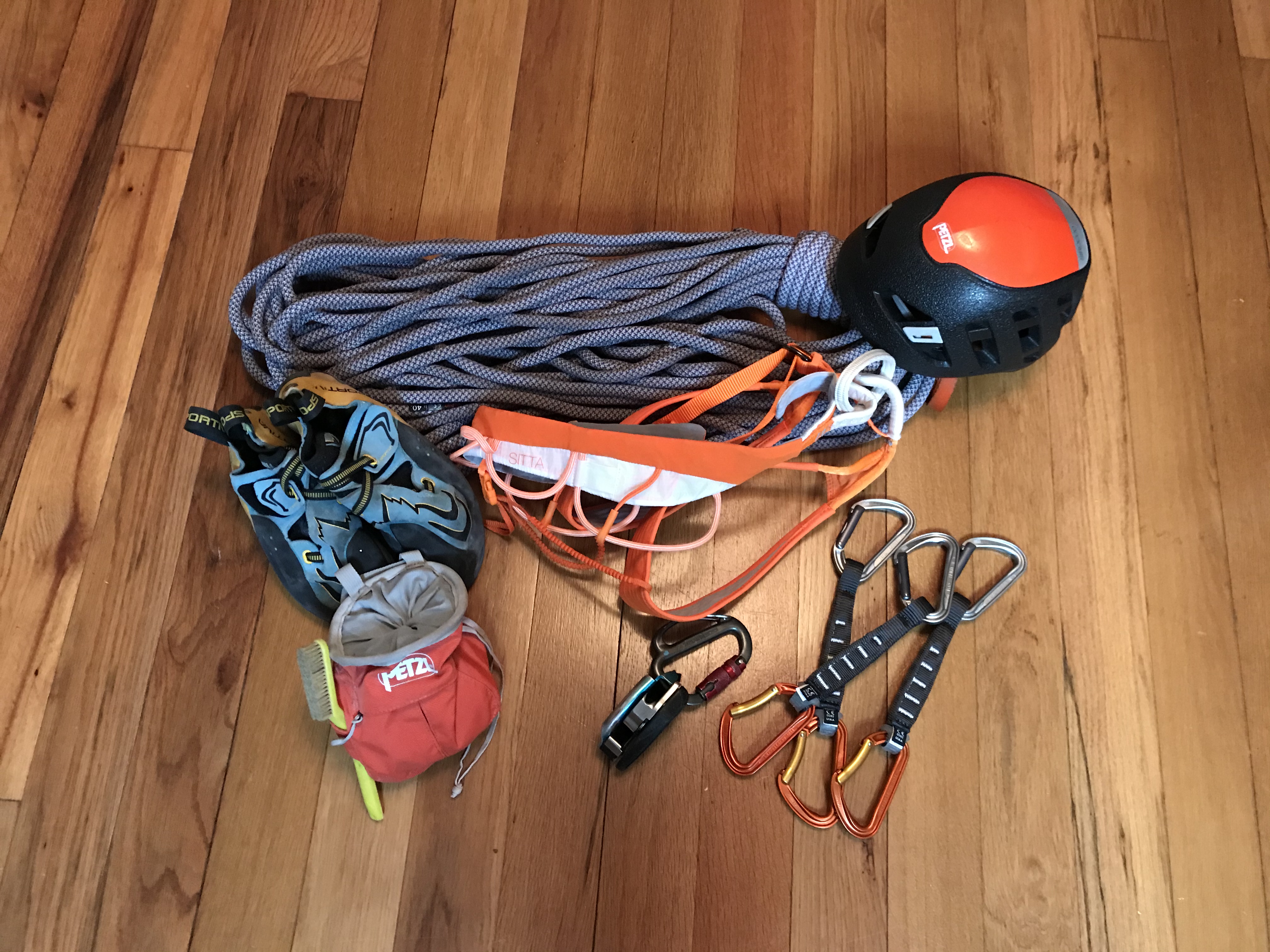
Sport Climbing
Sport climbing (or Bolted climbing) is a form of rock climbing that relies on permanent anchors (or bolts), permanently fixed into the rock for climber protection, in which a rope that is attached to the climber is clipped into the anchors to arrest a fall; it can also involve climbing short distances with a crash pad underneath as protection. This is in contrast to traditional climbing where climbers must place removable protection as they climb. Sport climbing usually involves lead climbing and toproping techniques, but free solo and deep-water solo (i.e. no protection) climbing on sport routes is also sometimes possible. Since sport climbing routes do not need to follow traditional climbing route lines where protection can be placed into natural features (e.g. cracks), they tend to follow more direct lines up crags. This aspect, in addition to the lack of any need to install protection during the climb (e.g. the sport climber just clips into pre-installed bolts along th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yosemite Bowline
A Yosemite bowline is a loop knot often perceived as having better security than a bowline. If the knot is not dressed correctly, it can potentially collapse into a noose,Youtube Video of failure with poorly dressed Yosemite bowlineYosemite Bowline not safe for climbing/ref> however testing reveals this alternative configuration to be strong and safe as a climbing tie-in. A Yosemite bowline is made from a bowline with the free end wrapped around one leg of the loop and tucked back through the knot, a final round turn and wiktionary:reeve, reeve commonly known as a "Yosemite finish." The knot's security is enhanced by preventing the bowline list of knot terminology#Capsizing, capsizing to form a highly dangerous slip knot. Additional safety is achieved by tying with a tail (see below). When finished, the working end forms a figure eight. Because of the danger of incorrectly dressing the Yosemite bowline and capsizing it even before it is set, it may be safer and less error-prone t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figure-eight Follow Through
Figure-eight loop (also figure-eight on a bight, figure-eight follow-through, figure-eight retrace, Flemish loop, or Flemish eight) is a type of knot created by a loop (knot), loop on the Bight (knot), bight. It is used in climbing and caving. The double figure eight is used to put a loop in the end of a rope, or around an object. It is relatively easy to tie and is secure, but can become difficult to untie after heavy loading, and can jam badly in any rope type. Tying methods On a bight A figure-eight loop is created by doubling the rope into a bight, then tying the standard figure-eight knot. In climbing, this knot is used to save time when repeatedly attaching the rope to climbing harnesses, using locking Carabiner, carabiners, such as when a group of people are climbing on the same top-rope. Follow-through Alternatively, to tie the knot directly around an object, the follow-through method must be used. * Tie a regular figure eight knot with a significant amount of ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bight (knot)
In knot tying, a bight is a curved section or slack part between the two ends of a rope, string, or yarn.. "Any slack part of a rope between the two ends, particularly when curved or looped." A knot that can be tied using only the bight of a rope, without access to the ends, is described as in the bight. The term "bight" is also used in a more specific way when describing Turk's head knots, indicating how many repetitions of braiding are made in the circuit of a given knot. Bight vs. open loop Sources differ on whether an open loop or U-shaped curve in a rope qualifies as a bight. treats bights and loops as distinct, stating that a curve "no narrower than a semicircle" is a bight, while an open loop is a curve "narrower than a bight but with separated ends". However, ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Knots'' (2002) states: "Any section of line that is bent into a U-shape is a bight." Slipped knot In order to make a slipped knot (also slipped loop and quick release knot), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowline On A Bight
The bowline on a bight is a knot which makes a pair of fixed-size loops in the middle of a rope. Its advantage is that it is reasonably easy to untie after being exposed to load. This knot can replace the figure-eight loop knot when tying into a climbing harness. It is one of the two tie-in knots that are being taught by the German Alpine Club (DAV), generally being considered secure. Dangers 2011 testing shows that the knot might slip when only one loop is loaded. Cavers and canyoneers ought to fasten their cow-tail carabiner through both loops. Video with genuine ''et voilà!'' ending European cavers widely advocate the use of a figure eight twisted version of the bowline on a bight. Applications This knot can be used to provide a toe hold in the middle of a rope; to make an emergency bosun's chair; and to create an upper rope "block" to make a crude purchase by threading the rope round an anchor point and then back up through the loop. It is sometimes used in sport climbin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clifford Ashley
Clifford Warren Ashley (December 18, 1881 – September 18, 1947) was an American artist, author, sailor, and knot expert. Life Ashley was born in New Bedford, Massachusetts, son of Abiel Davis Ashley and Caroline Morse. He married Sarah Scudder Clark in 1932, with whom he had two daughters, one of whom is practicing painter Jane Ashley. He also adopted his wife's daughter from a previous marriage. He died in Westport Point, Massachusetts. Education and early work Taking an interest in art while still in high school, he went on to attend the Eric Pape Art School in Boston. In the summer of 1901 Ashley, along with friends N.C. Wyeth and Henry J. Peck, studied under George Noyes in Annisquam, Massachusetts. In the fall, he went on to become a student of Howard Pyle's school in Wilmington, Delaware. Pyle helped secure commissions for his students, and Ashley's early work included book frontispieces and illustrations for magazines such as ''The Delineator'', '' Leslies'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Turn
A turn is one round of rope on a pin or cleat, or one round of a coil. Turns can be made around various objects, through rings, or around the standing part of the rope itself or another rope. A turn also denotes a component of a knot. When the legs of a loop are brought together and crossed the rope has taken a turn. One distinguishes between single turn, round turn, and two round turns depending on the number of revolutions around an object. The benefit of round turns is best understood from the capstan equation. Riding turn A riding turn is a section of rope that passes on top of another section of rope, often parallel or at only a slight angle to the section below. Examples of riding turns can be seen in both the constrictor knot and the strangle knot. The second course of wrappings in some seizing knots can be referred to as riding turns. The formation of an unintentional riding turn on a sailing winch can cause it to jam. Single hitch A single hitch is a type of knot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Bowline
The water bowline is a type of knot designed for use in wet conditions where other knots may slip or jam. Although similar in finished appearance to the double bowline, the water bowline is formed with a clove hitch as the loop in the standing part of the rope. This is similar to the double bowline, which puts the running end through a round turn. The additional friction from the clove hitch increases the security of this knot. Image:Waterbowline-1.jpg, 1. Make a half hitch Image:Waterbowline-2.jpg, 2. Complete the clove hitch Image:Waterbowline-3.jpg, 3. Through the clove hitch Image:Waterbowline-4.jpg, 4. Around standing end Image:Waterbowline-5.jpg, 5. Back through hitches The Water Bowline can be tied very quickly by throwing two half hitches over the working end and then running the working end around the standing line and back through both half hitches. This is illustrated in the three pictures below. Image:Waterbowline-A.jpg, Throw the first hitch Image:Waterbowline- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowline
The bowline ( or ) is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as ''King of the knots'' because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend and the clove hitch, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots. The common bowline shares some structural similarity with the sheet bend. Virtually all end-to-end joining knots (i.e., bends) have a corresponding loop knot. Although the bowline is generally considered a reliable knot, its main deficiencies are a tendency to work loose when not under load (or under cyclic loading), to slip when pulled sideways, and the bight portion of the knot to capsize in certain circumstances. To address these shortcomings, a number of more secure variations of the bowline have been developed for use in safety-critical applications, or by s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ''bend'' fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a ''loop knot'' is any knot creating a loop; and ''splice'' denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory. History Knots and knotting have been used and studied throughout history. For example, Chinese knotting is a decorative handicraft art that began as a form of Chinese folk art in the Tang and Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD) in China, later popularized in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |