|
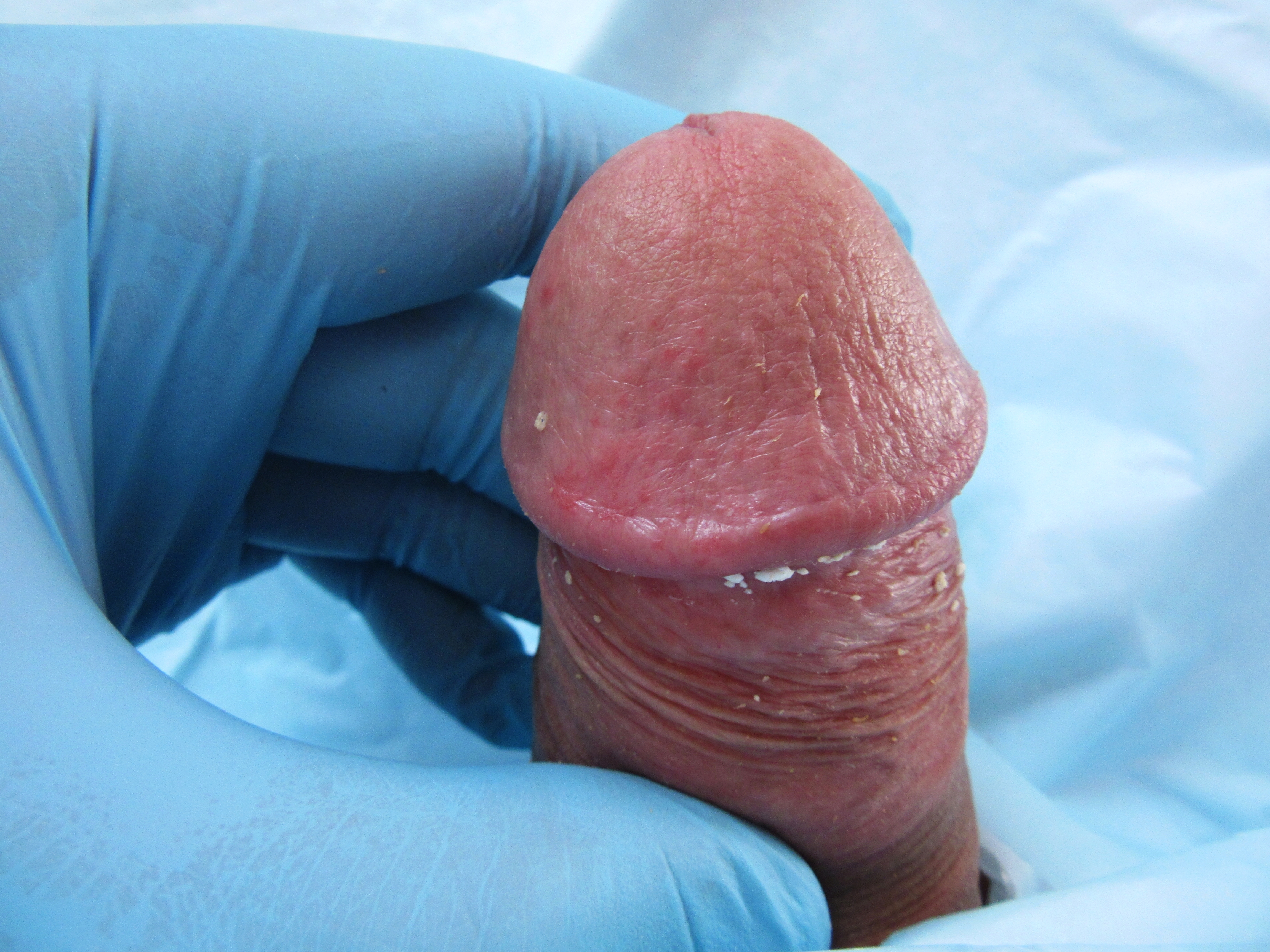
Dorsal Slit
A dorsal slit (often referred to in anthropology as superincision or supercision) is a single incision along the upper length of the foreskin from the tip to the corona, exposing the glans without removing any tissue. An ancient practice, it has been a traditional custom among a number of peoples, particularly Filipinos and Pacific Islanders, probably for thousands of years. In Western medicine, it was used as an alternative to circumcision to relieve conditions such as failure of the foreskin to retract (phimosis) or failure to cover the glans penis (paraphimosis), although a perception of poor appearance limited its popularity. While it is a less invasive surgery than circumcision, it is more invasive than preputioplasty since it leaves the incision open. It is still used when circumcision or other measures are considered impractical or undesirable. Traditional custom Since superincision and circumcision are both forms of genital cutting that expose the glans, it can often be d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milton Diamond
Milton Diamond (born March 6, 1934) is an American Professor Emeritus of anatomy and reproductive biology at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa. After a career in the study of human sexuality, Diamond retired from the university in December 2009 but continued with his research and writing until retiring fully in 2018. Early career Milton Diamond graduated from the City College of New York with a BS in biophysics in 1955, after which he spent three years in the Army as an engineering officer, stationed in Japan. On returning to the United States, he attended graduate school at University of Kansas from 1958–1962 and earned a PhD in anatomy and psychology from that University. His first job was teaching at the University of Louisville, School of Medicine where he simultaneously completed two years toward an MD, passing his Basic Medicine Boards, and in 1967 he moved to Hawaii to take up a post at the recently established John A. Burns School of Medicine. Milton Diamond had a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gikuyu Language
Kikuyu or Gikuyu ( ki, Gĩkũyũ, link=no ) is a Bantu language spoken by the Gĩkũyũ (''Agĩkũyũ'') of Kenya. Kikuyu is mainly spoken in the area between Nyeri and Nairobi. The Kikuyu people usually identify their lands by the surrounding mountain ranges in Central Kenya which they call ''Kĩrĩnyaga''. The Gikuyu language is intelligibly similar to its surrounding neighbors, the Meru and Embu. Dialects Kikuyu has four main mutually intelligible dialects. The Central Province districts are divided along the traditional boundaries of these dialects, which are Kĩrĩnyaga, Mũrang'a, Nyeri and Kiambu. The Kikuyu from Kĩrĩnyaga are composed of two main sub-dialects – the Ndia and Gichugu who speak the dialects ''Kĩndia'' and ''Gĩgĩcũgũ''. The Gicugus and the Ndias do not have the "ch" or "sh" sound, and will use the "s" sound instead, hence the pronunciation of "Gĩcũgũ" as opposed to "Gĩchũgũ". To hear Ndia being spoken, one needs to be in Kerugoya, the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maa Languages
The Maa languages are a group of closely related Eastern Nilotic languages (or from a linguistic perspective, dialects, as they appear to be mutually intelligible) spoken in parts of Kenya and Tanzania by more than a million speakers. They are subdivided into North and South Maa. The Maa languages are related to the Lotuko languages spoken in South Sudan. History In the past, several peoples have abandoned their languages in favor of a Maa language, usually following a period of intensive cultural and economic contact. Among peoples that have assimilated to Maa peoples are the Aasáx (Asa) and the El Molo, former hunter-gatherers who spoke Cushitic languages, and the Mukogodo-Maasai (Yaaku), former bee-keepers and hunter-gatherers (Eastern Cushitic). The Okiek of northern Tanzania, speakers of a Southern Nilotic Kalenjin tongue, are under heavy influence from Maasai. Languages *Northern Maa ** Samburu (spoken by the Samburu people) ** Camus (or il-Chamus, the preferred auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carol Beckwith
Carol Beckwith (born July 10, 1945) is an American photographer, author, and artist known for her photojournalism documenting the indigenous tribal cultures of Africa, most notably in partnership with the Australian photographer Angela Fisher. Between them, Beckwith and Fisher have published 14 books, and have had their photos appear in '' National Geographic'', '' Natural History'', ''African Arts'', ''The Observer Magazine'', ''Time'', ''Life'', ''Vogue'', ''Marie Claire'' and ''Elle''. They continue to exhibit and lecture at galleries and museums worldwide, including The American Museum of Natural History and The Explorers Club in New York City, The Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC, and the Royal Geographical Society in London. They have also collaborated on four films about African traditions. Together they have received numerous accolades, including the United Nations Award for Excellence, the Royal Geographical Society's Cherry Kearton Medal, two Anisfield-Wolf B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kikuyu People
The Kikuyu (also ''Agĩkũyũ/Gĩkũyũ'') are a Bantu ethnic group native to Central Kenya. At a population of 8,148,668 as of 2019, they account for 17.13% of the total population of Kenya, making them Kenya's largest ethnic group. The term ''Kikuyu'' is derived from the Swahili form of the word Gĩkũyũ. is derived from the word mũkũyũ which means sycamore fig (''mũkũyũ'') tree". Hence ''Agĩkũyũ'' in the Kikuyu language translates to "Children Of The Big Sycamore". The alternative name ''Nyũmba ya Mũmbi'', which encompasses ''Embu'', ''Gikuyu'', and ''Meru'', translates to "House of the Potter" (or "Creator"). History Origin The Kikuyu belong to the Northeastern Bantu branch. Their language is most closely related to that of the Embu and Mbeere. Geographically, they are concentrated in the vicinity of Mount Kenya. The exact place that the Northeast Bantu speakers migrated from after the initial Bantu expansion is uncertain. Some authorities sugge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus '' Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of ''Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
) , national_anthem = " Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"() , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Nairobi , coordinates = , largest_city = Nairobi , official_languages = Constitution (2009) Art. 7 ational, official and other languages"(1) The national language of the Republic is Swahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are Swahili and English. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities." , languages_type = National language , languages = Swahili , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2019 census , religion = , religion_year = 2019 census , demonym = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maasai People
The Maasai (; sw, Wamasai) are a Nilotic ethnic group inhabiting northern, central and southern Kenya and northern Tanzania. They are among the best-known local populations internationally due to their residence near the many game parks of the African Great Lakes and their distinctive customs and dress.Maasai - Introduction Jens Fincke, 2000–2003 The Maasai speak the Maa language (ɔl Maa), a member of the Nilotic language family that is related to the Dinka, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanitis
Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. When the foreskin is also affected, the proper term is balanoposthitis. Balanitis on boys still in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis. The word ''balanitis'' is from the Greek βάλανος'' '', literally meaning 'acorn', used because of the similarity in shape to the glans penis. Signs and symptoms * Small red erosions on the glans (first sign) * Redness of the foreskin * Redness of the penis * Other rashes on the head of the penis * Foul smelling discharge * Painful foreskin and penis Complications Recurrent bouts of balanitis may cause scarring of the preputial orifice; the reduced elasticity may lead to pathologic phimosis. Furthecomplicationsmay include: * Stricture of urethral meatus * Phimosis * Paraphimosis Cause Inflammation has many possible causes, including irritation by environmental substances, physical trauma, and infection such as bacterial, viral, or fungal. Some of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenulum
A frenulum (or frenum, plural: frenula or frena, from the Latin ''frēnulum'', "little bridle", the diminutive of ''frēnum'') is a small fold of tissue that secures the motion of a mobile organ in the body. In human anatomy Frenula on the human body include several in the mouth, some in the digestive tract, and some connected to the external genitalia. *Brain: ''Frenulum of superior medullary velum'' or ''frenulum veli'' *Digestive tract: ''frenulum valvae ileocaecalis'' *Oral tissue: Frenula of the mouth include the '' frenulum linguae'' under the tongue, the '' frenulum labii superioris'' inside the upper lip, the '' frenulum labii inferioris'' inside the lower lip, and the buccal frena which connect the cheeks to the gum. These can easily be torn by violent blows to the face or mouth, thus a torn frenulum is sometimes a warning sign of physical abuse. *Penile tissue: The word ''frenulum'' on its own is often used for the frenulum of prepuce of penis or ''frenulum pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)