|
Dorig (Vanuatu)
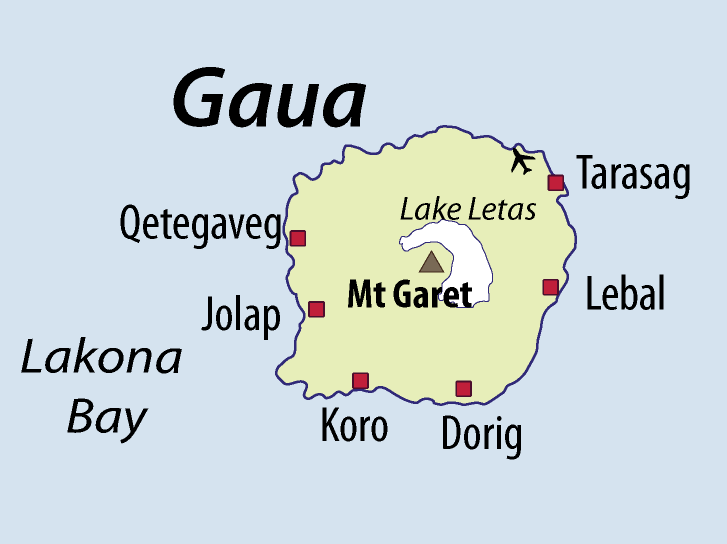
Dorig () is a village located on the south coast of Gaua, in the Banks Islands of Vanuatu. Its population counts approximately 250 individuals. Their language is also called Dorig. Name The name ''Dorig'', spelled ''Dōrig'', is derived from the name of the village where it is spoken. The term is related to ''Dōlav'' (the Dorig name of a village that is called in Lakon as ''Jōlap'' ), with the ''-rig'' and ''-lav'' parts meaning "small" and "big" respectively. The element ''dō'' is probably related to |
Gaua
Gaua (formerly known as ''Santa Maria Island'') is the largest and second most populous of the Banks Islands in Torba Province in northern Vanuatu. It covers 342 km². History Gaua was first sighted by Europeans during the Spanish expedition of Pedro Fernández de Quirós, from 25 to 29 April 1606. The island’s name was then charted as ''Santa María''. Geography Gaua is subject to frequent earthquakes and cyclones. The climate is humid tropical; the average annual rainfall exceeds 3500 mm. It has rugged terrain, reaching up to Mount Gharat (797 m), the peak of the active stratovolcano which lies at the center of the island. Its most recent eruption was in 2013. The volcano has a 6 × 9 km caldera, within which lies a crater lake, known as Lake Letas, which is the largest lake in Vanuatu. To the east of the lake is Siri Waterfall (120 m drop). Natural history The upper slopes of the island have been recognised as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by Bir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banks Islands
The Banks Islands (in Bislama ''Bankis'') are a group of islands in northern Vanuatu. Together with the Torres Islands to their northwest, they make up the northernmost province of Torba. The island group lies about north of Maewo, and includes Gaua and Vanua Lava, two of the 13 largest islands in Vanuatu. In 2009, the islands had a population of 8,533. The island group's combined land area is 780 km2. Geography The largest island is Gaua (formerly called Santa Maria), which has a rugged terrain, rising to Mount Gharat, an active volcano at the centre of the island, at . Gaua's freshwater Lake Letas, in its volcanic crater, is the largest lake in Vanuatu. A slightly smaller island in the group, Vanua Lava, is higher, at ; it too has an active volcano: Mount Suretamate (also spelled Süretimiat or Sere'ama, ). To the east of Vanua Lava are two islets in the groupo, Ravenga and Kwakea (also spelled Qakea). Sola, the provincial capital, is on Vanua Lava. The third largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanuatu
Vanuatu ( or ; ), officially the Republic of Vanuatu (french: link=no, République de Vanuatu; bi, Ripablik blong Vanuatu), is an island country located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, east of New Guinea, southeast of the Solomon Islands, and west of Fiji. Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. The first Europeans to visit the islands were a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Fernandes de Queirós, who arrived on the largest island, Espíritu Santo, in 1606. Queirós claimed the archipelago for Spain, as part of the colonial Spanish East Indies, and named it . In the 1880s, France and the United Kingdom claimed parts of the archipelago, and in 1906, they agreed on a framework for jointly managing the archipelago as the New Hebrides through an Anglo-French condominium. An independence movement arose in the 1970s, and the Republic of Vanuatu was fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorig Language
Dorig (formerly called ''Wetamut'') is an Oceanic language spoken on Gaua island in Vanuatu. The language’s 300 speakers live mostly in the village of Dorig (), on the south coast of Gaua. Smaller speaker communities can be found in the villages of Qteon (east coast) and Qtevut (west coast). Dorig's immediate neighbours are Koro and Mwerlap. Name The name ''Dorig'', spelled ''Dōrig'', is derived from the name of the village where it is spoken. The term is related to ''Dōlav'' (the Dorig name of a village that is called in Lakon as ''Jōlap'' ), with the ''-rig'' and ''-lav'' parts meaning "small" and "big" respectively. The element ''dō'' is obscure; hence the only term that can be reconstructed for Proto-Torres-Banks is ''*-riɣi''. Phonology Dorig has 8 phonemic vowels. These include 7 short monophthongs and one long vowel . Dorig has 15 consonant phonemes. The phonotactic template for a syllable in Dorig is: — e.g. ‘woman’; ‘poor’; ‘octopus’. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakon Language
Lakon is an Oceanic language, spoken on the west coast of Gaua island in Vanuatu. Names The language name ''Lakon'' refers originally to the area where it is spoken ‒ namely Lakona Bay, corresponding to the west coast of Gaua. The alternative name ''Lakona'' is from the Mota language. These names are derived from a Proto-Torres-Banks form *''laᵑgona'', of unknown meaning. Lakon had four dialects, named Qatareu (''Qätärew'' ), Vure (''Vurē'' ), Toglatareu, and Togla. Phonology Consonants Lakon has 16 phonemic consonants. François (2022). The glottal stop only occurs before vowels in syllable-initial position. While non-phonemic, it is sometimes noted in the orthography, using a mark. Vowels Lakon has 16 phonemic vowels. These include 8 short /i ɪ ɛ æ a ɔ ʊ u/ and 8 long vowels /iː ɪː ɛː æː aː ɔː ʊː uː/. Historically, the phonemicisation of vowel length originates in the compensatory lengthening of short vowels when the alveolar trill w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mota Language
Mota is an Oceanic language spoken by about 750 people on Mota island, in the Banks Islands of Vanuatu. The language (named after the island) is one of the most conservative Torres–Banks languages, and the only one to keep its inherited five-vowel system intact while also preserving most final vowels. History During the period 1840-1940, Mota was used as a missionary ''lingua franca'' throughout areas of Oceania included in the Melanesian Mission, an Anglican missionary agency. Mota was used on Norfolk Island, in religious education; on other islands with different vernacular languages, it served as the language of liturgical prayers, hymns, and some other religious purposes. Elizabeth Fairburn Colenso translated religious material into the language. Robert Henry Codrington compiled the first dictionary of Mota (1896), and worked with George Sarawia and others to produce a large number of early publications in this language. Phonology Phoneme inventory Mota phonemically con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |