|
Doon, County Cavan
Doon is the name of three townlands in County Cavan, Ireland, with one situated in the civil parishes of Drumreilly, Mullagh, and Tomregan. All three derive their name from the Irish term ''Dún'', meaning "fort". * Doon (Drumreilly), in the civil parish of Drumreilly, is in the electoral division of Benbrack. It is also situated in the former barony of Tullyhaw. * Doon (Mullagh), in the civil parish of Mullagh, is in the electoral division of Crossbane. It is also situated in the former barony of Castlerahan Castlerahan () is a barony in County Cavan, Republic of Ireland. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Loca .... * Doon (Tomregan), in the civil parish of Tomregan, is in the electoral division of Ballyconnell. It is also situated in the barony of Tullyhaw. References External linksThe IreAtlas Townland Data Base {{coord missin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townland
A townland ( ga, baile fearainn; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a small geographical division of land, historically and currently used in Ireland and in the Western Isles in Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of Gaelic origin, pre-dating the Norman invasion, and most have names of Irish origin. However, some townland names and boundaries come from Norman manors, plantation divisions, or later creations of the Ordnance Survey.Connolly, S. J., ''The Oxford Companion to Irish History, page 577. Oxford University Press, 2002. ''Maxwell, Ian, ''How to Trace Your Irish Ancestors'', page 16. howtobooks, 2009. The total number of inhabited townlands in Ireland was 60,679 in 1911. The total number recognised by the Irish Place Names database as of 2014 was 61,098, including uninhabited townlands, mainly small islands. Background In Ireland a townland is generally the smallest administrative division of land, though a few large townlands are further divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Cavan
County Cavan ( ; gle, Contae an Chabháin) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Ulster and is part of the Border Region. It is named after the town of Cavan and is based on the historic Gaelic territory of East Breffny (''Bréifne''). Cavan County Council is the local authority for the county, which had a population of 76,176 at the 2016 census. Geography Cavan borders six counties: Leitrim to the west, Fermanagh and Monaghan to the north, Meath to the south-east, Longford to the south-west and Westmeath to the south. Cavan shares a border with County Fermanagh in Northern Ireland. Cavan is the 19th largest of the 32 counties in area and the 25th largest by population. The county is part of the Northern and Western Region, a NUTS II area, and in that region, is part of the Border strategic planning area, a NUTS III entity. The county is characterised by drumlin countryside dotted with many lakes and hills. The north-western area of the county is spar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 Counties of Ireland, counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. Around 2.1 million of the country's population of 5.13 million people resides in the Greater Dublin Area. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, which is Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a Unitary state, unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the , consists of a lower house, ; an upper house, ; and an elected President of Ireland, President () who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the (Prime Minister, liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In Ireland
Civil parishes () are units of territory in the island of Ireland that have their origins in old Gaelic territorial divisions. They were adopted by the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Ireland and then by the Elizabethan Kingdom of Ireland, and were formalised as land divisions at the time of the Plantations of Ireland. They no longer correspond to the boundaries of Roman Catholic or Church of Ireland parishes, which are generally larger. Their use as administrative units was gradually replaced by Poor Law Divisions in the 19th century, although they were not formally abolished. Today they are still sometimes used for legal purposes, such as to locate property in deeds of property registered between 1833 and 1946. Origins The Irish parish was based on the Gaelic territorial unit called a '' túath'' or '' Trícha cét''. Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the Anglo-Norman barons retained the ''tuath'', later renamed a parish or manor, as a unit of taxation. The civil parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
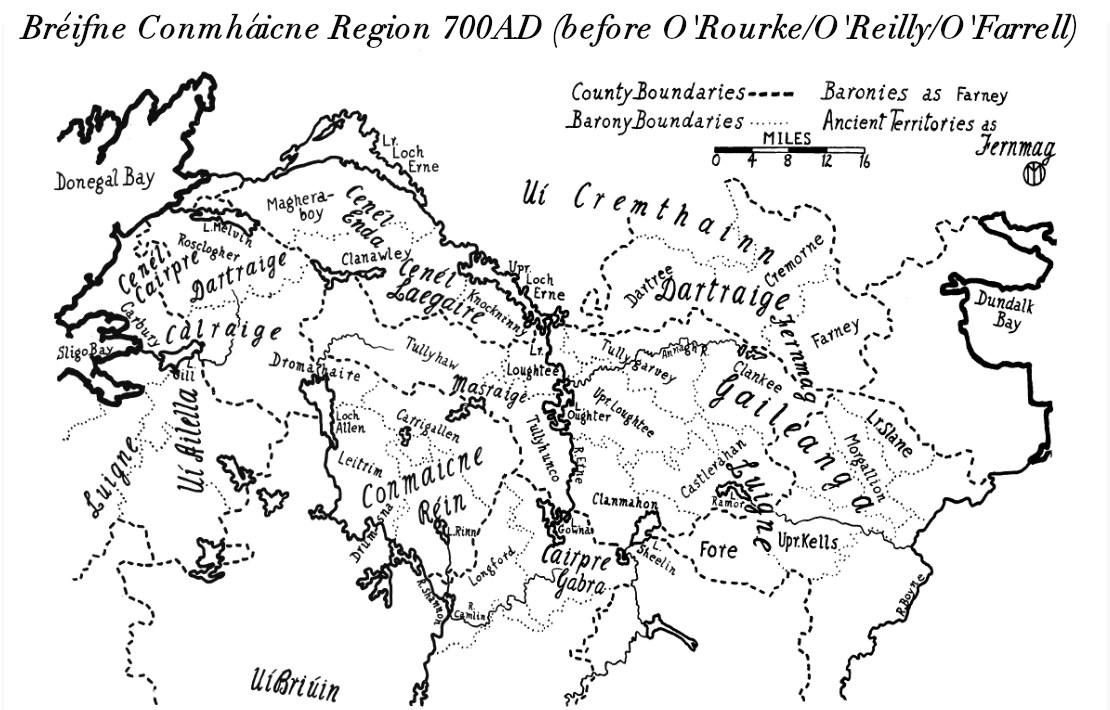
Drumreilly
Drumreilly civil parish is situated partly in the baronies of Carrigallen and Dromahaire, County Leitrim and partly in the barony of Tullyhaw, County Cavan, Ireland. Etymology The name of the parish derives from Drumreilly townland in the parish, which is an Anglicisation of the Gaelic ''Druim Air Belaigh'' meaning 'The Hill-Ridge of the Eastern Road'. The earliest surviving reference to the name is c.800 in the Martyrology of Tallaght, where it is spelled ''Dromma Airbelaig''. History The parish is in an area originally called Cenel Luacháin inhabited from early times by the Conmhaícne tribe. The reference above in the Martyrology of Tallaght is to a feast day on 15 January referring to the ''Seven bishops of Dromma Airbelaig'', who probably lived in a monastery in the area in early Christian times."Drumreilly and Its Clergy, A.D. 1401-1481" by John D. Seymour, in 'The Journal of the Royal Society of Antiquaries of Ireland', Seventh Series, Vol. 5, No. 2 (Dec. 31, 1935), pp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullagh, County Cavan
Mullagh (; ) is a town, civil parish and townland in County Cavan, Ireland. , the town's population was 1,348. It lies in the south-east of the county, at the junction of the R191 and the R194 regional roads near the towns of Virginia and Bailieborough. St Kilian and churches The town has a heritage centre dedicated to St Kilian, who was born in Mullagh c 640 and was martyred in Würzburg in Franconia in northern Bavaria, Germany, in circa 689. The centre also has an exhibition related to ogham script and the development of illuminated manuscripts. The Catholic church, a Victorian neo-Gothic structure located 400m from the village on the Virginia Road (R194), is named in memory of its patron, Saint Kilian. It was built in the late 1850s. Ruins of an earlier church, known as the ''Teampeall Ceallaigh'', remain in what is now part of the Church of Ireland grounds located approximately 600m along the same road. Development Mullagh's population has seen an increase from 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomregan
Tomregan ( ga, Tuaim Dreagain, ) is a civil parish in the ancient barony of Tullyhaw. The parish straddles the international border between the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland. The largest population centre in the parish is Ballyconnell, County Cavan. The total area of the civil parish is 10,600 statute acres. Most of Tomregan's constituent townlands are situated in County Cavan while the remainder lie in County Fermanagh. In the Catholic Church, the ecclesiastical parish of Tomregan was split in the early 18th century, with the County Fermanagh townlands being assigned to the parish of Knockninny while the County Cavan townlands were united with the parish of Kildallan. The townlands The Fermanagh townlands in Tomregan civil parish are- Aghindisert, Carickaleese, Cloncoohy, Derrintony, Derryart, Garvary, Gortahurk, Gortaree, Gortineddan, Gortmullan, Knockadoois, Knockateggal, Tonymore and Ummera. The Cavan townlands in Tomregan civil parish are- Agharas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (an Caighdeán Oifigiúil, Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic languages, Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous language, indigenous to the Ireland, island of Ireland and was the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became Linguistic imperialism, dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century. Irish is still spoken as a first language in a small number of areas of certain counties such as County Cork, Cork, County Donegal, Donegal, County Galway, Galway, and County Kerry, Kerry, as well as smaller areas of counties County Mayo, Mayo, County Meath, Meath, and County Waterford, Waterford. It is also spoken by a larger group of habitual but non-traditional speakers, mostly in urban areas where the majority are second language, second-language speakers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doon (Drumreilly)
Doon () is a townland in the civil parish of Drumreilly, barony of Tullyhaw, County Cavan, Ireland. Geography Doon is bounded on the north by Derrynananta Upper townland, on the west by Moneensauran, Seltanahunshin and Slievenakilla townlands and on the east by Ardmoneen, Garryfliugh, Lannanerriagh and Moher (Drumreilly) townlands. Its chief geographical features are Bartonny Top mountain (Irish = Bharr an Tonnaigh = The Top of the Mound) which reaches a height of 411 metres, Bartonny Lough, mountain pools, the Yellow River, forestry plantations, small streams and river swallow holes. Doon is traversed by minor public roads and rural lanes. The townland covers 1,190 statute acres. History The 1665 Down Survey map depicts the townland as ''Bartunny''. An Inquisition held in Cavan Town on 20 September 1630 found that, at the date of his death on 26 June 1625, Walter Talbot of Ballyconnell owned, inter alia, ''2 polls in Bartony''. The lands passed to his son James Talbot, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral Division (Ireland)
An electoral division (ED, ) is a legally defined administrative area in the Republic of Ireland, generally comprising multiple townlands, and formerly a subdivision of urban and rural districts. Until 1996, EDs were known as district electoral divisions (DEDs, ) in the 29 county council areas and wards in the five county boroughs. Until 1972, DEDs also existed in Northern Ireland. The predecessor poor law electoral divisions were introduced throughout the island of Ireland in the 1830s. The divisions were used as local-government electoral areas until 1919 in what is now the Republic and until 1972 in Northern Ireland. History until partition Electoral divisions originated under the Poor Relief (Ireland) Act 1838 as "poor law electoral divisions": electoral divisions of a poor law union (PLU) returning one or more members to the PLU's board of guardians. The boundaries of these were drawn by Poor Law Commissioners, with the intention of producing areas roughly equivalent in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
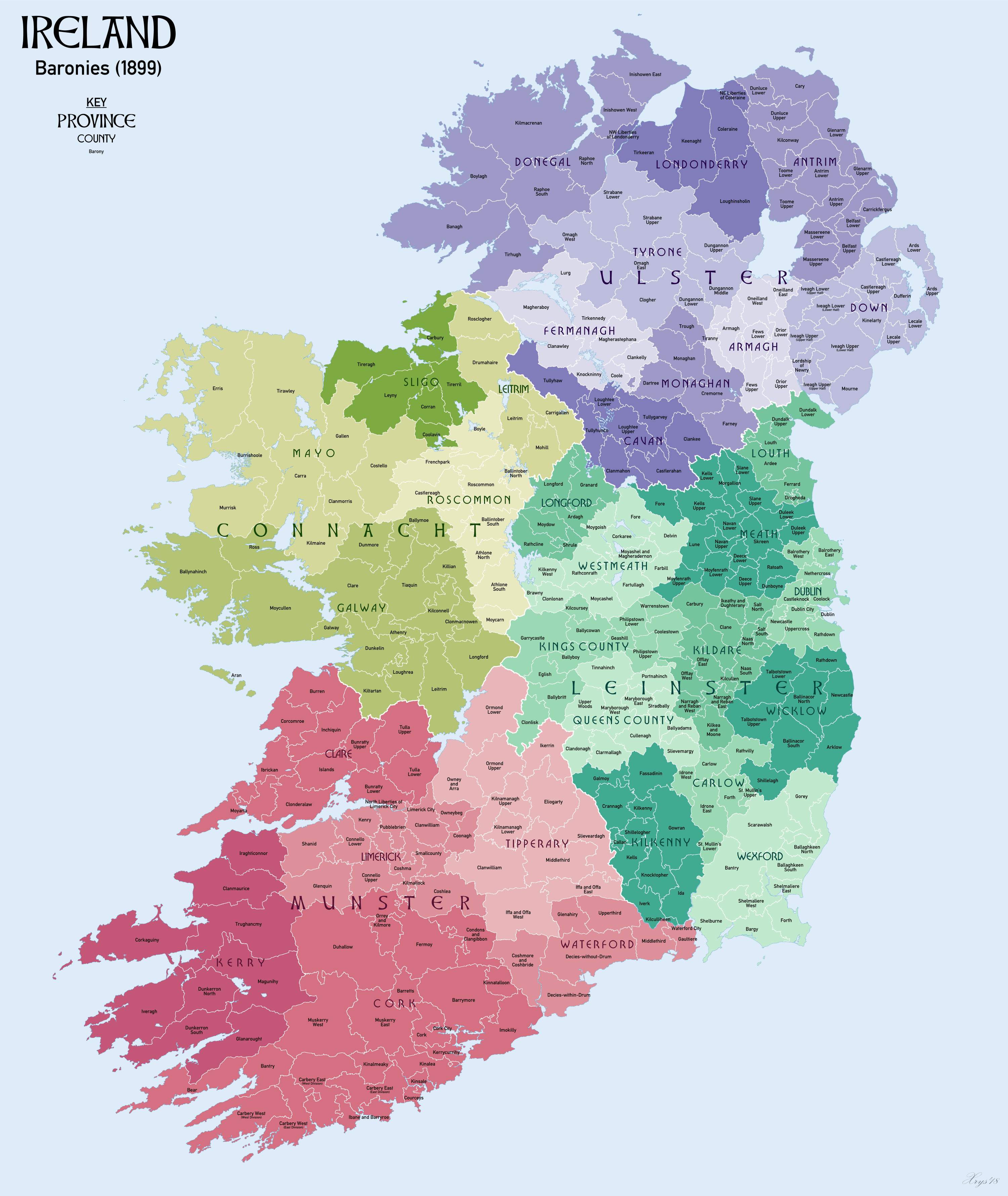
Barony (Ireland)
In Ireland, a barony ( ga, barúntacht, plural ) is a historical subdivision of a county, analogous to the hundreds into which the counties of England were divided. Baronies were created during the Tudor reconquest of Ireland, replacing the earlier cantreds formed after the original Norman invasion.Mac Cotter 2005, pp.327–330 Some early baronies were later subdivided into half baronies with the same standing as full baronies. Baronies were mainly cadastral rather than administrative units. They acquired modest local taxation and spending functions in the 19th century before being superseded by the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898. Subsequent adjustments of county boundaries mean that some baronies now straddle two counties. The final catalogue of baronies numbered 331, with an average area of ; therefore, each county was divided, on average, into 10 or 11 baronies. Creation The island of Ireland was "shired" into counties in two distinct periods: the east and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tullyhaw
Tullyhaw ( ga, Teallach Eathach) (which means 'The Territory of Eochaidh', an ancestor of the McGoverns, who lived ) is a Barony in County Cavan in the Republic of Ireland. The area has been in constant occupation since pre-4000 BC. Located in the northwest of the county, it has been referred to as Cavan's panhandle. In 1579, East Breifne, then part of Connacht, was made a shire. The shire was named County Cavan ( ga, An Cabhán) after Cavan, the area's main town. The administration remained in the control of the local Irish dynasty and subject to the Brehon and Canon Law. In 1584, Sir John Perrot formed the shire into a county in Ulster. It was subdivided into seven baronies: *two of which were assigned to Sir John O'Reilly and *three to other members of the family; *two remaining, possessed by the septs of **McKiernan Clan and ** McGovern (a.k.a. ''Magauran'') The last one, Tullyhaw, encompassed the mountains bordering on O'Rourke's country, and was left subj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |