|
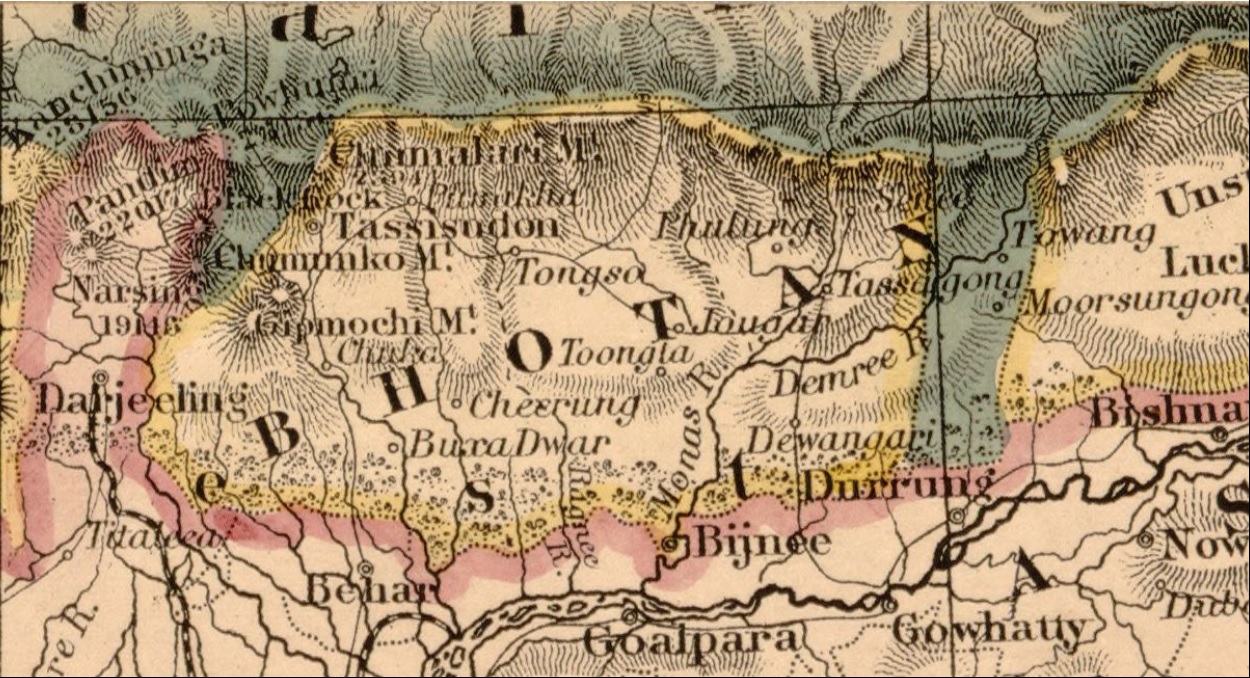
Donga Range
The mountains of Bhutan are some of the most prominent natural geographic features of the kingdom. Located on the southern end of the Eastern Himalaya, Bhutan has one of the most rugged mountain terrains in the world, whose elevations range from to more than above sea level, in some cases within distances of less than of each other. Bhutan's highest peak, at above sea level, is north-central Gangkhar Puensum, close to the border with Tibet; the third highest peak, Jomolhari, overlooking the Chumbi Valley in the west, is above sea level; nineteen other peaks exceed . Weather is extreme in the mountains: the high peaks have perpetual snow, and the lesser mountains and hewn gorges have high winds all year round, making them barren brown wind tunnels in summer, and frozen wastelands in winter. The blizzards generated in the north each winter often drift southward into the central highlands. The mountains of Bhutan define its three main geographic zones: the Great Himalaya, the Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous country, Bhutan is known as "Druk Yul," or "Land of the Thunder Dragon". Nepal and Bangladesh are located near Bhutan but do not share a land border. The country has a population of over 727,145 and territory of and ranks 133rd in terms of land area and 160th in population. Bhutan is a Constitutional Democratic Monarchy with King as head of state and Prime Minister as head of government. Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism is the state religion and the Je Khenpo is the head of state religion. The subalpine Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest uncl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trashigang District
Trashigang District ( Dzongkha: བཀྲ་ཤིས་སྒང་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie: ''Bkra-shis-sgang rdzong-khag''; also spelled "Tashigang") is Bhutan's easternmost dzongkhag (district). Culture The population of the district is mainly Sharchop, which means "easterner" in Dzongkha, the national language. Languages The dominant language of Trashigang is Tshangla (Sharchopkha), the ''lingua franca'' of eastern Bhutan. Two significant minority languages are spoken in the far eastern region of the district: the East Bodish Dakpa language and the Southern Bodish Brokpa language. Dakpa is spoken by descendants of yakherding communities, and may in fact be a divergent dialect of Brokpake, heavily influenced by Dzalakha. Economy and education While it has no major urban area, Trashigang has the densest population in Bhutan. It used to be part of an important trade route connecting Assam to Tibet, and still is a primary route for Bhutanese trade with India. Tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Himalayan Range
The Lower Himalayan Range ( ne, पर्वत शृङ्खला parbat shrinkhalā) – also called the Middle Himalayas or Lesser Himalayas or Himachal – is a major east–west mountain range with elevations 3,700 to 4,500 m (12,000 to 14,500 feet) in the northernmost regions of the Indian subcontinent along the crest, paralleling the much higher High Himalayas range from the Indus River in Pakistan across northern India, Nepal and Bhutan but then the two ranges become increasingly difficult to differentiate east of Bhutan as the ranges approach the Brahmaputra River. The Himachal range also parallels the lower Shiwalik or Churia Range (Outer Himalaya) to the south. The Pir Panjal is the largest range of the Lesser Himalayas. Background Southern slopes of the Himachal Range are steep and nearly uninhabited due to a major fault system called the 'Main Boundary Thrust". The crest and northern slopes slope gently enough to support upland pastures and terraced fields. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Himalaya
The Great Himalayas or Greater Himalayas or Himadri is the highest mountain range of the Himalayan Range.Hussain, MajidGeography of India/ref> The world's highest peak, Mount Everest, as well as other "near−highest" peaks, such as Kangchenjunga, Lhotse, and Nanga Parbat, are part of the Greater Himalayas range. The total west to east extension of the Great Himalayas is 2400 km (1500 miles) and their average elevation is 6000 m (20000 ft.). Several glaciers are contained within the range, including Gangotri Glacier, and Satopanth Glacier. Political entities which have territory in this range include India, China, Nepal, Pakistan, Bhutan, and Tibet Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman .... See also * * References G Mountain ranges of China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland (geography)
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is usually reserved for ranges of low mountains. However, the two terms are sometimes interchangeable. Highlands internationally Probably the best-known area officially or unofficially referred to as ''highlands'' in the Anglosphere is the Scottish Highlands in northern Scotland, the mountainous region north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault. The Highland council area is a local government area in the Scottish Highlands and Britain's largest local government area. Other highland or upland areas reaching 400-500 m or higher in the United Kingdom include the Southern Uplands in Scotland, the Pennines, North York Moors, Dartmoor and Exmoor in England, and the Cambrian Mountains in Wales. Many countries and regions also have areas referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blizzard
A blizzard is a severe snowstorm characterized by strong sustained winds and low visibility, lasting for a prolonged period of time—typically at least three or four hours. A ground blizzard is a weather condition where snow is not falling but loose snow on the ground is lifted and blown by strong winds. Blizzards can have an immense size and usually stretch to hundreds or thousands of kilometres. Definition and etymology In the United States, the National Weather Service defines a blizzard as a severe snow storm characterized by strong winds causing blowing snow that results in low visibilities. The difference between a blizzard and a snowstorm is the strength of the wind, not the amount of snow. To be a blizzard, a snow storm must have sustained winds or frequent gusts that are greater than or equal to with blowing or drifting snow which reduces visibility to or less and must last for a prolonged period of time—typically three hours or more. Environment Canada defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumbi Valley
The Chumbi Valley, called Dromo or Tromo in Tibetan, is a valley in the Himalayas that projects southwards from the Tibetan plateau, intervening between Sikkim and Bhutan. It is coextensive with the administrative unit Yadong County in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China. The Chumbi Valley is connected to Sikkim to the southwest via the mountain passes of Nathu La and Jelep La. The valley is at an altitude of , and being on the south side of the Himalayas, enjoys a wetter and more temperate climate than most of Tibet. The valley supports some vegetation in the form of the Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests and transitions to the Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows in the north. The plant ''Pedicularis chumbica'' ( 春丕马先蒿) is named after the valley. The 1904 Younghusband Expedition of British India passed through the Chumbi Vally on its way to Lhasa. At the end of the expedition, the British took control of the Chumbi Valley in lieu of a war indemnity. Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jomolhari
Jomolhari or Chomolhari (; ) sometimes known as "the bride of Kangchenjunga”, is a mountain in the Himalayas, straddling the border between Yadong County of Tibet, China and the Paro district of Bhutan. The north face rises over above the barren plains. The mountain is the source of the Paro Chu (Paro river) which flows from the south side and the Amo Chu which flows from the north side. Religious significance The mountain is sacred to Tibetan Buddhists who believe it is the abode of one of the Five Tsheringma Sisters; ''(jo mo tshe ring mched lnga)'' — female protector goddesses (Jomo) of Tibet and Bhutan, who were bound under oath by Padmasambhava to protect the land, the Buddhist faith and the local people. On the Bhutanese side is a Jomolhari Temple, toward the south side of the mountain about a half-day's journey from the army outpost between Thangthangkha and Jangothang at an altitude of 4150 meters. Religious practitioners and pilgrims visiting Mt. Jomolhari stay at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gangkhar Puensum
Gangkhar Puensum ( dz, གངས་དཀར་སྤུན་གསུམ་, translit=Kangkar Punsum, alternatively, Gangkar Punsum or Gankar Punzum) is the highest mountain in Bhutan and the highest unclimbed mountain in the world, with an elevation of and a prominence of . Its name means "White Peak of the Three Spiritual Brothers" in Dzongkha. Gangkhar Puensum lies on the border between Bhutan and Tibet, China. After Bhutan was opened for mountaineering in 1983 there were four expeditions that resulted in failed summit attempts in 1985 and 1986. In 1999, a Japanese expedition successfully climbed Liankang Kangri, a subsidiary peak (not an independent mountain), separated from the main peak by a long ridge to the north-northwest. Since 2003, mountaineering has been banned in Bhutan. History The elevation of Gangkhar Puensum was first measured in 1922 but, until recent years, maps of the region were not at all accurate and the mountain was shown in different locations an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Himalaya
] The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity. Geologic strata The Eastern Himalayas have a much more sophisticated geomorphic history and pervasive topographic features than the Central Himalayas. In the southwest of the Sub-Himalayan Range, Sub-Himalayas lies the Singalila Ridge, the western end of a group of uplands in Nepal. Most of the Sub-Himalayas are in Nepal; a small portion reaches into Sikkim, India and a fragment is in the southern half of Bhutan. The region's topography, in part, has facilitated the region's rich biological diversity and ecosystem structure. The Buxa range of Indo-Bhutan is also a part of the ancient rocks of the Himalayas. The ancient folds, running mainly along an east-west axis, were worn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhemgang District
Zhemgang District (Dzongkha: གཞམས་སྒང་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie transliteration: ''Gzhams-sgang rdzong-khag''; previously "Shemgang"), is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Sarpang, Trongsa, Bumthang, Mongar and Pemagatshel Districts, and borders Assam in India to the south. The administrative center of the district is Zhemgang. Languages The dominant language in Zhemgang is Khengkha. Historically, Khengkha and its speakers have had close contact with speakers of Kurtöpkha, Nupbikha, and Bumthangkha to the north, to the extent that they may be considered part of a wider collection of "Bumthang languages." The term Ngalop may subsume several related linguistic and cultural groups, such as the Kheng people and speakers of Bumthang language. S.R. Chakravarty asserts that Kheng are one of the earliest inhabitants that language spread upwards from Kheng into Bumthang and Kurtöp. By all accounts the Kheng are more clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wangdue Phodrang District
Wangdue Phodrang District ( Dzongkha: དབང་འདུས་ཕོ་བྲང་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie: ''Dbang-'dus Pho-brang rdzong-khag''; previously spelled "Wangdi Phodrang") is a dzongkhag (district) of central Bhutan. This is also the name of the dzong (built in 1638) which dominates the district, and the name of the small market town outside the gates of the dzong—it is the capital (dzongkhag thromde) of Wangdue Phodrang District). The name is said to have been given by the Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal who was searching for the best location for a dzong to prevent incursions from the south. The word "wangdue" means unification of Country, and "Phodrang" means Palace in Dzongkha. Wangdue Phodrang is the largest dzongkhag in Bhutan by area and is bordered by Dagana and Tsirang dzongkhags to the south, Tongsa dzongkhag to the east, Thimphu and Punakha dzongkhag to the west, and Gasa dzongkhag and a small section of border with Tibet to the north. It is lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |