|
Dominican Nationality Law
Dominican nationality law is regulated by the 1978 Constitution of the Commonwealth of Dominica, as amended; the Citizenship Act, and its revisions; and various British Nationality laws. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Dominica. Dominican nationality is typically obtained either on the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Dominica; or under the rules of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth abroad to parents with Dominican nationality. It can also be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalisation. There is also, currently a program in Dominica for acquiring nationality by investment. Nationality establishes one's international identity as a member of a sovereign nation. Though it is not synonymous with citizenship, for rights granted under domestic law for domestic purposes, the United Kingdom, and thus the commonwealth, have traditionally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated language known as Island Carib. They also spoke a pidgin language associated with the Mainland Caribs. At the time of Spanish contact, the Kalinago were one of the dominant groups in the Caribbean, which owes its name to them. They lived throughout northeastern South America, Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, the Windward Islands, Dominica, and possibly the southern Leeward Islands. Historically, it was thought their ancestors were mainland peoples who had conquered the islands from their previous inhabitants, the Igneri. However, linguistic and archaeological evidence contradicts the notion of a mass emigration and conquest; the Kalinago language appears not to have been Cariban, but like that of their neighbors, the Taíno. Irving Rouse and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of France, France and Spanish Empire, Spain, with Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the Seven Years' War. The signing of the treaty formally ended conflict between France and Great Britain over control of North America (the Seven Years' War, known as the French and Indian War in the United States), and marked the beginning of an era of British dominance outside Europe. Great Britain and France each returned much of the territory that they had captured during the war, but Great Britain gained much of France's possessions in North America. Additionally, Great Britain agreed to protect Roman Catholicism in the New World. The treaty did not involve Prussia and Habsburg monarchy, Austria as they signed a separate agreement, the Treaty of Hubertusburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Colonial And Departmental Heads Of Martinique
(Dates in italics indicate ''de facto'' continuation of office) Ancien regime and First Republic (1635-1794) British occupation (1794–1814) Restoration, Second Republic, Second Empire (1814–70) Third Republic (1870–1940) Fourth and Fifth Republics (1945-present) See also *Martinique *Politics of Martinique External linksWorld Statesmen - Martinique References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code Noir
The (, ''Black code'') was a decree passed by the French King Louis XIV in 1685 defining the conditions of slavery in the French colonial empire. The decree restricted the activities of free people of color, mandated the conversion of all enslaved people throughout the empire to Roman Catholicism, defined the punishments meted out to slaves, and ordered the expulsion of all Jews from France's colonies. The code's effects on the enslaved population of the French colonial empire were complex and multifaceted. It outlawed the worst punishments owners could inflict upon their slaves, and led to an increase in the free population. Despite this, enslaved persons were still subject to harsh treatment at the hands of their owners, and the expulsion of Jews was an extension of antisemitic trends in the Kingdom of France. Free people of color were still placed under restrictions via the , but were otherwise free to pursue their own careers. Compared to other European colonies in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars. Logging is the beginning of a supply chain that provides raw material for many products societies worldwide use for housing, construction, energy, and consumer paper products. Logging systems are also used to manage forests, reduce the risk of wildfires, and restore ecosystem functions, though their efficiency for these purposes has been challenged. In forestry, the term logging is sometimes used narrowly to describe the logistics of moving wood from the stump to somewhere outside the forest, usually a sawmill or a lumber yard. In common usage, however, the term may cover a range of forestry or silviculture activities. Illegal logging refers to the harvesting, transportation, purchase, or sale of timber in violation of laws. The harvesting procedure itself may be illegal, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Hay, 1st Earl Of Carlisle
James Hay, 1st Earl of Carlisle KB (c. 1580March 1636) was a British noble. Life A Scot, he was the son of Sir James Hay of Fingask, second son of Peter Hay of Megginch (a branch member of Hay of Leys, a younger branch of the Erroll family) and his wife Margaret, daughter of Crichton of Ruthven.''Historical Account of the Family of Hay of Leys'' (Edinburgh, 1832), pp. 20-1. Accessed January 2020. His mother was Margaret Murray, cousin of George Hay, afterwards 1st Earl of Kinnoull. His aunts married well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
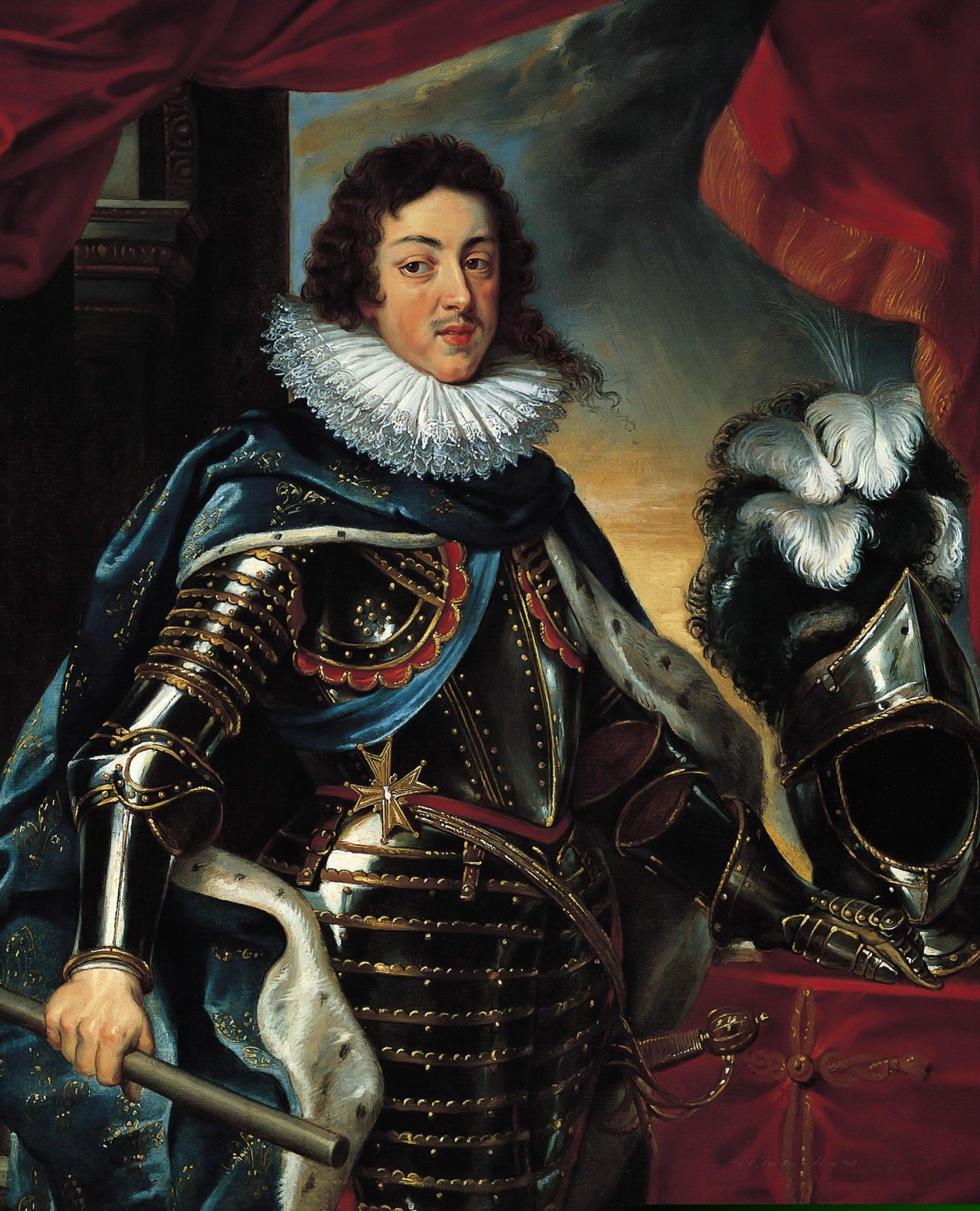
Charles I Of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after his father inherited the English throne in 1603, he moved to England, where he spent much of the rest of his life. He became heir apparent to the kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland in 1612 upon the death of his elder brother, Henry Frederick, Prince of Wales. An unsuccessful and unpopular attempt to marry him to the Spanish Habsburg princess Maria Anna of Spain, Maria Anna culminated in an eight-month visit to Spain in 1623 that demonstrated the futility of the marriage negotiation. Two years later, he married the House of Bourbon, Bourbon princess Henrietta Maria of France. After his 1625 succession, Charles quarrelled with the Parliament of England, English Parliament, which sought to curb his royal prerogati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc between the Greater Antilles to the north-west and the continent of South America."West Indies." ''Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary'', 3rd ed. 2001. () Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 1298. The islands of the Lesser Antilles form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea where it meets the Atlantic Ocean. Together, the Lesser Antilles and the Greater Antilles make up the Antilles. (Somewhat confusingly, the word Caribbean is sometimes used to refer only to the Antilles, and sometimes used to refer to a much larger region.) The Lesser and Greater Antilles, together with the Lucayan Archipelago, are collectively known as the West Indies. History after European arrival The Spanish were the first Europeans to arrive on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, Duke of Richelieu (; 9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a French clergyman and statesman. He was also known as ''l'Éminence rouge'', or "the Red Eminence", a term derived from the title "Eminence" applied to cardinals and the red robes that they customarily wear. Consecrated a bishop in 1607, Richelieu was appointed Foreign Secretary in 1616. He continued to rise through the hierarchy of both the Catholic Church and the French government by becoming a cardinal in 1622 and chief minister to King Louis XIII of France in 1624. He retained that office until his death in 1642, when he was succeeded by Cardinal Mazarin, whose career he had fostered. He also became engaged in a bitter dispute with the king's mother, Marie de Médicis, who had once been a close ally. Richelieu sought to consolidate royal power and restrained the power of the nobility in order to transform France into a strong centralized state. In foreig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
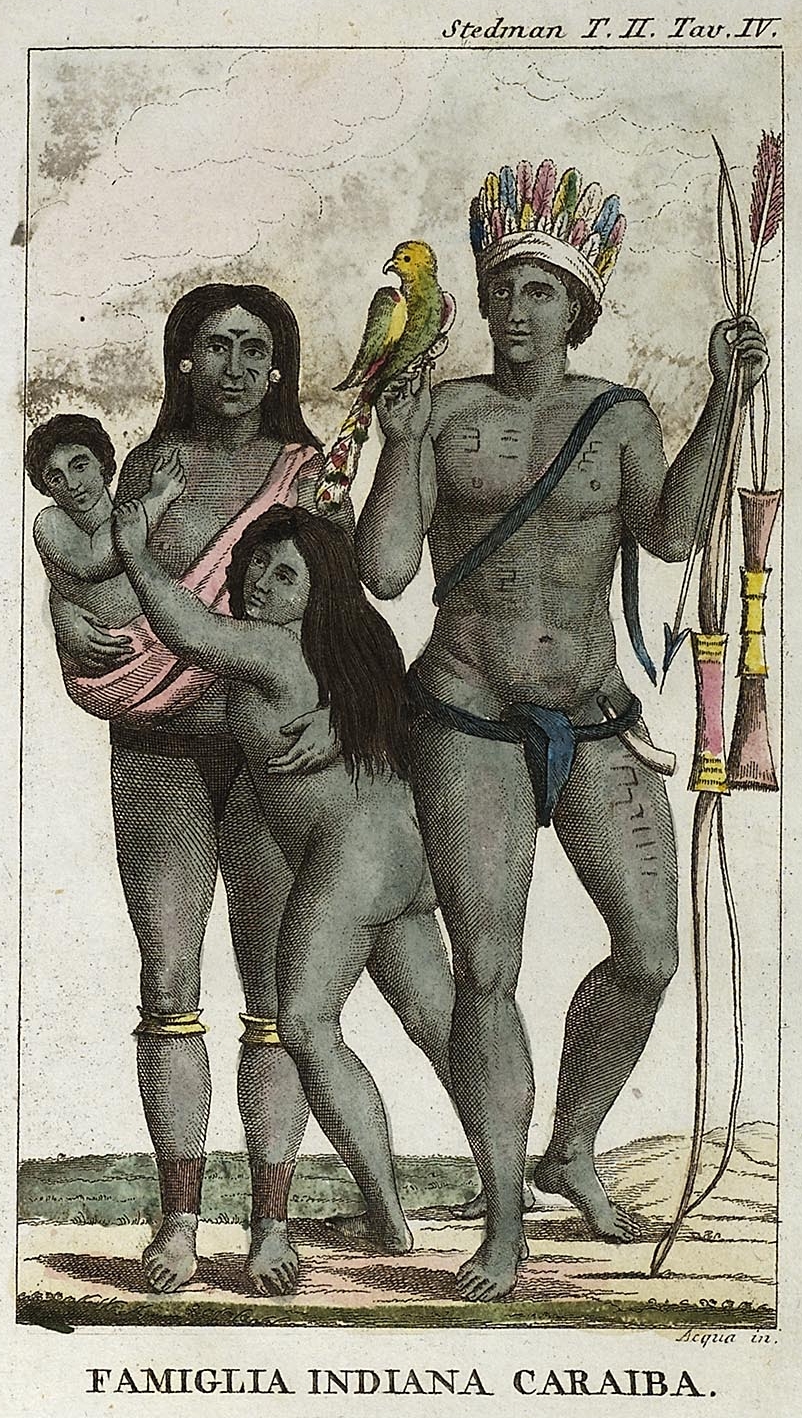





.jpg)
