|
Domenico Fontana
Domenico Fontana (154328 June 1607) was an Italian architect of the late Renaissance, born in today's Ticino. He worked primarily in Italy, at Rome and Naples. Biography He was born at Melide, a village on the Lake Lugano, at that time joint possession of some Swiss cantons of the old Swiss Confederacy, and presently part of Ticino, Switzerland, and died at Naples. He went to Rome in 1563, to join his elder brother. He began his career as a plasterer, and then as a mason and master builder, with particular expertise in measuring and technical skills. Fontana’s first architectural project was a villa in the Piazza Pasquino for Cardinal Montalto, constructed between 1577-78. Montalto later entrusted him in 1584 with the erection of the Cappella del Presepio (Chapel of the Manger) in Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore, a powerful domical building over a Greek cross. It is a marvellously well-balanced structure, notwithstanding the profusion of detail and overloading of rich ornam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federico Zuccari, Ritratto Di Domenico Fontana
Federico (; ) is a given name and surname. It is a form of Frederick (given name), Frederick, most commonly found in Spanish language, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese and Italian language, Italian. People with the given name Federico Artists * Federico Ágreda, Venezuelan composer and DJ. * Federico Aguilar Alcuaz, renowned Filipino painter. * Federico Andahazi, Argentine writer and psychologist. * Federico Casagrande, Italian jazz guitarist * Federico Castelluccio, Italian-American actor who is most famous for his role as Furio Giunta on the HBO TV series, The Sopranos * Federico Cortese, Italian conductor, Music Director of the Boston Youth Symphony Orchestras and the Harvard Radcliffe Orchestra * Fred Elizalde, Federico Elizalde, Filipino marksman and musician * Federico Fellini, Italian film-maker and director * Federico García Lorca, Spanish poet and playwright * Federico Luppi, Argentine film, TV, radio and theatre actor * Federico Ricci, Italian composer Athletes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
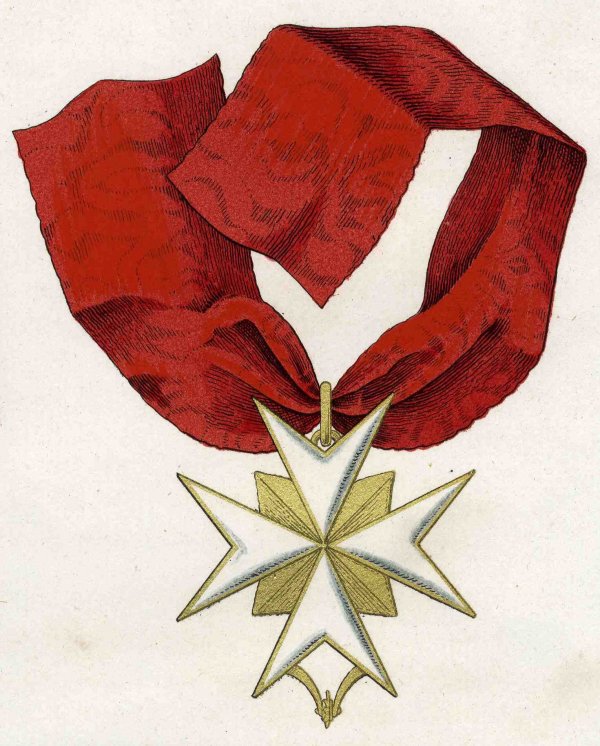
Order Of The Golden Spur
The Order of the Golden Spur ( it, Ordine dello Speron d'Oro, french: Ordre de l'Éperon d'or), officially known also as the Order of the Golden Militia ( la, Ordo Militia Aurata, it, Milizia Aurata), is a papal order of knighthood conferred upon those who have rendered distinguished service in propagating the Catholic faith, or who have contributed to the glory of the Church, either by feat of arms, by writings, or by other illustrious acts. History Before 19th century: a noble order It is accounted the earliest papal chivalric institution. The Order of the Golden Spur had its origins in the title ''Count palatine of the Lateran Palace'', which was in the gift of the Holy Roman Emperor in the fourteenth century: Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor conferred the title on one Fenzio di Albertino di Prato, 15 August 1357, at Prague. The Order began to be associated with the inheritable patent of nobility in the form of count palatinate during the Renaissance; Emperor Frederick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Clement VIII
Pope Clement VIII ( la, Clemens VIII; it, Clemente VIII; 24 February 1536 – 3 March 1605), born Ippolito Aldobrandini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 2 February 1592 to his death in March 1605. Born in Fano, Italy to a prominent Florentine family, he initially came to prominence as a canon lawyer before being made a Cardinal-Priest in 1585. In 1592 he was elected Pope and took the name of Clement. During his papacy he effected the reconciliation of Henry IV of France to the Catholic faith and was instrumental in setting up an alliance of Christian nations to oppose the Ottoman Empire in the so-called Long War. He also successfully adjudicated in a bitter dispute between the Dominicans and the Jesuits on the issue of efficacious grace and free will. In 1600 he presided over a jubilee which saw many pilgrimages to Rome. He presided over the trial and execution of Giordano Bruno and implementing strict measures against Jewish resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatican Library
The Vatican Apostolic Library ( la, Bibliotheca Apostolica Vaticana, it, Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana), more commonly known as the Vatican Library or informally as the Vat, is the library of the Holy See, located in Vatican City. Formally established in 1475, although it is much older—it is one of the oldest libraries in the world and contains one of the most significant collections of historical texts. It has 75,000 codices from throughout history, as well as 1.1 million printed books, which include some 8,500 incunabula. The Vatican Library is a research library for history, law, philosophy, science, and theology. The Vatican Library is open to anyone who can document their qualifications and research needs. Photocopies for private study of pages from books published between 1801 and 1990 can be requested in person or by mail. Pope Nicholas V (1447–1455) envisioned a new Rome with extensive public works to lure pilgrims and scholars to the city to begin its tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque (also called moment) acting on physical systems that do not experience an acceleration (''a''=0), but rather, are in static equilibrium with their environment. The application of Newton's second law to a system gives: : \textbf F = m \textbf a \, . Where bold font indicates a vector that has magnitude and direction. \textbf F is the total of the forces acting on the system, m is the mass of the system and \textbf a is the acceleration of the system. The summation of forces will give the direction and the magnitude of the acceleration and will be inversely proportional to the mass. The assumption of static equilibrium of \textbf a = 0 leads to: : \textbf F = 0 \, . The summation of forces, one of which might be unknown, allows that unknown to be found. So when in static equilibrium, the acceleration of the system is zero and the system is either at rest, or its center of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignazio Danti
Ignazio (Egnation or Egnazio) Danti, O.P. (April 1536 – 10 October 1586), born Pellegrino Rainaldi Danti, was an Italian Roman Catholic prelate, mathematician, astronomer, and cosmographer, who served as Bishop of Alatri (1583–1586). ''(in Latin)'' Early life Danti was born in Perugia in 1536 to a family of artists and scientists. As a boy he learned the rudiments of painting and architecture from his father Giulio, an architect and engineer who studied under Antonio da Sangallo, and his aunt Teodora,Brock, Henry. "Ignazio Danti." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 4. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1908. 15 December 2022 who was said to have studied under the painter [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obelisks In Rome
The city of Rome harbours thirteen ancient obelisks, the most in the world. There are eight ancient Egyptian and five ancient Roman obelisks in Rome, together with a number of more modern obelisks; there was also until 2005 an ancient Ethiopian obelisk in Rome. The Romans used special heavy cargo carriers called obelisk ships to transport the monuments down the Nile to Alexandria and from there across the Mediterranean Sea to Rome. On site, large Roman cranes were employed to erect the monoliths. Ancient Egyptian obelisks At least eight obelisks created in antiquity by the Egyptians were taken from Egypt after the Roman conquest and brought to Rome. Ancient Roman obelisks At least five obelisks were manufactured in Egypt in the Roman period at the request of the wealthy Romans, or made in Rome as copies of ancient Egyptian originals. Obelisk of Axum There was also an Ethiopian obelisk in Rome, the Obelisk of Axum, 24 m, placed in the Piazza di Porta Capen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fountain In The Pedestal Of The Obelisk In Front Of S
A fountain, from the Latin "fons" (genitive "fontis"), meaning source or spring, is a decorative reservoir used for discharging water. It is also a structure that jets water into the air for a decorative or dramatic effect. Fountains were originally purely functional, connected to springs or aqueducts and used to provide drinking water and water for bathing and washing to the residents of cities, towns and villages. Until the late 19th century most fountains operated by gravity, and needed a source of water higher than the fountain, such as a reservoir or aqueduct, to make the water flow or jet into the air. In addition to providing drinking water, fountains were used for decoration and to celebrate their builders. Roman fountains were decorated with bronze or stone masks of animals or heroes. In the Middle Ages, Moorish and Muslim garden designers used fountains to create miniature versions of the gardens of paradise. King Louis XIV of France used fountains in the Gardens of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1586 Rome Obelisk Erection
Events * January 18 – The 7.9 Tenshō earthquake strikes the Chubu region of Japan, triggering a tsunami and causing at least 8,000 deaths. * June 16 – The deposed and imprisoned Mary, Queen of Scots, recognizes Philip II of Spain as her heir. * July 6 – The Treaty of Berwick is signed between Queen Elizabeth I of England and King James VI of Scotland. * July 21 – English explorer Thomas Cavendish begins the first deliberately planned circumnavigation of the globe. * September 20– 21 – Execution of the Babington Plotters: The 14 men convicted of a plot (uncovered on July 17) to murder Queen Elizabeth and replace her with Mary, Queen of Scots, are hanged, drawn and quartered (the first seven being disembowelled before death) in St Giles Field, London. * September 22 – Battle of Zutphen: Spanish troops defeat the Dutch rebels and their English allies. English poet and courtier Sir Philip Sidney is mortally wounded. * October 15– 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quirinal Palace
The Quirinal Palace ( it, Palazzo del Quirinale ) is a historic building in Rome, Italy, one of the three current official residences of the president of the Italian Republic, together with Villa Rosebery in Naples and the Tenuta di Castelporziano, an estate on the outskirts of Rome, some 25 km from the centre of the city. It is located on the Quirinal Hill, the highest of the seven hills of Rome in an area colloquially called Monte Cavallo. It has served as the residence for thirty popes, four kings of Italy and twelve presidents of the Italian Republic. The Quirinal Palace was selected by Napoleon to be his residence ''par excellence'' as emperor. However, he never stayed there because of the French defeat in 1814 and the subsequent European Restoration. The palace extends for an area of 110,500 square meters and is the twelfth-largest palace in the world in terms of area, some twenty times the area of the White House. History Origins The current site of the palac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
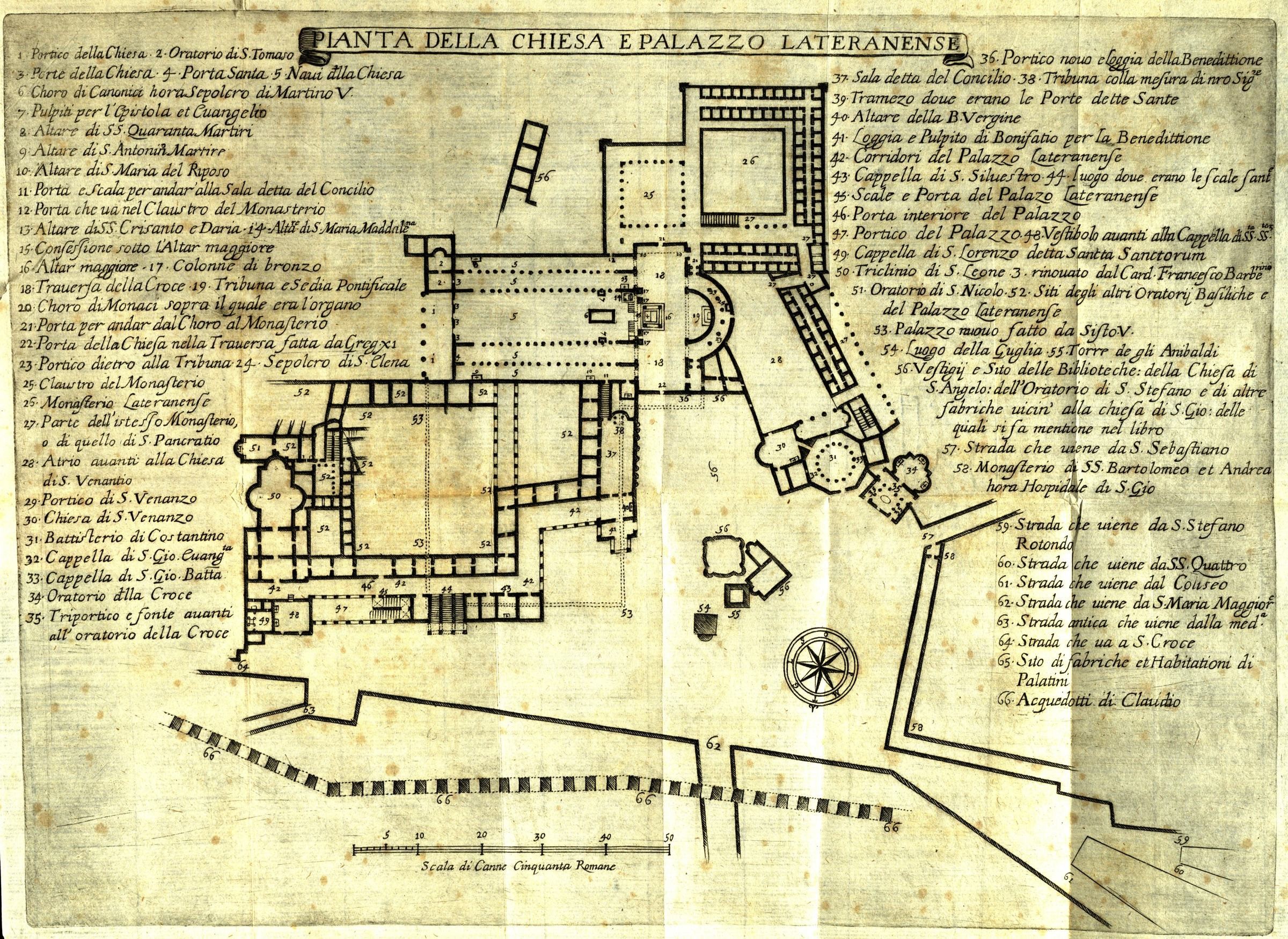
Lateran Palace
The Lateran Palace ( la, Palatium Lateranense), formally the Apostolic Palace of the Lateran ( la, Palatium Apostolicum Lateranense), is an ancient palace of the Roman Empire and later the main papal residence in southeast Rome. Located on St. John's Square in Lateran on the Caelian Hill, the palace is adjacent to the Archbasilica of Saint John Lateran, the cathedral church of Rome. From the fourth century, the palace was the principal residence of the popes, and continued so for about a thousand years until the Apostolic Residence ultimately moved to the Vatican. The palace is now used by the Vatican Historical Museum, which illustrates the history of the Papal States. The palace also houses the offices of the Vicariate of Rome, as well as the residential apartments of the Cardinal Vicar, the pope's delegate for the daily administration of the diocese. Until 1970, the palace was also home to the important collections of the Lateran Museum, now dispersed among other parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacopo Barozzi Da Vignola
Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola ( , , ; 1 October 15077 July 1573), often simply called Vignola, was one of the great Italian architects of 16th century Mannerism. His two great masterpieces are the Villa Farnese at Caprarola and the Jesuits' Church of the Gesù in Rome. The three architects who spread the Italian Renaissance style throughout Western Europe are Vignola, Serlio and Palladio. He is often considered the most important architect in Rome in the Mannerist era. Biography Giacomo Barozzi was born at Vignola, near Modena (Emilia-Romagna). He began his career as architect in Bologna, supporting himself by painting and making perspective templates for inlay craftsmen. He made a first trip to Rome in 1536 to make measured drawings of Roman temples, with a thought to publish an illustrated Vitruvius. Then François I called him to Fontainebleau, where he spent the years 1541–1543. Here he probably met his fellow Bolognese, the architect Sebastiano Serlio and the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |