|
Dolní Věstonice (archaeological Site)
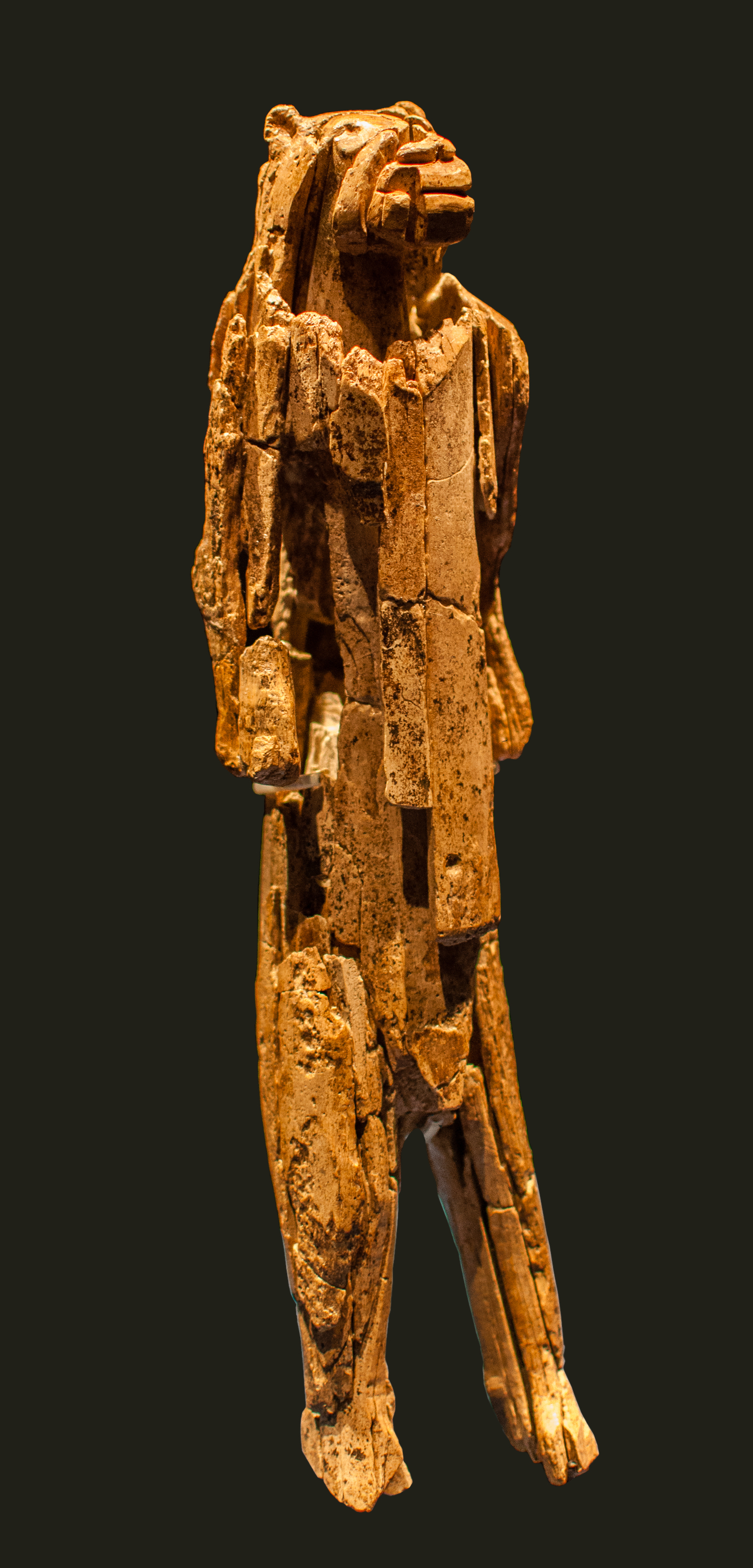
Dolní Věstonice (often without diacritics as Dolni Vestonice) is an Upper Paleolithic archaeological site near the village of Dolní Věstonice in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic, at the base of Děvín, Mount Děvín, . It dates to approximately 26,000 BP, as supported by radiocarbon dating. The site is unique in that it has been a particularly abundant source of prehistoric artifacts (especially art) dating from the Gravettian period, which spanned roughly from 27,000 to 20,000 BC. In addition to the abundance of art, this site also includes carved representations of men, women, and animals, along with personal ornaments, human burials and enigmatic engravings. Introduction Soon after excavations of this site began in 1924, the significance of Dolní Věstonice became apparent. Thousands of ceramic artifacts, many of which depicted animals, were found associated with the site. The animals molded in the clay include lions, rhinoceroses, and mammoths. These fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Paleolithic
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture. Anatomically modern humans (i.e. ''Homo sapiens'') are believed to have emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago, it has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of Artefact (archaeology), artefacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to early human migrations, expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which contributed to the Neanderthal extinction, ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tally Mark
Tally marks, also called hash marks, are a unary numeral system ( arguably). They are a form of numeral used for counting. They are most useful in counting or tallying ongoing results, such as the score in a game or sport, as no intermediate results need to be erased or discarded. However, because of the length of large numbers, tallies are not commonly used for static text. Notched sticks, known as tally sticks, were also historically used for this purpose. Early history Counting aids other than body parts appear in the Upper Paleolithic. The oldest tally sticks date to between 35,000 and 25,000 years ago, in the form of notched bones found in the context of the European Aurignacian to Gravettian and in Africa's Late Stone Age. The so-called ''Wolf bone'' is a prehistoric artifact discovered in 1937 in Czechoslovakia during excavations at Vestonice, Moravia, led by Karl Absolon. Dated to the Aurignacian, approximately 30,000 years ago, the bone is marked with 55 marks wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. ''Cohort'' LEB is the mean length of life of a birth cohort (all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. ''Period'' LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year. National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of ''period'' LEB. In the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, human LEB was 26 years; in 2010, world LEB was 67.2 years. In recent years, LEB in Eswatini (formerly Swaziland) is 49, while LEB in Japan is 83. The combination of high infant mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as "shamanic" have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. In the 20th century, non-Indigenous Westerners involved in countercultural movements, such as hippies and the New Age created modern magicoreligious practices influenced by their ideas of various Indigenous religions, creating what has been ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KM - Altsteinzeit Frauenköpfchen
KM, Km, or km may stand for: Postnominal *Knight of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta, a chivalric order Businesses *KM Group, a multimedia group based in Kent *Kennis Music, a record label * Kia Motors, an automobile manufacturer * Kmart (former stock symbol "KM") * Konica Minolta, a manufacturer of electronics * Air Malta (IATA code KM) Organisations * Knight of Malta (other), a Christian order of knighthood *Kriegsmarine, name of the German navy during the Nazi regime * Koninklijke Marine, Dutch name of the Royal Netherlands Navy Places *Kamenz (district), Germany (license plate indication) * Messenia, Greece (license plate indication) * KM Junction, West Virginia *Comoros, country (ISO 3166-1 code KM) *Kysucké Nové Mesto, town in Slovakia (district code KM) * Kosovska Mitrovica, town in Serbia *Kosovo and Metohija, an autonomous province in Serbia (ISO 3166-2 code RS-KM) Science, technology, and mathematics *Kilometre (km), SI unit of distance *.km, Internet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Kansas
The University of Kansas (KU) is a public research university with its main campus in Lawrence, Kansas, United States, and several satellite campuses, research and educational centers, medical centers, and classes across the state of Kansas. Two branch campuses are in the Kansas City metropolitan area on the Kansas side: the university's medical school and hospital in Kansas City, Kansas, the Edwards Campus in Overland Park. There are also educational and research sites in Garden City, Hays, Leavenworth, Parsons, and Topeka, an agricultural education center in rural north Douglas County, and branches of the medical school in Salina and Wichita. The university is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Founded March 21, 1865, the university was opened in 1866, under a charter granted by the Kansas State Legislature in 1864 and legislation passed in 1863 under the State Cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggsbach
Aggsbach is a small wine-growing town in the Krems-Land district of Lower Austria, Austria. As of 2001, it has a population of 714 and an area of 13.72 km.² Aggsbach was first mentioned in an 1148 document calling it "Accusabah". Population Venus von Willendorf Today Aggsbach is most famous for being the place where the Venus of Willendorf was found, in the Willendorf in der Wachau, Willendorf hamlet. The actual female fertility figure is located in the Naturhistorisches Museum in Vienna, while a life size reproduction is located in a field in Willendorf. The other hamlets are Aggsbach Markt (the main town), Groisbach, and Köfering. References Cities and towns in Krems-Land District Venus of Willendorf {{LowerAustria-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Of Dolní Věstonice
The Venus of Dolní Věstonice ( cs, Věstonická venuše) is a Venus figurine, a ceramic statuette of a nude female figure dated to 29,000–25,000 BCE (Gravettian industry). It was found at the Paleolithic site Dolní Věstonice in the Moravian basin south of Brno, in the base of Děvín Mountain in what is today the Czech Republic. This figurine and a few others from locations nearby are the oldest known ceramic articles in the world. Description It has a height of , and a width of at its widest point and is made of a clay body fired at a relatively low temperature (500–800 °C). The statuette follows the general morphology of the other Venus figurines: exceptionally large breasts, belly and hips, perhaps symbols of fertility, relatively small head and little detail on the rest of the body. A feature which no longer remains a part of the sculpture, is the fact that it is thought to have been originally ornamented with four feathers. This is evidenced by the four small h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic (paranormal)
Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is an ancient praxis rooted in sacred rituals, spiritual divinations, and/or cultural lineage—with an intention to invoke, manipulate, or otherwise manifest supernatural forces, beings, or entities in the natural, incarnate world. It is a categorical yet often ambiguous term which has been used to refer to a wide variety of beliefs and practices, frequently considered separate from both religion and science. Although connotations have varied from positive to negative at times throughout history, magic continues to have an important religious and medicinal role in many cultures today. Within Western culture, magic has been linked to ideas of the Other, foreignness, and primitivism; indicating that it is "a powerful marker of cultural difference" and likewise, a non-modern phenomenon. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth century, Western intellectuals perceived the practice of magic to be a sign of a primitive mentality and also commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |