|
Dollyphyton
''Dollyphyton'' is a genus of fossil with controversial interpretation from the Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian, 460 million years old) Douglas Lake Member of the Lenoir Limestone from Douglas Dam Tennessee. The generic name honors Dolly Parton whose Dollywood resort is nearby. The epithet honors Art Boucot. Description ''Dollyphyton'' is considered as a fossil peat moss by Gregory Retallack. Its leaves are wide and have lateral teeth. Its capsule is terminal on a short pseudopodium. Interpretation Unlike most peat mosses ''Dollyphyton'' has broad leaves like those of the living peat moss Flatbergium, considered basal to Sphagnales. Interpretation of this fossil as a peat moss ''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store wa ... has been doubted in some quarters but accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dollyphyton Boucotii
''Dollyphyton'' is a genus of fossil with controversial interpretation from the Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian, 460 million years old) Douglas Lake Member of the Lenoir Limestone from Douglas Dam Tennessee. The generic name honors Dolly Parton whose Dollywood resort is nearby. The epithet honors Art Boucot. Description ''Dollyphyton'' is considered as a fossil peat moss by Gregory Retallack. Its leaves are wide and have lateral teeth. Its capsule is terminal on a short pseudopodium. Interpretation Unlike most peat mosses ''Dollyphyton'' has broad leaves like those of the living peat moss Flatbergium, considered basal to Sphagnales. Interpretation of this fossil as a peat moss ''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store wa ... has been doubted in some quarters but accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
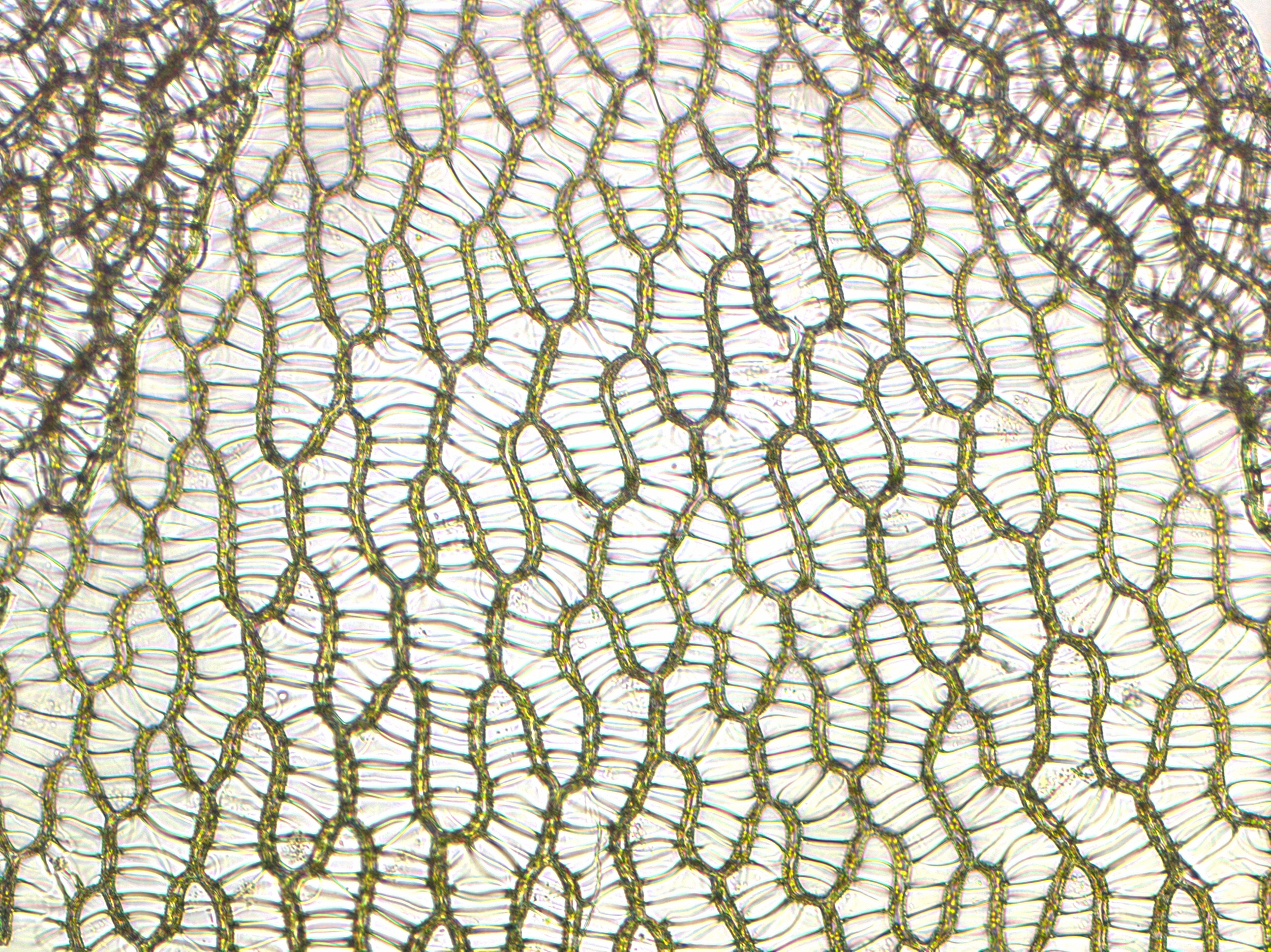
Dollyphyton Boucotii SEM
''Dollyphyton'' is a genus of fossil with controversial interpretation from the Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian, 460 million years old) Douglas Lake Member of the Lenoir Limestone from Douglas Dam Tennessee. The generic name honors Dolly Parton whose Dollywood resort is nearby. The epithet honors Art Boucot. Description ''Dollyphyton'' is considered as a fossil peat moss by Gregory Retallack. Its leaves are wide and have lateral teeth. Its capsule is terminal on a short pseudopodium. Interpretation Unlike most peat mosses ''Dollyphyton'' has broad leaves like those of the living peat moss Flatbergium, considered basal to Sphagnales. Interpretation of this fossil as a peat moss ''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store wa ... has been doubted in some quarters but accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dollyphyton Boucotii Leaf
''Dollyphyton'' is a genus of fossil with controversial interpretation from the Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian, 460 million years old) Douglas Lake Member of the Lenoir Limestone from Douglas Dam Tennessee. The generic name honors Dolly Parton whose Dollywood resort is nearby. The epithet honors Art Boucot. Description ''Dollyphyton'' is considered as a fossil peat moss by Gregory Retallack. Its leaves are wide and have lateral teeth. Its capsule is terminal on a short pseudopodium. Interpretation Unlike most peat mosses ''Dollyphyton'' has broad leaves like those of the living peat moss Flatbergium, considered basal to Sphagnales. Interpretation of this fossil as a peat moss ''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store wa ... has been doubted in some quarters but accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dollyphyton Boucotii Sketch
''Dollyphyton'' is a genus of fossil with controversial interpretation from the Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian, 460 million years old) Douglas Lake Member of the Lenoir Limestone from Douglas Dam Tennessee. The generic name honors Dolly Parton whose Dollywood resort is nearby. The epithet honors Art Boucot. Description ''Dollyphyton'' is considered as a fossil peat moss by Gregory Retallack. Its leaves are wide and have lateral teeth. Its capsule is terminal on a short pseudopodium. Interpretation Unlike most peat mosses ''Dollyphyton'' has broad leaves like those of the living peat moss Flatbergium, considered basal to Sphagnales. Interpretation of this fossil as a peat moss ''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store wa ... has been doubted in some quarters but accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Lake Member
The Douglas Lake Member is a geologic unit of member rank of the Lenoir Limestone that overlies the Mascot Dolomite and underlies typical nodular member of the Lenoir Limestone in Douglas Lake, Tennessee, region. It fills depressions that are part of a regional unconformity at the base of Middle Ordovician strata, locally the Lenoir Limestone, that separates them from the underlying Lower Ordovician strata, locally the Knox Group.U.S. Geological Survey, 2020Geologic Unit: Douglas Lake Walker, K.R., Steinhauff, D.M., and Roberson, K.E., 1992. ''Uppermost Knox Group, the Knox unconformity, the Middle Ordovician transition from shallow shelf to deeper basin at Dandridge, Tennessee'', In Driese, S.G., and others, eds., ''Paleosols, paleoweathering surfaces, and sequence boundaries'', ''University of Tennessee, Department of Geological Scienc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatbergiaceae
''Flatbergium'' is a genus of 2 accepted species. ''Flatbergium sericeum'' and ''Flatbergium novo-caledoniae'', originally described as species of ''Sphagnum'', are now considered part of a separate genus on the basis of genetic differences. The Ordovician The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. T ... fossil '' Dollyphyton'' has also been assigned to this family. References External links Sphagnales Monotypic moss genera {{bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatbergium
''Flatbergium'' is a genus of 2 accepted species. ''Flatbergium sericeum'' and ''Flatbergium novo-caledoniae'', originally described as species of ''Sphagnum'', are now considered part of a separate genus on the basis of genetic differences. The Ordovician The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. T ... fossil '' Dollyphyton'' has also been assigned to this family. References External links Sphagnales Monotypic moss genera {{bryophyte-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Boucot
Arthur James Boucot (May 26, 1924, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to 10 April 2017, Denver, Colorado) was an American paleontologist, biostratigrapher, and taphonomist who was an expert in Silurian and Devonian marine invertebrates, particularly brachiopods. Early life Boucot was born in Philadelphia, and raised in an academic family with early exposure to geology and paleontology. He began his studies at the University of Pennsylvania but dropped out in his freshman year to work at RCA. He was drafted into the United States Army during WWII, but enlisted in the United States Army Air Forces as a navigator with the Eighth Air Force on B-24 Bombers, and was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross. Education and academic career Boucot obtained his geology degrees from Harvard University with a B.S. in 1948, an MS in 1949, and a PhD in 1953. Although he began his geological studies focused on mineralogy and petrography, his interest in paleontology was sparked at Harvard by assis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician Plants
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya. The Ordovician, named after the Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official period of the Paleozoic Era by the International Geological Congress. Life continued to flourish during the Ordovician as it did in the earlier Cambrian Perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Record Of Plants
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Tennessee
Paleontology in Tennessee refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Tennessee. During the early part of the Paleozoic era, Tennessee was covered by a warm, shallow sea. This sea was home to brachiopods, bryozoans, cephalopods, corals, and trilobites. Tennessee is one of the best sources of Early Devonian fossils in North America. During the mid-to-late Carboniferous, the state became a swampy environment, home to a rich variety of plants including ferns and scale trees. A gap in the local rock record spans from the Permian through the Jurassic. During the Cretaceous, the western part of the state was submerged by seawater. The local waters were home to more fossil gastropods than are known from anywhere else in the world. Mosasaurs and sea turtles also inhabited these waters. On land the state was home to dinosaurs. Western Tennessee was still under the sea during the early part of the Cenozoic. Terrestrial portions of the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peat Moss
''Sphagnum'' is a genus of approximately 380 accepted species of mosses, commonly known as sphagnum moss, peat moss, also bog moss and quacker moss (although that term is also sometimes used for peat). Accumulations of ''Sphagnum'' can store water, since both living and dead plants can hold large quantities of water inside their cells; plants may hold 16 to 26 times as much water as their dry weight, depending on the species.Bold, H. C. 1967. Morphology of Plants. second ed. Harper and Row, New York. p. 225-229. The empty cells help retain water in drier conditions. As sphagnum moss grows, it can slowly spread into drier conditions, forming larger mires, both raised bogs and blanket bogs. Thus, sphagnum can influence the composition of such habitats, with some describing sphagnum as 'habitat manipulators'. These peat accumulations then provide habitat for a wide array of peatland plants, including sedges and ericaceous shrubs, as well as orchids and carnivorous plants.Keddy, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |