|
Doas
doas (“dedicated openbsd application subexecutor”) is a program to execute commands as another user. The system administrator can configure it to give specified users privileges to execute specified commands. It is free and open-source under the ISC license and available in Unix and Unix-like operating systems. doas was developed by Ted Unangst for OpenBSD as a simpler and safer sudo replacement. Unangst himself had issues with the default ''sudo'' config, which was his motivation to develop doas. doas was originally developed by Ted Unangst and was released with OpenBSD 5.8 in October 2015 replacing sudo. However, OpenBSD still provides sudo as a package. Configuration Definition of privileges should be written in the configuration file, /etc/doas.conf. The syntax used in the configuration file is inspired by the packet filter configuration file. Examples Allow user1 to execute procmap as root without password: permit nopass user1 as root cmd /usr/sbin/procmap Allow memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenBSD
OpenBSD is a security-focused operating system, security-focused, free and open-source, Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Theo de Raadt created OpenBSD in 1995 by fork (software development), forking NetBSD 1.0. According to the website, the OpenBSD project emphasizes "portability, standardization, correctness, proactive security and integrated cryptography." The OpenBSD project maintains software portability, portable versions of many subsystems as package manager, packages for other operating systems. Because of the project's preferred BSD license, many components are reused in proprietary and corporate-sponsored software projects. The firewall (computing), firewall code in Apple Inc., Apple's macOS is based on OpenBSD's PF (firewall), PF firewall code, Android (operating system), Android's Bionic (software), Bionic C standard library is based on OpenBSD code, LLVM uses OpenBSD's regular expression library, and Windows 10 uses OpenSSH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudo
sudo ( or ) is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that enables users to run programs with the security privileges of another user, by default the superuser. It originally stood for "superuser do", as that was all it did, and it is its most common usage; however, the official Sudo project page lists it as "su 'do'". The current Linux manual pages for su define it as "substitute user", making the correct meaning of sudo "substitute user, do", because sudo can run a command as other users as well. Unlike the similar command '' su'', users must, by default, supply their own password for authentication, rather than the password of the target user. After authentication, and if the configuration file (typically /etc/sudoers) permits the user access, the system invokes the requested command. The configuration file offers detailed access permissions, including enabling commands only from the invoking terminal; requiring a password per user or group; requiring re-entry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illumos
Illumos (stylized as illumos) is a partly free and open-source Unix operating system. It is based on OpenSolaris, which was based on System V Release 4 (SVR4) and the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Illumos comprises a kernel, device drivers, system libraries, and utility software for system administration. This core is now the base for many different open-sourced illumos distributions, in a similar way in which the Linux kernel is used in different Linux distributions. The maintainers write ''illumos'' in lowercase since some computer fonts do not clearly distinguish a lowercase ''L'' from an uppercase ''i'': ''Il'' (see homoglyph). The project name is a combination of words ''illuminare'' from Latin for ''to light'' and ''OS'' for ''Operating System''. Overview Illumos was announced via webinar on Thursday, 3 August 2010, as a community effort of some core Solaris engineers to create a truly open source Solaris by swapping closed source bits of OpenSolaris with o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NixOS
NixOS is a Linux distribution built on top of the Nix package manager. It uses declarative configuration and allows reliable system upgrades. Several official package "channels" are offered, including the current Stable release and the Unstable release which follows the latest development. NixOS has tools dedicated to DevOps and deployment tasks. History In 2003, Eelco Dolstra started NixOS as a research project. In 2015, the Stichting NixOS was founded aiming to support projects like NixOS that implement the purely functional deployment model. Versions NixOS publishes releases on a twice a year schedule. This used to happen around March and September but, starting with 21.05, NixOS targets May and November instead. Each version number has the format "YY.MM", for instance "20.03" was the version released in March 2020. Each version of NixOS has a name, such as "Markhor" for the release 20.03. Features Declarative configuration model In NixOS, the entire operating syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabola GNU/Linux-libre
Parabola GNU/Linux-libre is an operating system for the i686, x86-64 and ARMv7 architectures. It is based on many of the packages from Arch Linux and Arch Linux ARM, but distinguishes from the former by offering only free software. It includes the GNU operating system components common to many Linux distributions and the Linux-libre kernel instead of the generic Linux kernel. Parabola is listed by the Free Software Foundation as a completely free operating system, true to their Free System Distribution Guidelines. Parabola uses a rolling release model like Arch, such that a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest software. Development focuses on system simplicity, community involvement and use of the latest free software packages. History Parabola was originally proposed by members of the gNewSense IRC channel in 2009. Members of different Arch Linux communities, especially Spanish-speaking members, started the development and maintenance of the proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
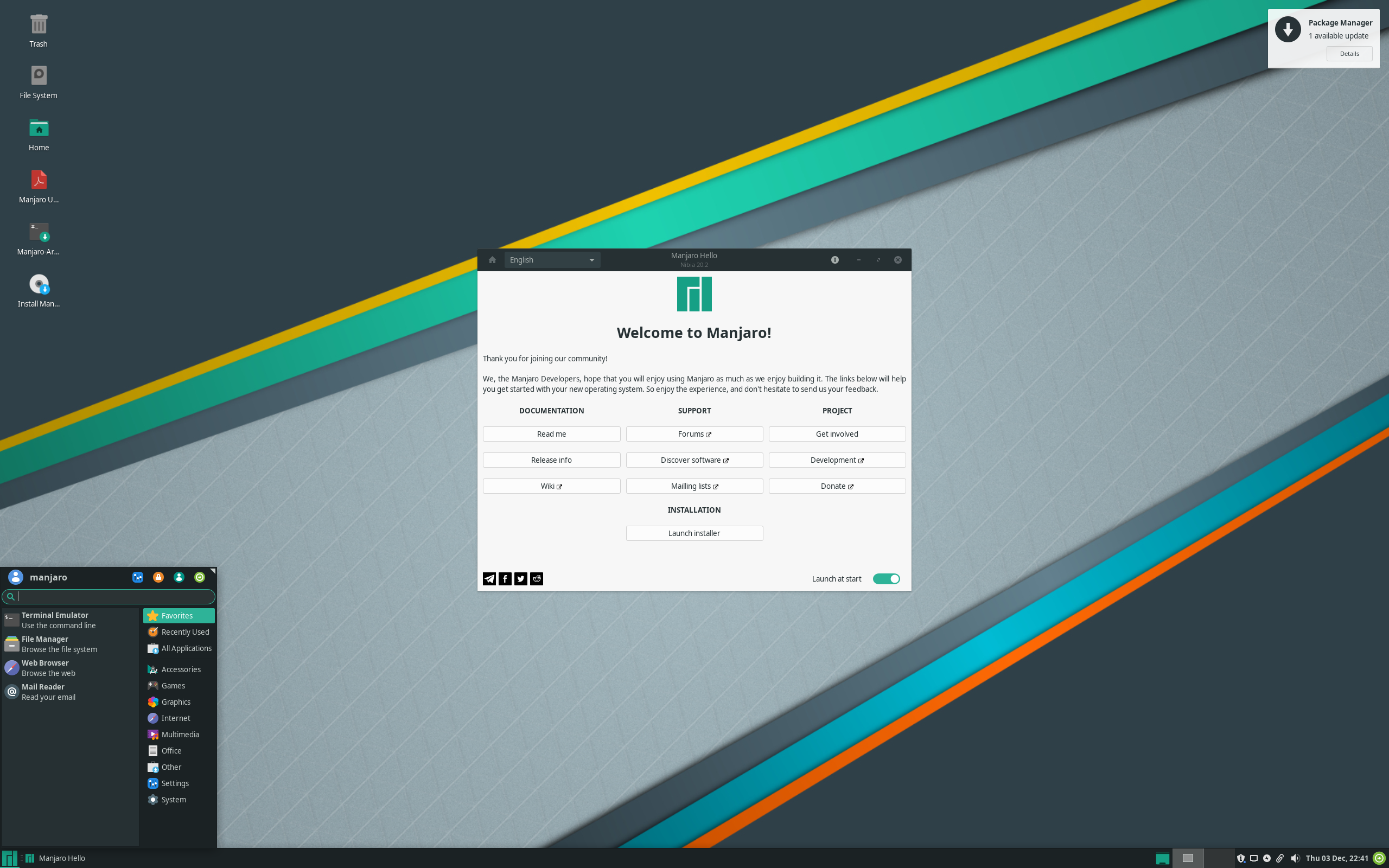
Manjaro
Manjaro ( ) is a free and open-source Linux distribution based on the Arch Linux operating system that has a focus on user-friendliness and accessibility. It uses a rolling release update model and Pacman as its package manager. It is developed mainly in Austria, France and Germany. History Manjaro was first released on July 10, 2011. By mid 2013, Manjaro was in the beta stage, though key elements of the final system had all been implemented such as: a GUI installer (then an Antergos installer fork); a package manager (Pacman) with its choice of frontends; Pamac ( GTK) for Xfce desktop and Octopi ( Qt) for its Openbox edition; MHWD (Manjaro Hardware Detection, for detection of free & proprietary video drivers); and Manjaro Settings Manager (for system-wide settings, user management, and graphics driver installation and management). GNOME Shell support was dropped with the release of version 0.8.3 in 2012. However, efforts within Arch Linux made it possible to restart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre
Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre is a Linux distribution for the i686 and x86-64 architectures. It is based on Arch Linux snapshots and Debian development. It includes the GNU operating system components and the Linux-libre kernel instead of the generic Linux kernel. Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre is listed by the Free Software Foundation as a completely free operating system, true to their Free System Distribution Guidelines. History Hyperbola was born at the 17th annual ''Fórum Internacional Software Livre'' (Porto Alegre, Brazil). On 5 August 2017, support for systemd was dropped in favor of OpenRC as its default init system to support the Init Freedom Campaign begun by Devuan. On 6 December 2018, Hyperbola was the first Brazilian distribution recognized as a completely free project by GNU, making it part of the FSF list of free distributions. On 23 September 2019, Hyperbola announced its first release with the implementation of Xenocara as its default display server for the X Wind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Guix
GNU Guix () is a functional cross-platform package manager and a tool to instantiate and manage Unix-like operating systems, based on the Nix package manager. Configuration and package recipes are written in Guile Scheme. GNU Guix is the default package manager of the GNU Guix System distribution. Differing from traditional package managers, Guix (like Nix) utilizes a purely functional deployment model where software is installed into unique directories generated through cryptographic hashes. All dependencies for each software are included within each hash. This solves the problem of dependency hell, allows multiple versions of the same software to coexist and makes packages portable and reproducible. Performing scientific computations in a Guix setup has been proposed as a promising response to the replication crisis. The development of GNU Guix is intertwined with the GNU Guix System, an installable operating system distribution using the Linux-libre kernel and GNU S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentoo Linux
Gentoo Linux (pronounced ) is a Linux distribution built using the Portage package management system. Unlike a binary software distribution, the source code is compiled locally according to the user's preferences and is often optimized for the specific type of computer. Precompiled binaries are available for some larger packages or those with no available source code. Gentoo Linux was named after the gentoo penguin, the fastest swimming species of penguin. The name was chosen to reflect the potential speed improvements of machine-specific optimization, which is a major feature of Gentoo. Gentoo package management is designed to be modular, portable, easy to maintain, and flexible. Gentoo describes itself as a meta-distribution because of its adaptability, in that the majority of users have configurations and sets of installed programs which are unique to the system and the applications they use. History Gentoo Linux was initially created by Daniel Robbins as the ''Enoch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fedora Linux
Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project. Fedora contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open-source technologies. Fedora is the upstream (software development), upstream source for Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Since the release of Fedora 35, six different editions are made available tailored to personal computer, server (computing), server, cloud computing, Container (computing), container and Internet of Things installations. A new version of Fedora Linux is released every six months. , Fedora Linux has an estimated 1.2 million users, including Linus Torvalds (), creator of the Linux kernel. Features Fedora has a reputation for focusing on innovation, integrating new technologies early on and working closely with Upstream (software development), upstream Linux communities. Making changes upstream instead of specifically for Fedora Linux ensures that the changes are available t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRUX
Crux () is a constellation of the southern sky that is centred on four bright stars in a cross-shaped asterism commonly known as the Southern Cross. It lies on the southern end of the Milky Way's visible band. The name ''Crux'' is Latin for cross. Even though it is the smallest of all 88 modern constellations, Crux is among the most easily distinguished as its four main stars each have an apparent visual magnitude brighter than +2.8. It has attained a high level of cultural significance in many Southern Hemisphere states and nations. Blue-white α Crucis (Acrux) is the most southerly member of the constellation and, at magnitude 0.8, the brightest. The three other stars of the cross appear clockwise and in order of lessening magnitude: β Crucis (Mimosa), γ Crucis (Gacrux), and δ Crucis (Imai). ε Crucis (Ginan) also lies within the cross asterism. Many of these brighter stars are members of the Scorpius–Centaurus association, a large but loose group of hot blue-whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Linux
Arch Linux () is an independently developed, x86-64 general-purpose Linux distribution that strives to provide the latest stable versions of most software by following a rolling-release model. The default installation is a minimal base system, configured by the user to only add what is purposely required. Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update software packages. Arch Linux uses a rolling release model, meaning there are no "major releases" of completely new versions of the system; a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest Arch software; the installation images released every month by the Arch team are simply up-to-date snapshots of the main system components. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation, consisting of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another minimalist distribution, Judd Vinet started the Arch Linux project in March 2002. The name w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |