|
Djedefra
Djedefre (also known as Djedefra and Radjedef – Modern Greek: ) was an ancient Egyptian king (pharaoh) of the 4th Dynasty during the Old Kingdom. He is well known by the Hellenized form of his name Rhatoisēs (Ῥατοίσης) by Manetho. Djedefre was the son and immediate throne successor of Khufu, the builder of the Great Pyramid of Giza; his mother is not known for certain. He is the king who introduced the royal title ''Sa-Rê'' (meaning “Son of Ra”) and the first to connect his cartouche name with the sun god Ra. Family Djedefre married his brother Kawab's widow, Hetepheres II, who was sister to both of them, and who perhaps married a third brother of theirs, Khafre, after Djedefre's death.Dodson & Hilton, p.55 Another queen, Khentetenka is known from statue fragments in the Abu Rowash mortuary temple. Known children of Djedefre are: * Hornit (“Eldest King's Son of His Body”) known from a statue depicting him and his wife.Dodson & Hilton, p.58 * Baka (“ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djedefra Wearing The Crown Of Lower Egypt-E 11167-IMG 9702-gradient
Djedefre (also known as Djedefra and Radjedef – Modern Greek: ) was an ancient Egyptian king (pharaoh) of the 4th Dynasty during the Old Kingdom. He is well known by the Hellenized form of his name Rhatoisēs (Ῥατοίσης) by Manetho. Djedefre was the son and immediate throne successor of Khufu, the builder of the Great Pyramid of Giza; his mother is not known for certain. He is the king who introduced the royal title ''Sa-Rê'' (meaning “Son of Ra”) and the first to connect his cartouche name with the sun god Ra. Family Djedefre married his brother Kawab's widow, Hetepheres II, who was sister to both of them, and who perhaps married a third brother of theirs, Khafre, after Djedefre's death.Dodson & Hilton, p.55 Another queen, Khentetenka is known from statue fragments in the Abu Rowash mortuary temple. Known children of Djedefre are: * Hornit (“Eldest King's Son of His Body”) known from a statue depicting him and his wife.Dodson & Hilton, p.58 * Baka (“Eld ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khufu
Khufu or Cheops was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom period ( 26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his father Sneferu as king. He is generally accepted as having commissioned the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, but many other aspects of his reign are poorly documented. The only completely preserved portrait of the king is a three-inch high ivory figurine found in a temple ruin of a later period at Abydos in 1903. All other reliefs and statues were found in fragments, and many buildings of Khufu are lost. Everything known about Khufu comes from inscriptions in his necropolis at Giza and later documents. For example, Khufu is the main character noted in the Westcar Papyrus from the 13th dynasty. Most documents that mention king Khufu were written by ancient Egyptian and Greek historians around 300 BC. Khufu's obituary is presented there in a conflicting wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara Tablet
The Saqqara Tablet, now in the Egyptian Museum, is an ancient stone engraving surviving from the Ramesside Period of Egypt which features a list of pharaohs. It was found in 1861 in Saqqara, in the tomb of Tjuneroy (or Tjenry), an official ("chief lector priest" and "Overseer of Works on All Royal Monuments") of the pharaoh Ramesses II. The inscription lists fifty-eight kings, from Anedjib and Qa'a ( First Dynasty) to Ramesses II (Nineteenth Dynasty), in reverse chronological order, omitting "rulers from the Second Intermediate Period, the Hyksos, and those rulers... who had been close to the heretic Akhenaten". The names (each surrounded by a border known as a cartouche), of which only forty-seven survive, are badly damaged. As with other Egyptian king lists, the Saqqara Tablet omits certain kings and entire dynasties. The list counts backward from Ramesses II to the mid-point of the First Dynasty, except for the Eleventh and Twelfth Dynasties, which are reversed. A well known p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
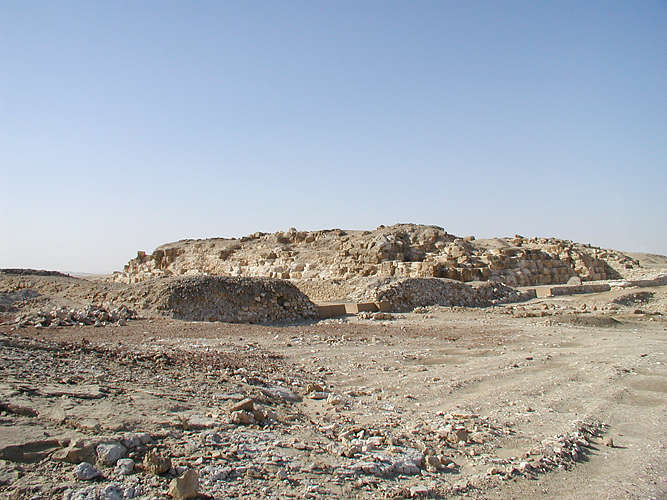
Abu Rawash
Abu Rawash (also spelled ''Abu Roach'', Abu Roash; ar, ابو رواش , , , "flesh of sensual pleasures"), north of Giza, is the site of Egypt's most northerly pyramid, also known as the lost pyramid – the mostly ruined Pyramid of Djedefre, the son and successor of Khufu. Originally, it was thought that this pyramid had never been completed, but the current archaeological consensus is that not only was it completed, but that it was built about the same size as the Pyramid of Menkaure – the third largest of the Giza pyramids. It is the location of the northernmost pyramid in Egypt (known as Lepsius Number One), the pyramid of Djedefre (also known as Radjedef) and around fifty mastabas (located one and a half kilometres from Djedefre’s pyramid). Location Its location adjacent to a major crossroads made it an easy source of stone. Quarrying, which began in Roman times, has left little apart from a few courses of stone superimposed upon the natural hillock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Pyramid Of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the biggest Egyptian pyramid and the tomb of Fourth Dynasty pharaoh Khufu. Built in the early 26th century BC during a period of around 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only one to remain largely intact. As part of the Giza pyramid complex, it borders present-day Giza in Greater Cairo, Egypt. Initially standing at , the Great Pyramid was the tallest man-made structure in the world for more than 3,800 years. Over time, most of the smooth white limestone casing was removed, which lowered the pyramid's height to the present . What is seen today is the underlying core structure. The base was measured to be about square, giving a volume of roughly , which includes an internal hillock. The dimensions of the pyramid were high, a base length of , with a seked of palms (a slope of 51°50'40"). The Great Pyramid was built by quarrying an estimated 2.3 million large blocks weighing 6 million tonnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miroslav Verner
Miroslav Verner (born October 31, 1941 in Brno) is a Czech egyptologist, who specializes in the history and archaeology of Ancient Egypt of the Old Kingdom and especially of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt. Biography Verner was the director of the Czechoslovak and later Czech Institute of Egyptology at the Faculty of Arts, Charles University in Prague for twenty-five years, and led the Czech excavations at Abusir. He has also been associated with the Universities of Vienna and Hamburg as well as the Charles University in Prague and the American University in Cairo. Verner has been active in archaeological work since 1964, and he has been excavating at Abusir since 1976. In 1998, the tomb of Iufaa Iufaa was an Egyptian priest and administer of palaces who lived around 500 BC. His mummy was discovered in an unmolested tomb by Czech archaeologists under the direction of Ladislav Bareš and Miroslav Verner in February 1998. The discovery of an ..., an Egyptian priest and administer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
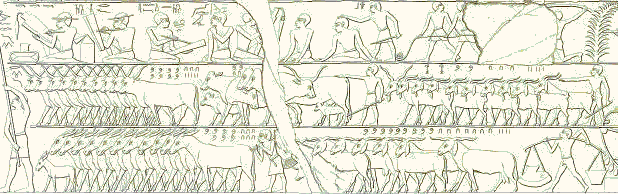
Cattle Count
In ancient Egypt, the cattle count was one of the two main means of evaluating the amount of taxes to be levied, the other one being the height of the annual inundation. A very important economic event, the cattle count was controlled by high officials, and was connected to several cultic feasts. In addition it served as a means of dating other events, with the entire year when it occurred being called "year of the Xth cattle count under the person of the king Y". The frequency of cattle counts varied through the history of ancient Egypt; in the Old Kingdom it was most likely biennial, i.e. occurring every two years, and became more frequent subsequently. Process and purpose To perform the cattle count, all chattel (including productive livestock such as cows and oxen, sheep, pigs, goats and donkeys) were rounded up and counted. Following the count, the percentage of chattel to be taxed by the state would be calculated. The cattle count was performed in every nome of Egypt. Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin King List
The Turin King List, also known as the Turin Royal Canon, is an ancient Egyptian hieratic papyrus thought to date from the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses II, now in the Museo Egizio (Egyptian Museum) in Turin. The papyrus is the most extensive list available of kings compiled by the ancient Egyptians, and is the basis for most chronology before the reign of Ramesses II. Creation and use The papyrus is believed to date from the reign of Ramesses II, during the middle of the New Kingdom, or the 19th Dynasty. The beginning and ending of the list are now lost; there is no introduction, and the list does not continue after the 19th Dynasty. The composition may thus have occurred at any subsequent time, from the reign of Ramesses II to as late as the 20th Dynasty. The papyrus lists the names of rulers, the lengths of reigns in years, with months and days for some kings. In some cases they are grouped together by family, which corresponds approximately to the dynasties of Manetho's book. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abydos KL 04-03 N22 , in southwestern France
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Abydos may refer to: *Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz *Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor * Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the ''Stargate'' science fiction universe *Abydos, Egypt, a city in ancient Egypt *Abydos Station, a pastoral lease and cattle station in Western Australia See also *Abidu, a village in Iran *Abidos, Pyrénées-Atlantiques Abidos (; oc, Avidòs) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in southwestern France. Geography Abidos is a Béarnais commune located some 13 km south-east of Orthez and 4 km north of Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahure
Sahure (also Sahura, meaning "He who is close to Re") was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the second ruler of the Fifth Dynasty (c. 2465 – c. 2325 BC). He reigned for about 13 years in the early 25th century BC during the Old Kingdom Period. Sahure's reign marks the political and cultural high point of the Fifth Dynasty. He was probably the son of his predecessor Userkaf with Queen NeferhetepesII, and was in turn succeeded by his son Neferirkare Kakai. During Sahure's rule, Egypt had important trade relations with the Levantine coast. Sahure launched several naval expeditions to modern-day Lebanon to procure cedar trees, slaves and exotic items. His reign may have witnessed the flourishing of the Egyptian navy, which included a high-seas fleet as well as specialized racing boats. Relying on this, Sahure ordered the earliest attested expedition to the land of Punt, which brought back large quantities of myrrh, malachite and electrum. Sahure is shown celebrating the success o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Userkaf
Userkaf (known in Ancient Greek as , ) was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Fifth Dynasty. He reigned for seven to eight years in the early 25th century BC, during the Old Kingdom period. He probably belonged to a branch of the Fourth Dynasty royal family, although his parentage is uncertain; he could have been the son of Khentkaus I. He had at least one daughter and very probably a son, Sahure, with his consort Neferhetepes. This son succeeded him as pharaoh. His reign heralded the ascendancy of the cult of Ra, who effectively became Egypt's state god during the Fifth Dynasty. Userkaf may have been a high-priest of Ra before ascending the throne, and built a sun temple, known as the '' Nekhenre'', between Abusir and Abu Gurab. In doing so, he instituted a tradition followed by his successors over a period of 80 years. The ''Nekhenre'' mainly functioned as a mortuary temple for the setting sun. Rites performed in the temple were primarily concerned with Ra's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neferhetepes
Neferhetepes (''nefer-hetep-es''; '' nfr-ḥtp- s,'' "Her Peace/Grace Is Beautiful") was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 4th Dynasty; a daughter of Pharaoh Djedefre who ruled between his father Khufu and his brother Khafre. Her mother was Hetepheres II. Biography The name of Neferhetepes is known to us from a statue fragment found in Abu Rawash where her father had a pyramid complex built. She had the titles ''King's Daughter of His Body'' and ''God's Wife''. Neferhetepes was also a Priestess of Hathor, mistress of the sycamore (''hemet-netjer-hut-hor nebet-nehet, ḥmt-nṯr- ḥwt-ḥr nb .t- nht''). She is the earliest attested priestess of Hathor. The title appears on the base of a statue from Abu Rawash. Neferhetepes has been proposed as the mother of pharaoh Shepseskaf by Ariel Kozloff, although for Vivienne Gae Callender there is no evidence in support of this hypothesis. Until recently, Egyptologists thought it as possible that Neferhetepes was identical to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |