|
Djahy
Djahi, Djahy or Tjahi (Egyptian: ''ḏhj'', ''ḏꜣhy'') was the Egyptian designation for southern Retjenu. It ran from approximately Ashkelon in Israel to Lebanon and inland as far as Galilee.Steindorff, George. ''When Egypt Ruled the East.'' p. 47. University of Chicago Press, 1942. It was described as the drainage basin of the Jordan River during the battles with Kadesh of the Eighteenth and Nineteenth Dynasties of Egypt. It was the scene of the Battle of Djahy between Rameses III and the Sea Peoples. See also *Names of the Levant Over recorded history, there have been many names of the Levant, a large area in the Middle East, or its constituent parts. These names have applied to a part or the whole of the Levant. On occasion, two or more of these names have been used at th ... References Geography of ancient Egypt Historical regions in Israel Canaan Geography of Phoenicia {{AncientEgypt-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
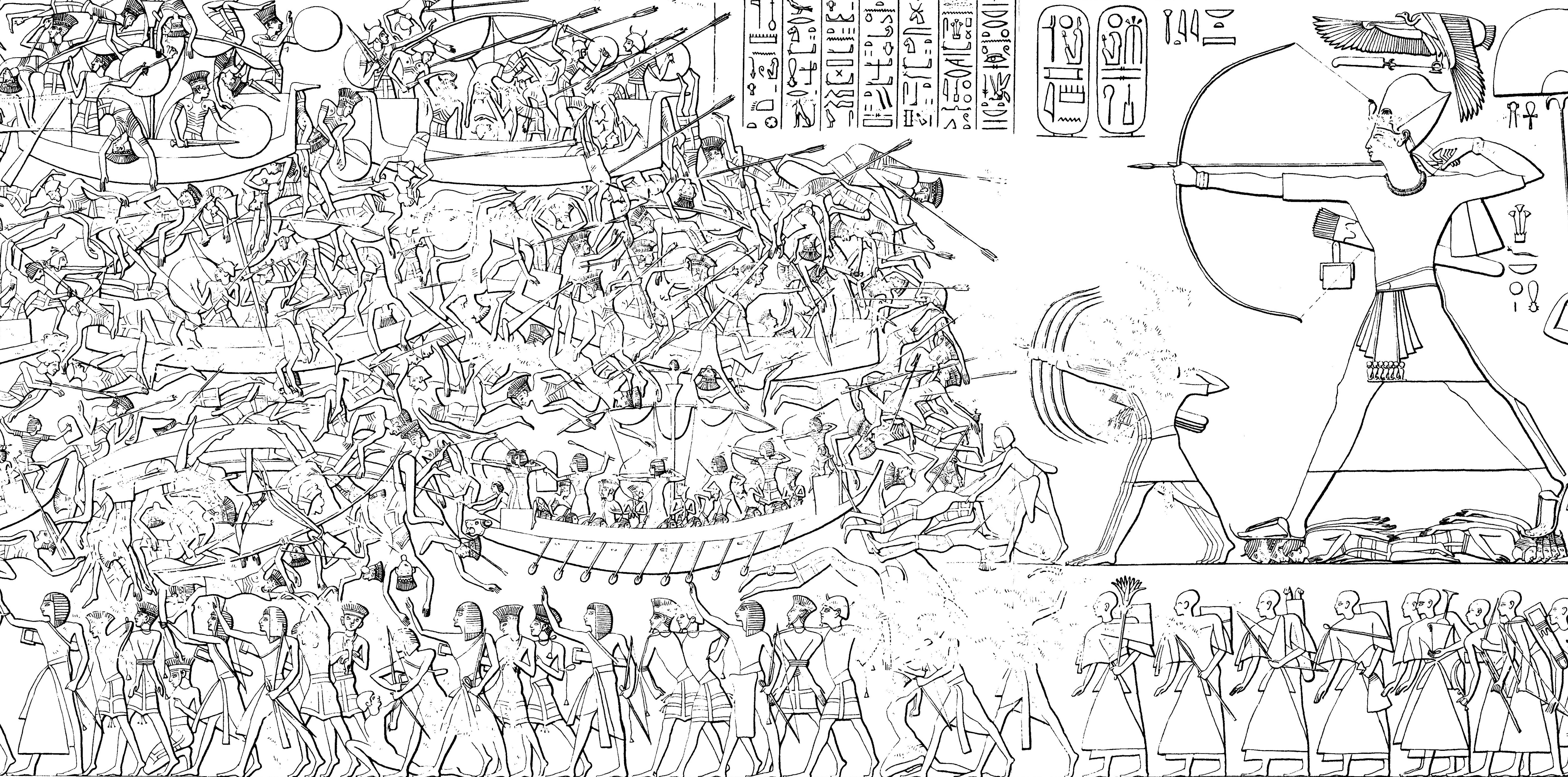
Battle Of Djahy
The Battle of Djahy was a major land battle between the forces of pharaoh Ramesses III and the Sea Peoples who intended to invade and conquer Egypt. The conflict occurred on the Egyptian Empire's easternmost frontier in Djahy or modern-day southern Lebanon, in the eighth year of pharaoh Ramesses III or about c. 1178 BC. In this battle the Egyptians, led by Ramesses III, defeated the Sea Peoples, who were attempting to invade Egypt by land and sea. Almost all that is known about the battle comes from the mortuary temple of Ramesses III in Medinet Habu. The description of the battle and prisoners is documented in detail on the temple's walls, which also contain the longest hieroglyphic inscription known. Temple reliefs feature many bound prisoners defeated in battle. Historical background The battle occurred during the Bronze Age collapse, a prolonged period of region-wide droughts, crop failures, depopulation, invasions, and collapse of urban centers. It is likely that the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retjenu
Retjenu ('' rṯnw; Reṯenu, Retenu''), was an ancient Egyptian name for Canaan and Syria. It covered the region from the Negev Desert north to the Orontes River. The borders of Retjenu shifted with time, but it generally consisted of three regions. The southernmost was Djahy, which had about the same boundaries as Canaan.Steindorff, George. ''When Egypt Ruled the East.'' p. 47. University of Chicago Press, 1942. Lebanon proper was located in the middle, between the Mediterranean and the Orontes River. North of Lebanon was designated Amurru, the land of the Amorites. Occurrences of the term Overall, numerous mentions of the Retjenu appear in Egyptian inscriptions. 12th Dynasty The earliest attestation of the name occurs in the Sebek-khu Stele, dated to the reign of Senusret III (reign: 1878–1839 BCE), recording the earliest known Egyptian military campaign in the Levant and their victory over the Retjenu: "His Majesty proceeded northward to overthrow the Asiatics. His Majesty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Kadesh
The Battle of Kadesh or Battle of Qadesh took place between the forces of the New Kingdom of Egypt under Ramesses II and the Hittite Empire under Muwatalli II at the city of Kadesh on the Orontes River, just upstream of Lake Homs near the modern Lebanon–Syria border. The battle is generally dated to 1274 BC from the Egyptian chronology, and is the earliest pitched battle in recorded history for which details of tactics and formations are known. It is believed to have been the largest chariot battle ever fought, involving between 5,000 and 6,000 chariots in total. As a result of discovery of multiple Kadesh inscriptions and the Egyptian–Hittite peace treaty, it is the best documented battle in all of ancient history. Background After expelling the Hyksos' 15th Dynasty around 1550 BC, the Egyptian New Kingdom rulers became more aggressive in reclaiming control of their state's borders. Thutmose I, Thutmose III and his son and coregent Amenhotep II fought battles from Meg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of The Levant
Over recorded history, there have been many names of the Levant, a large area in the Middle East, or its constituent parts. These names have applied to a part or the whole of the Levant. On occasion, two or more of these names have been used at the same time by different cultures or sects. As a natural result, some of the names of the Levant are highly politically charged. Perhaps the least politicized name is ''Levant'' itself, which simply means "where the sun rises" or "where the land rises out of the sea", a meaning attributed to the region's easterly location on the shore of the Mediterranean Sea. Antiquity Retjenu Ancient Egyptian texts (c. 14th century BC) called the entire coastal area along the Mediterranean Sea between modern Egypt and Turkey ''rṯnw'' (conventionally '' Reṯenu''). In the Amarna letters, written in Akkadian cuneiform, Reṯenu is subdivided into five regions: * ''kꜣnꜥnꜥ'' (''Kanana'') or Canaan proper (Idumea, Judea, Samaria); **''pꜣ-k� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineteenth Dynasty Of Egypt
The Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XIX), also known as the Ramessid dynasty, is classified as the second Dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1292 BC to 1189 BC. The 19th Dynasty and the 20th Dynasty furthermore together constitute an era known as the ''Ramesside period''. This Dynasty was founded by Vizier Ramesses I, whom Pharaoh Horemheb chose as his successor to the throne. History Background The warrior kings of the early 18th Dynasty had encountered only little resistance from neighbouring kingdoms, allowing them to expand their realm of influence easily, but the international situation had changed radically towards the end of the dynasty. The Hittites had gradually extended their influence into Syria and Canaan to become a major power in international politics, a power that both Seti I and his son Ramesses II would confront in the future. 19th Dynasty Seti and Ramesses II The New Kingdom of Egypt reached the zenith of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Regions In Israel
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Ancient Egypt
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Language
The Egyptian language or Ancient Egyptian ( ) is a dead language, dead Afroasiatic languages, Afro-Asiatic language that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large Text corpus, corpus of surviving texts which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of ancient Egyptian scripts, decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the List of languages by first written accounts, earliest written languages, first being recorded in the Egyptian hieroglyphs, hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4000 years. Its classical language, classical form is known as Middle Egyptian, the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt which remained the literary language of Egypt until the Egypt (Roman province), Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity the spoken language had evolved into Demotic (Egyptian), Dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
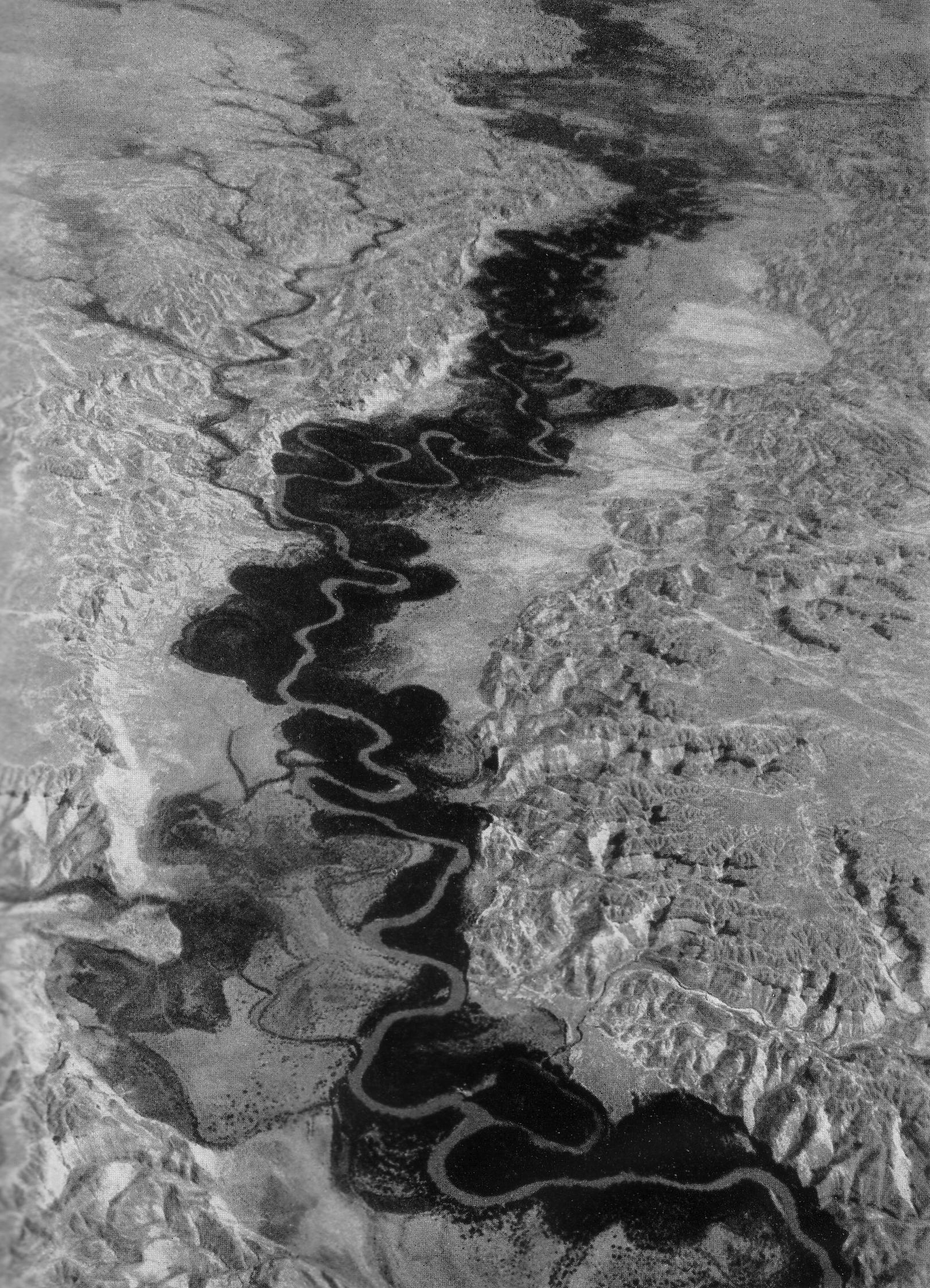
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan ( ar, نَهْر الْأُرْدُنّ, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn'', he, נְהַר הַיַּרְדֵּן, ''Nəhar hayYardēn''; syc, ܢܗܪܐ ܕܝܘܪܕܢܢ ''Nahrāʾ Yurdnan''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' ( ar, نهر الشريعة), is a river in the Middle East that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee (Hebrew: כנרת Kinneret, Arabic: Bohayrat Tabaraya, meaning Lake of Tiberias) and on to the Dead Sea. Jordan and the Golan Heights border the river to the east, while the West Bank and Israel lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank take their names from the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Geography The Jordan River has an upper course from its sources to the Sea of Galilee (via the Bethsaida Valley), and a lower course south of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_and_Tsakkaras_(painting).png)
_in_the_Battle_of_Khadesh.jpg)

.jpg)
