|
Diwata
''Anito'', also spelled ''anitu'', refers to ancestor spirits, nature spirits, and deities in the indigenous Philippine folk religions from the precolonial age to the present, although the term itself may have other meanings and associations depending on the Filipino ethnic group. It can also refer to carved humanoid figures, the ''taotao'', made of wood, stone, or ivory, that represent these spirits. ''Anito'' (a term predominantly used in Luzon) is also sometimes known as ''diwata'' in certain ethnic groups (especially among Visayans). ''Pag-anito'' refers to a séance, often accompanied by other rituals or celebrations, in which a shaman (Visayan: ''babaylan'', Tagalog: ''katalonan'') acts as a medium to communicate directly with the spirits. When a nature spirit or deity is specifically involved, the ritual is called ''pagdiwata''. The act of worship or a religious sacrifice to a spirit is also sometimes simply referred to as ''anito''. The belief in ''anito'' are so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anitos Of Northern Tribes (c
''Anito'', also spelled ''anitu'', refers to ancestor spirits, nature spirits, and deities in the indigenous Philippine folk religions from the History of the Philippines (900–1521), precolonial age to the present, although the term itself may have other meanings and associations depending on the Filipino ethnic group. It can also refer to carved humanoid figures, the ''taotao'', made of wood, stone, or ivory, that represent these spirits. ''Anito'' (a term predominantly used in Luzon) is also sometimes known as ''diwata'' in certain ethnic groups (especially among Visayans). ''Pag-anito'' refers to a séance, often accompanied by other rituals or celebrations, in which a Philippine shamans, shaman (Visayan languages, Visayan: ''babaylan'', Tagalog language, Tagalog: ''katalonan'') acts as a mediumship, medium to communicate directly with the spirits. When a nature spirit or deity is specifically involved, the ritual is called ''pagdiwata''. The act of worship or a religi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Philippine Folk Religions
Indigenous Philippine folk religions are the distinct native religions of various ethnic groups in the Philippines, where most follow belief systems in line with animism. Generally, these indigenous folk religions are referred to as Anito or Anitism or the more modern and less ethnocentric Dayawism.Almocera, Ruel A., (2005) Popular Filipino Spiritual Beliefs with a proposed Theological Response. in Doing Theology in the Philippines. Suk, John., Ed. Mandaluyong: OMF Literature Inc. Pp 78-98Maggay, Melba Padilla (1999). Filipino Religious Consciousness. Quezon City: Institute for Studies in Asian Church and Culture. Around 0.2% of the population of the Philippines were affiliated with the so-called "tribal religions", according to the 2010 national census. The profusion of different terms arises from the fact that these indigenous religions mostly flourished in the pre-colonial period before the Philippines had become a single nation. The various peoples of the Philippines spoke d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Philippine Folk Religions
Indigenous Philippine folk religions are the distinct native religions of various ethnic groups in the Philippines, where most follow belief systems in line with animism. Generally, these indigenous folk religions are referred to as Anito or Anitism or the more modern and less ethnocentric Dayawism.Almocera, Ruel A., (2005) Popular Filipino Spiritual Beliefs with a proposed Theological Response. in Doing Theology in the Philippines. Suk, John., Ed. Mandaluyong: OMF Literature Inc. Pp 78-98Maggay, Melba Padilla (1999). Filipino Religious Consciousness. Quezon City: Institute for Studies in Asian Church and Culture. Around 0.2% of the population of the Philippines were affiliated with the so-called "tribal religions", according to the 2010 national census. The profusion of different terms arises from the fact that these indigenous religions mostly flourished in the pre-colonial period before the Philippines had become a single nation. The various peoples of the Philippines spoke d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
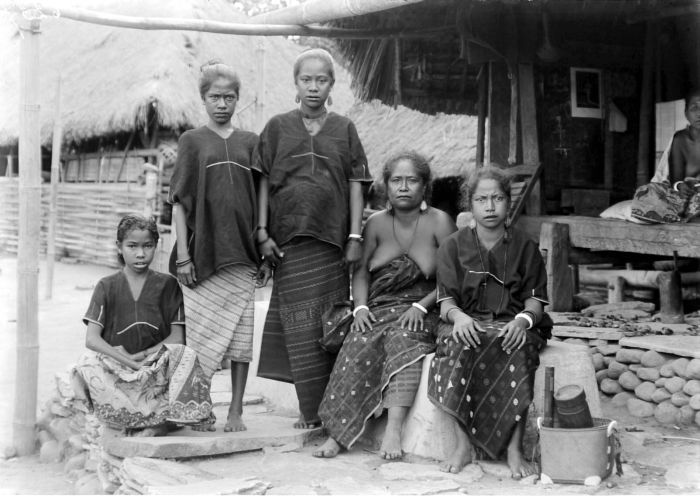
Philippine Shamans
Filipino shamans, commonly known as (also ''Balian'' or , among many other names), were shamans of the various ethnic groups of the pre-colonial Philippine islands. These shamans specialized in communicating, appeasing, or harnessing the spirits of the dead and the spirits of nature. They were almost always women or feminized men ( or ). They were believed to have spirit guides, by which they could contact and interact with the spirits and deities (''anito'' or '' diwata'') and the spirit world. Their primary role were as mediums during ''pag-anito'' séance rituals. There were also various subtypes of specializing in the arts of healing and herbalism, divination, and sorcery. Terminology The most common native terms for shamans among Austronesian groups in Island Southeast Asia are ''balian'', ''baylan'', or cognates and spelling variants thereof. They are all derived from Proto-Western-Malayo-Polynesian ''*balian'', meaning "shaman" (probably originally female, transv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayans
Visayans (Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group, they are both the most numerous in the entire country at around 33.5 million, as well as the most geographically widespread. The Visayans broadly share a maritime culture with strong Roman Catholic traditions integrated into a precolonial indigenous core through centuries of interaction and migration mainly across the Visayan, Sibuyan, Camotes, Bohol and Sulu seas. In more inland or otherwise secluded areas, ancient animistic-polytheistic beliefs and traditions either were reinterpreted within a Roman Catholic framework or syncretized with the new religion. Visayans are generally speakers of one or more of the Bisayan languages, the most widely spoken being Cebuano, followed by Hiligaynon (Ilonggo) and Waray-Waray. Terminology '' K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Philippines (900–1521)
Earliest hominin activity in the Philippine archipelago is dated back to at least 709,000 years ago. ''Homo luzonensis'', a species of archaic humans, was present on the island of Luzon at least 67,000 years ago. The earliest known anatomically modern human was from Tabon Caves in Palawan dating about 47,000 years. Negrito groups were the first inhabitants to settle in the prehistoric Philippines. By around 3000 BC, seafaring Austronesians, who form the majority of the current population, migrated southward from Taiwan. Scholars generally believe that these ethnic and social groups eventually developed into various settlements or polities with varying degrees of economic specialization, social stratification, and political organization. Some of these settlements (mostly those located on major river deltas) achieved such a scale of social complexity that some scholars believe they should be considered early states. This includes the predecessors of modern-day population centers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian People
Indonesians (Indonesian: ''orang Indonesia'') are citizens or people originally from Indonesia, regardless of their ethnic or religious background. There are more than 1,300 ethnicities in Indonesia, making it a multicultural archipelagic country with a diversity of languages, culture and religious beliefs. The population of Indonesia according to the 2020 national census was 270.2 million. 56% live on the island of Java, the world's most populous island. Around 95% of Indonesians are Native Indonesians (formerly grouped as "Pribumi"), with 40% Javanese and 15% Sundanese forming the majority, while the other 5% are Indonesians with ancestry from foreign origin, such as Arab Indonesians, Chinese Indonesians, Indian Indonesians, and Indos. Population As of 2020, Indonesians make up 3.4% of world total population and Indonesia is the fourth most populous country after China, India and the United States. Despite a fairly effective family planning program that has been in pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hantu Demon
Hantu is the Malay and Indonesian word for spirit or ghost, sometimes it is also the Tagalog word for ghost . In modern usage it generally means spirits of the dead but has also come to refer to any legendary invisible being, such as demons. In its traditional context the term also referred to animistic nature spirits or ancestral souls. The word is derived from Proto-Malayo-Polynesian ''*qanitu'' and Proto-Austronesian ''*qaNiCu''. Cognates in other Austronesian languages include the Micronesian ''aniti'', Lio language ''nitu'', Yami ''anito'', Taivoan ''alid'', Seediq and Atayal ''utux'', Bunun ''hanitu'' or ''hanidu'', Polynesian ''aitu'' or ''atua'', and Tsou ''hicu'' among the Formosan languages. In terms of concept and place in traditional folklore, it is most similar to the Filipino anito. Types Aside from generic spirits of the dead, there exist various forms of Hantu including both the benign and malevolent. * Hantu Air: spirit inhabiting the water * Hantu Beruk: ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nage
The Nage are an indigenous people living on the eastern Indonesian island of Flores and Timor. They descended from the indigenous population of Flores They are largely assimilated by the neighboring people. They speak Nage, one of the major languages in the Austronesian languages group. Agriculture The Nage people mainly engaged in manual slash-and-burn farming (tubers, rice, corn), hunting and gathering. Until the middle of the 20th century, communal land ownership with large families participation were still preserved. They live in cumulus-type settlements, located on the slopes of mountains and surrounded by stone walls. Houses are piled up in rectangular position and connected by an open gallery into a single complex, which is intended for joint residence of several large families. Lifestyle The clothes of the Nage people are loincloth and skirt or ''kain''. Women fasten it over the breast, and men around the waist. The diet is dominated by plant based foods (cooked groats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian People
Polynesians form an ethnolinguistic group of closely related people who are native to Polynesia (islands in the Polynesian Triangle), an expansive region of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. They trace their early prehistoric origins to Island Southeast Asia and form part of the larger Austronesian ethnolinguistic group with an Urheimat in Taiwan. They speak the Polynesian languages, a branch of the Oceanic subfamily of the Austronesian language family. there were an estimated 2 million ethnic Polynesians (full and part) worldwide, the vast majority of whom either inhabit independent Polynesian nation-states (Samoa, Niue, Cook Islands, Tonga, and Tuvalu) or form minorities in countries such as Australia, Chile (Easter Island), New Zealand, France (French Polynesia and Wallis and Futuna), and the United States (Hawaii and American Samoa), in addition to the British Overseas Territory of the Pitcairn Islands. New Zealand had the highest population of Polynesians, estimated at 110, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tao People
The Tao people are an Austronesian ethnic group native to the tiny outlying Orchid Island of Taiwan. They have a maritime culture, with great ritual and spiritual significance placed on boat-building and fishing. Their ways of life have been threatened by the continued emigration to the mainland of Taiwan in search of jobs and education. As a result, the continuation of past traditions has been hindered. Despite being linked to both other Taiwanese indigenous peoples and Filipino populations, the Tao people remain unique in their customs and cultural practices. The Tao people have been more commonly recorded under the exonym "Yami people" by official documents and academic literature, following Japanese anthropologist Torii Ryuzo's coining of the name in 1897. However, as a collective, these Orchid Island inhabitants typically prefer "Tao people" as their group identifier. Recently, they have successfully petitioned the Council of Indigenous Peoples of the Taiwanese government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atua
Atua are the gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori mythology, Māori or the Hawaiian religion, Hawaiians (see also ); the Polynesian languages, Polynesian word literally means "power" or "strength" and so the concept is similar to that of ''mana''. Today, it is also used for the monotheistic conception of God. Especially powerful atua included: * ''Rongo, Rongo-mā-Tāne'' – god of agriculture and peace * ''Tāne, Tāne Mahuta'' – creator of all living things such as animals, birds and trees * ''Tangaroa'' – god of the sea * ''Tūmatauenga'' – a god of war * ''Whiro'' – god of darkness and evil In Samoa, where means "god" in the Samoan language, traditional pe'a, tattooing was based on the doctrine of tutelary spirits. There is also a district on the island of Upolu in Samoa called Atua (district), Atua. Atua or gods were also the center of Māori mythology, Māori religion. In Māori mythology, Māori's belief, there was no such word as "reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)