|
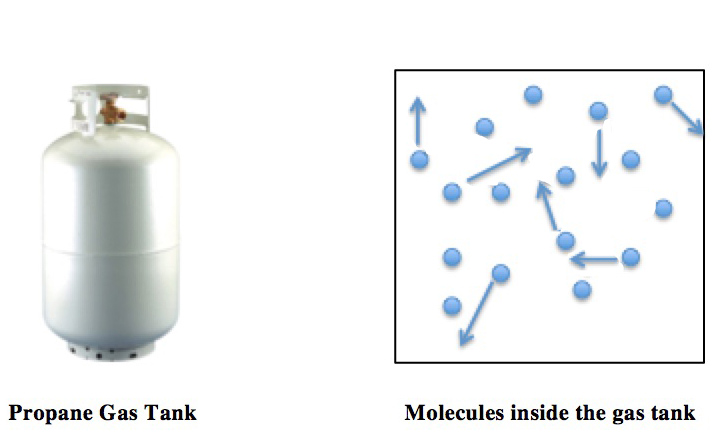
Diving Physics
Diving physics, or the physics of underwater diving is the basic aspects of physics which describe the effects of the underwater environment on the underwater diver and their equipment, and the effects of blending, compressing, and storing breathing gas mixtures, and supplying them for use at ambient pressure. These effects are mostly consequences of immersion in water, the hydrostatic pressure of depth and the effects of pressure and temperature on breathing gases. An understanding of the physics is useful when considering the physiological effects of diving, breathing gas planning and management, diver buoyancy control and trim, and the hazards and risks of diving. Changes in density of breathing gas affect the ability of the diver to breathe effectively, and variations in partial pressure of breathing gas constituents have profound effects on the health and ability to function underwater of the diver. Aspects of physics with particular relevance to diving The main laws of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the SI unit of pressure, the pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the pound-force per square inch (psi) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial and U.S. customary systems. Pressure may also be expressed in terms of standard atmospheric pressure; the atmosphere (atm) is equal to this pressure, and the torr is defined as of this. Manometric u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boyle's Law
Boyle's law, also referred to as the Boyle–Mariotte law, or Mariotte's law (especially in France), is an experimental gas law that describes the relationship between pressure and volume of a confined gas. Boyle's law has been stated as: The absolute pressure exerted by a given mass of an ideal gas is inversely proportional to the volume it occupies if the temperature and amount of gas remain unchanged within a closed system.Levine, Ira. N. (1978), p. 12 gives the original definition. Mathematically, Boyle's law can be stated as: or where is the pressure of the gas, is the volume of the gas, and is a constant. Boyle's Law states that when the temperature of a given mass of confined gas is constant, the product of its pressure and volume is also constant. When comparing the same substance under two different sets of conditions, the law can be expressed as: :P_1 V_1 = P_2 V_2. showing that as volume increases, the pressure of a gas decreases proportionally, and vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and temperature; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory, as was achieved (apparently independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature used in the equation of state is an absolute temperature: the appropria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and temperature; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory, as was achieved (apparently independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature used in the equation of state is an absolute temperature: the appropriat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
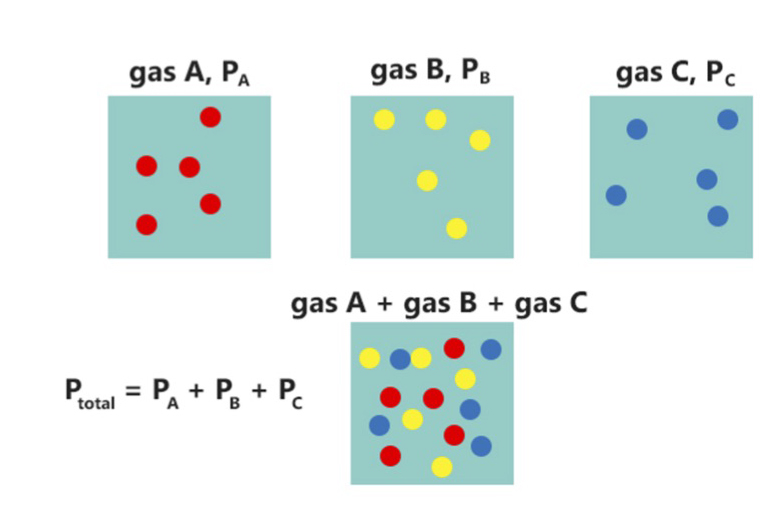
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of thermodynamic activity of the gas's molecules. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react according to their partial pressures but not according to their concentrations in gas mixtures or liquids. This general property of gases is also true in chemical reactions of gases in biology. For example, the necessary amount of oxygen for human respiration, and the amount that is toxic, is set by the partial pressure of oxygen alone. This is true across a very wide range of different concentrations of oxygen present in various inhaled breathing gases or dissolved in blood; consequently, mixture ratios, like that of breathab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Sea Water
The metre (or meter) sea water (msw) is a metric unit of pressure used in underwater diving. It is defined as one tenth of a bar. The unit used in the US is the foot sea water (fsw), based on standard gravity and a sea-water density of 64 lb/ft3. According to the US Navy Diving Manual, one fsw equals 0.30643 msw, , or , though elsewhere it states that 33 fsw is (one atmosphere), which gives one fsw equal to about 0.445 psi.Page 2-12. The msw and fsw are the conventional units for measurement of diver pressure exposure used in decompression tables and the unit of calibration for pneumofathometers and hyperbaric chamber pressure gauges. Feet of sea water One atmosphere is approximately equal to 33 feet of sea water or 14.7 psi, which gives 4.9/11 or about 0.445 psi per foot. Atmospheric pressure may be considered constant at sea level, and minor fluctuations caused by the weather are usually ignored. Pressures measured in fsw and msw are gauge pressure, rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is the force acting on the object due to gravity. Some standard textbooks define weight as a Euclidean vector, vector quantity, the gravitational force acting on the object. Others define weight as a scalar quantity, the magnitude of the gravitational force. Yet others define it as the magnitude of the reaction (physics), reaction force exerted on a body by mechanisms that counteract the effects of gravity: the weight is the quantity that is measured by, for example, a spring scale. Thus, in a state of free fall, the weight would be zero. In this sense of weight, terrestrial objects can be weightless: ignoring Drag (physics), air resistance, the famous apple falling from the tree, on its way to meet the ground near Isaac Newton, would be weightless. The unit of measurement for weight is that of force, which in the International System of Units (SI) is the newton (unit), newton. For example, an object with a mass of one kilogram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambient Pressure
Ambient or Ambiance or Ambience may refer to: Music and sound * Ambience (sound recording), also known as atmospheres or backgrounds * Ambient music, a genre of music that puts an emphasis on tone and atmosphere * ''Ambient'' (album), by Moby * ''Ambience'' (album), by the Lambrettas * Virgin Ambient series, a series of 24 albums released on the UK Virgin Records label between 1993 and 1997 *''Ambient 1–4'', a set of four albums by Brian Eno, released by Obscure Records between 1978 and 1982 Other * Ambient (computation), a process calculus * Ambient (desktop environment), a MUI-based desktop environment for MorphOS * ''Ambient'' (novel), a novel by Jack Womack * Mark Ambient (1860–1937), pen name of Harold Harley, English dramatist * ''Ambiancé ''Ambiancé'' was an experimental film directed by Swedish director Anders Weberg. The film was expected to have a running time of 720 hours (or 30 days) and initially had a projected release date of 31 December 2020. Once the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrostatic Pressure
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body "fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an immersed body". It encompasses the study of the conditions under which fluids are at rest in stable equilibrium as opposed to fluid dynamics, the study of fluids in motion. Hydrostatics is a subcategory of fluid statics, which is the study of all fluids, both compressible or incompressible, at rest. Hydrostatics is fundamental to hydraulics, the engineering of equipment for storing, transporting and using fluids. It is also relevant to geophysics and astrophysics (for example, in understanding plate tectonics and the anomalies of the Earth's gravitational field), to meteorology, to medicine (in the context of blood pressure), and many other fields. Hydrostatics offers physical explanations for many phenomena of everyday life, such as why ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 760mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitudes—the Earth's gravi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Pressure
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |