|
District Of Ungava
The District of Ungava was a regional administrative district of Canada's Northwest Territories from 1895 to 1920, although it effectively ceased operation in 1912. It covered the northern portion of what is today Quebec, the interior of Labrador, and the offshore islands to the west and north of Quebec, which are now part of Nunavut. The name "Ungava" is of Inuktitut origin, meaning "towards the open water". It is believed to be in reference to the lands inhabited by the Ungava Inuit, who lived at the mouth of the Arnaud River which flows into Ungava Bay. Political history When created in 1895, the District of Ungava covered all of modern-day northern Quebec, the interior of modern-day Labrador, and all the islands in James Bay, the Hudson Strait, Ungava Bay, and the eastern side of Hudson Bay. Ungava's southern continental boundaries initially ranged as far south as Lake Timiskaming, well below James Bay on the modern Ontario/Quebec border. Note, however, that a dispute over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of Canada
The Parliament of Canada (french: Parlement du Canada) is the federal legislature of Canada, seated at Parliament Hill in Ottawa, and is composed of three parts: the King, the Senate, and the House of Commons. By constitutional convention, the House of Commons is dominant, with the Senate rarely opposing its will. The Senate reviews legislation from a less partisan standpoint and may initiate certain bills. The monarch or his representative, normally the governor general, provides royal assent to make bills into law. The governor general, on behalf of the monarch, summons and appoints the 105 senators on the advice of the prime minister, while each of the 338 members of the House of Commons – called members of Parliament (MPs) – represents an electoral district, commonly referred to as a ''riding'', and are elected by Canadian voters residing in the riding. The governor general also summons and calls together the House of Commons, and may prorogue or dissolve Parliament, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akpatok Island
Akpatok Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian Arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest island in Ungava Bay on the northern coast of Quebec. The island is named for the Akpat, the thick-billed murre (''Uria lomvia''), which live on ledges along the limestone cliffs surrounding the island. Geography With an area of , Akpatok Island is predominantly limestone, ringed with steep cliffs that rise above sea level. The cliffs are broken in many places by deep ravines allowing access to the flat plateau wide and long. Fauna Akpatok Island has International Biological Program status. It is a Canadian Important Bird Area (#NU007), as well as a Key Migratory Bird Terrestrial Habitat site (NU Site 50). In addition to the thick-billed murre, notable bird species include black guillemot and peregrine falcon. Polar bear, seal, and walrus are common in the area. History At the southern end of the island there are remains of a Dorset settlement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
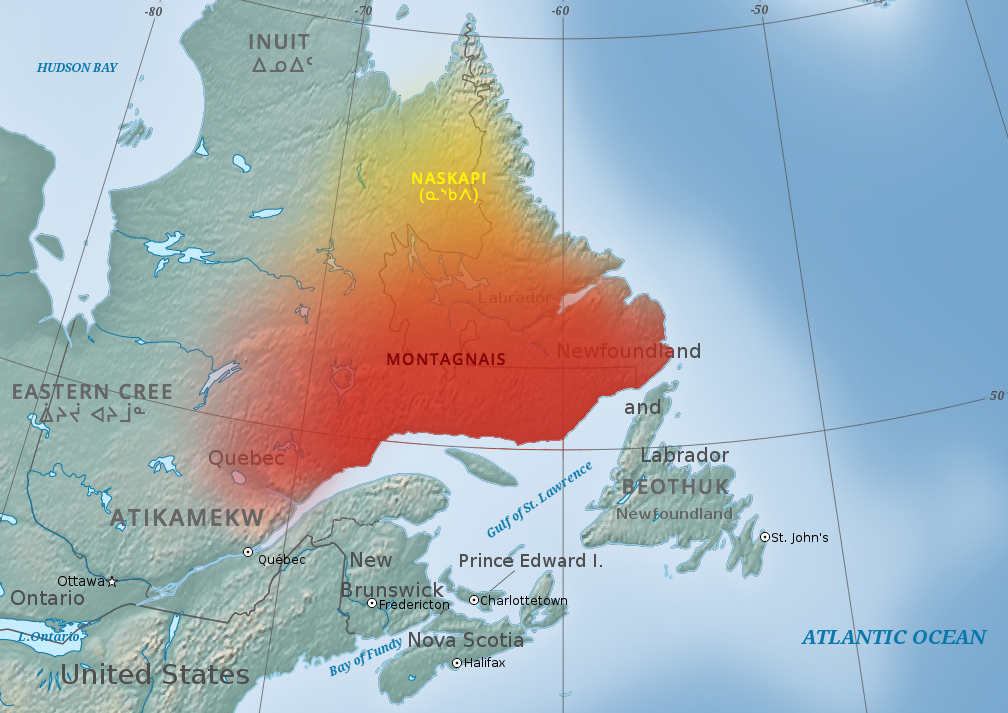
Naskapi
The Naskapi (Nascapi, Naskapee, Nascapee) are an Indigenous people of the Subarctic native to the historical country St'aschinuw (ᒋᑦ ᐊᔅᒋᓄᐤ, meaning 'our nclusiveland'), which is located in northern Quebec and Labrador, neighbouring Nunavik. They are closely related to Innu Nation, who call their homeland ''Nitassinan''. Innu people are frequently divided into two groups, the Neenoilno (called ''Montagnais'' by French people) who live along the north shore of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence, in Quebec, and the less numerous Naskapi who live farther north. The Innu themselves recognize several distinctions (e.g. Mushuau Innuat, Maskuanu Innut, Uashau Innuat) based on different regional affiliations and various dialects of the Innu language. The word "Naskapi" (meaning "people beyond the horizon") first made an appearance in the 17th century and was subsequently applied to Innu groups beyond the reach of missionary influence, most notably those living in the lands wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innu People
The Innu / Ilnu ("man", "person") or Innut / Innuat / Ilnuatsh ("people"), formerly called Montagnais from the French colonial period ( French for "mountain people", English pronunciation: ), are the Indigenous inhabitants of territory in the northeastern portion of the present-day province of Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to their traditional homeland as ''Nitassinan'' ("Our Land", ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) or ''Innu-assi'' ("Innu Land"). The Innu are divided into several bands, with the Montagnais being the southernmost group and the Naskapi being the northernmost. Their ancestors were known to have lived on these lands as hunter-gatherers for several thousand years. To support their seasonal hunting migrations, they created portable tents made of animal skins. Their subsistence activities were historically centred on hunting and trapping caribou, moose, deer, and small game. Their language, Ilnu-Aimun or Innu-Aimun (popularly known since the French colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree or have Cree ancestry. The major proportion of Cree in Canada live north and west of Lake Superior, in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and the Northwest Territories. About 27,000 live in Quebec. In the United States, Cree people historically lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana, where they share the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation with Ojibwe (Chippewa) people. The documented westward migration over time has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade. Sub-groups / Geography The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Peoples In Canada
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations, Inuit and Métis. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and '' Eskimo'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative. ''Aboriginal peoples'' as a collective noun is a specific term of art used in some legal documents, including the ''Constitution Act, 1982'', though in most Indigenous circles ''Aboriginal'' has also fallen into disfavour. Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are some of the earliest known sites of human habitation in Canada. The Paleo-Indian Clovis, Plano and Pre-Dorset cultures pre-date the current Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Projectile point tools, spears, pottery, bangles, chisels and scrapers mark archaeological sites, thus distinguishing cultural periods, traditions, and lithic reduction styles. The characteristics of Indigenous culture in Canada includes a long history of permanent settlements, agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlton Island
Charlton Island (Sivukutaitiarruvik) is an uninhabited island located in James Bay, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located northwest of Rupert Bay, it has an area of . Thomas James, who gave his name to James Bay, wintered here in 1631 and named the island after Prince Charles.Arthur S. Morton,"A History of the Canadian West",page 34 The founders of Fort-Rupert (1668) must have seen it and Charles Bayly was nearly driven ashore here in 1674. Some time before 1679 Bayly proposed making Charlton Island a central depot and meeting place for the three posts around James Bay. This seems to have been done until 1685 or later. After the Hudson Bay expedition (1686) the French planned to send their prisoners there. Little is heard of the island until 1803. About 1802 the North West Company acquired the brig A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square rig, square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitchequon
Nitchequon (pronounced NITCH-e-kun) is a ghost town that was an inland trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the remote geographic centre of Quebec, Canada. It is believed to have operated during 1816–22, 1825 and 1834–1943. History Historically, there was a community of Cree inhabiting Nitchequon as well as some Naskapi residents. The Hudson Bay Company used Nitchequon as a stop or trading post along the fur-trader routes. French-Canadian canoe voyageurs (brigades) would stop at Nitchequon to exchange furs for supplies. However, due to its remote location and the fact it was the Hudson's Bay Company's farthest trading post, it was not cost-effective for the Hudson's Bay Company to continue running it. As a result, it closed in 1943. The Hudson's Bay Company re-opened the Nitchequon trade post around 1950, using air transport instead of canoe brigades. However, it was closed again around the 1960s it is believed, and most Cree residents moved to Mistissini. Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada 1911 Census
The 1911 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population. The census was started on June 1, 1911. All reports had been received by February 26, 1912. The total population count of Canada was 7,206,643. This was an increase of 34% over the 1901 census of 5,371,315. The previous census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1906 census and the following census was the Northwest Provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba 1916 census. Census summary Information was collected on the following subjects, with a separate "schedule" or census data collection form associated with each subject: # Population # Mortality, Disability and Compensation # Houses, Buildings and Fruit # Agriculture: Field Crops - Grain and Other Field Crops for the Harvest Year 1910 # Agriculture: Hoed Crops, Tobacco, Hops and Grass Seeds in 1910 and Field Crop Areas in 1911 # Agriculture: Animal and Animal Products # Farm and Urban Values # Forest Products # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuujjuarapik
Kuujjuarapik (also spelled Kuujjuaraapik; iu, ᑰᔾᔪᐊᕌᐱᒃ ''little great river'') is the southernmost northern village (Inuit community) at the mouth of the Great Whale River (french: Grande Rivière de la Baleine) on the coast of Hudson Bay in Nunavik, Quebec, Canada. Almost 1000 people, mostly Cree, live in the adjacent village of Whapmagoostui. The community is only accessible by air, Kuujjuarapik Airport and, in late summer, by boat. The nearest Inuit village is Umiujaq, about north-northeast of Kuujjuarapik. The police services in Kuujjuaraapik are provided by the Nunavik Police Service, formerly the Kativik Regional Police Force. Like most other northern villages in Quebec, there is an Inuit reserved land of the same name, Kuujjuarapik. However, unlike most other Inuit reserved lands, the Inuit reserved land of Kuujjuarapik is not adjacent to its eponymous northern village; rather, it is located considerably farther north and in fact borders on the Inuit rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories. It was created in 1876 by the ''Keewatin Act'', and originally it covered a large area west of Hudson Bay. In 1905, it became a part of the Northwest Territories and in 1912, its southern parts were adjoined to the provinces of Manitoba and Ontario, leaving the remainder, now called the Keewatin Region, with a population of a few thousand people. On April 1, 1999, the Keewatin Region was formally dissolved, as Nunavut was created from eastern parts of the Northwest Territories, including all of Keewatin. The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either in Cree or in Ojibwe—both of which mean ''north wind'' in their respective languages. In Inuktitut, it was called —a name which persists as the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut. History as a territory, 1876–1905 The District of Keewatin was created by the passage of the ''Keewatin Act'' on October 7, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)