|
District Councils Act (1841) ...
The District Councils Act, "An Act to provide for the better internal Government of that part of this Province which formerly constituted the Province of Upper Canada, by the establishment of Local or Municipal Authorities therein", was passed in August 1841 and went into effect at the start of January 1842. A separate District Councils Act was also passed in 1840 in Lower Canada by the Special Council which administered the province before the passing of the Act of Union. Previously, local government in Canada East and Canada West was based on judicial bodies appointed by the Lieutenant-Governor, the Courts of Quarter Session, which were presided over by justices of the peace. The Act, proposed by Lord Sydenham Charles Poulett Thomson, 1st Baron Sydenham, (13 September 1799 – 19 September 1841) was a British businessman, politician, diplomat and the first Governor General of the united Province of Canada. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Canada
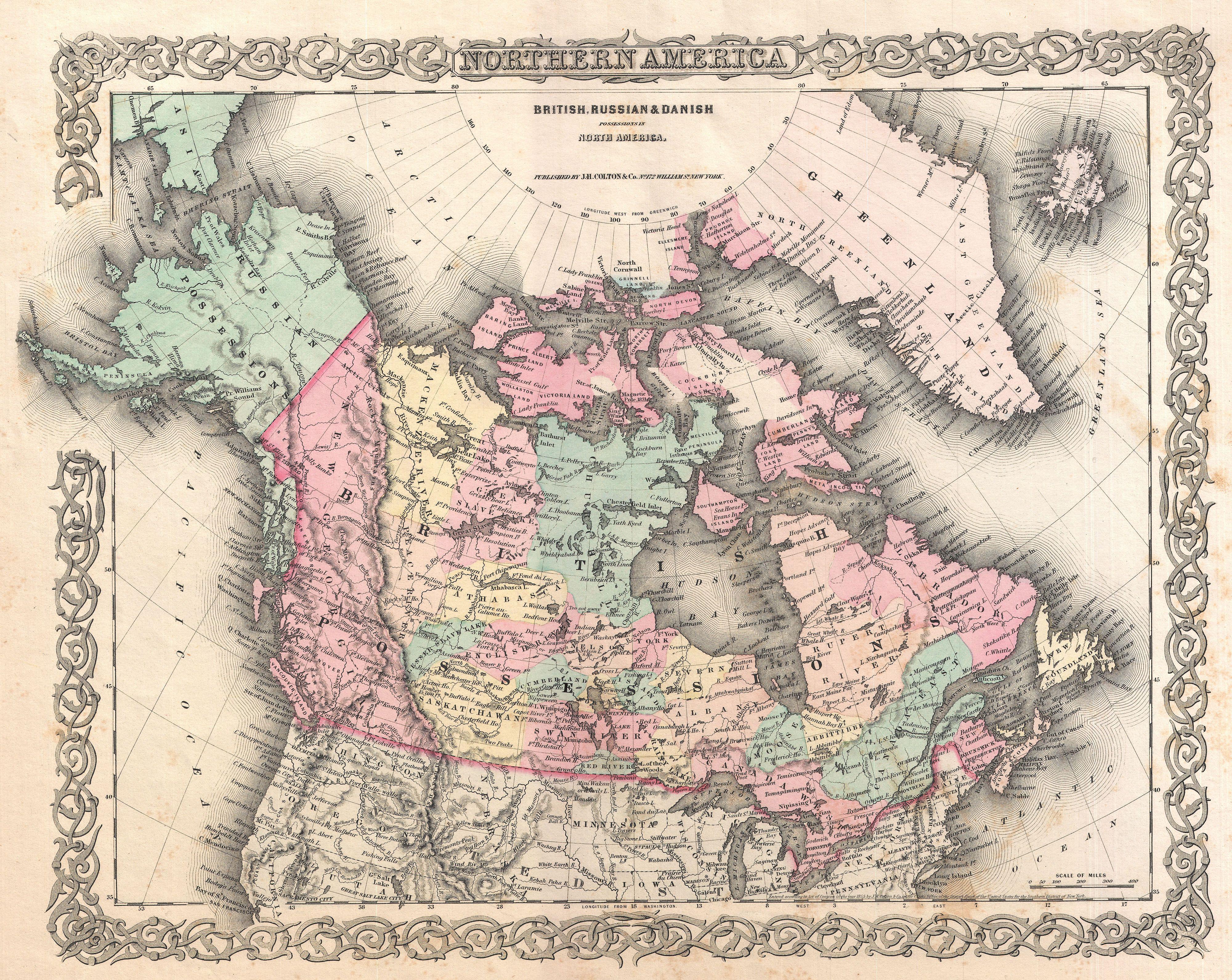
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec and the Labrador region of the current Province of Newfoundland and Labrador (until the Labrador region was transferred to Newfoundland in 1809). Lower Canada consisted of part of the former colony of Canada of New France, conquered by Great Britain in the Seven Years' War ending in 1763 (also called the French and Indian War in the United States). Other parts of New France conquered by Britain became the Colonies of Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island. The Province of Lower Canada was created by the ''Constitutional Act 1791'' from the partition of the British colony of the Province of Quebec (1763–1791) into the Province of Lower Canada and the Province of Upper Canada. The prefix "lower" in its name refers to its geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Council Of Lower Canada
The Special Council of Lower Canada was an appointed body which administered Lower Canada until the Union Act of 1840 created the Province of Canada. Following the Lower Canada Rebellion, on March 27, 1838, the Constitutional Act of 1791 was suspended and both the Legislative Assembly and Legislative Council were dissolved. The Act of Union united Upper and Lower Canada into a single province with a single parliament, consisting of an upper and lower house. Upon the first meeting of this parliament, the Special Council was dissolved. In November 1839, the Special Council approved proposals made by Governor Sydenham for the union of the two Canadas. There were three Special Councils: * the first, consisting of 24 members, was appointed by the acting Governor General, Sir John Colborne, and served from April 2, 1838 to June 1, 1838, when its members were dismissed by the newly arrived Governor General, Lord Durham within a week of his arrival in Canada. * the second, appointed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Union 1840
The ''British North America Act, 1840'' (3 & 4 Victoria, c.35), also known as the ''Act of Union 1840'', (the ''Act'') was approved by Parliament in July 1840 and proclaimed February 10, 1841, in Montreal. It abolished the legislatures of Lower Canada and Upper Canada and established a new political entity, the Province of Canada to replace them. The ''Act'' was similar in nature and in goals to the other Acts of Union enacted by the British Parliament. Background Rebellion of Lower Canada After the War of 1812, the elected assembly of Lower Canada was dominated by French Canadians. A strong sense of nationalism sprung up among the francophones living in Lower Canada. The nationalists were led by Louis-Joseph Papineau, who was a part of what would later be known as the Patriot Party. One of its biggest demands was to determine how the colony's revenue would be spent. It challenged the authority of the upper house or legislative government. As well, the party sought to ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada East
Canada East (french: links=no, Canada-Est) was the northeastern portion of the United Province of Canada. Lord Durham's Report investigating the causes of the Upper and Lower Canada Rebellions recommended merging those two colonies. The new colony, known as the Province of Canada, was created by the Act of Union 1840 passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, having effect in 1841. For administrative purposes, the new Province was subdivided into Canada West and Canada East. The former name of "Lower Canada" came back into official use in 1849, and as of the Canadian Confederation of 1867 it formed the newly created province of Quebec. An estimated 890,000 people lived in Canada East in 1851. Geography It consisted of the southern portion of the modern-day Canadian province of Quebec. Formerly a British colony called the Province of Lower Canada, based on Lord Durham's report it was merged with the Province of Upper Canada (present-day southern portion of the Provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada West
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838. The Act of Union 1840, passed on 23 July 1840 by the British Parliament and proclaimed by the Crown on 10 February 1841, merged the Colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada by abolishing their separate parliaments and replacing them with a single one with two houses, a Legislative Council as the upper chamber and the Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber. In the aftermath of the Rebellions of 1837–1838, unification of the two Canadas was driven by two factors. Firstly, Upper Canada was near bankruptcy because it lacked stable tax revenues, and needed the resources of the more populous Lower Canada to fund its internal transportation improvements. Secondly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Session
The courts of quarter sessions or quarter sessions were local courts traditionally held at four set times each year in the Kingdom of England from 1388 (extending also to Wales following the Laws in Wales Act 1535). They were also established in Scotland, Ireland and in various other dominions of the British Empire. Quarter sessions generally sat in the seat of each county and county borough, and in numerous non-county boroughs (mainly, but not exclusively, ancient boroughs), which were entitled to hold their own quarter sessions''Whitaker's Almanack'' 1968, pp 465-6. (see below), although some of the smaller boroughs lost their own quarter sessions in 1951 (see below). All quarter sessions were abolished in England and Wales in 1972, when the Courts Act 1971 replaced them and the assizes with a single permanent Crown Court. In Scotland, they survived until 1975, when they were abolished and replaced by district courts and later by justice of the peace courts. The quarter sessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justice Of The Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or ''puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission ( letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the same meaning. Depending on the jurisdiction, such justices dispense summary justice or merely deal with local administrative applications in common law jurisdictions. Justices of the peace are appointed or elected from the citizens of the jurisdiction in which they serve, and are (or were) usually not required to have any formal legal education in order to qualify for the office. Some jurisdictions have varying forms of training for JPs. History In 1195, Richard I ("the Lionheart") of England and his Minister Hubert Walter commissioned certain knights to preserve the peace in unruly areas. They were responsible to the King in ensuring that the law was upheld and preserving the " King's peace". Therefore, they were known as "keepers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Poulett Thomson, 1st Baron Sydenham
Charles Poulett Thomson, 1st Baron Sydenham, (13 September 1799 – 19 September 1841) was a British businessman, politician, diplomat and the first Governor General of the united Province of Canada.Baron Sydenham Retrieved on 19 Feb 2018 Early life, family, education Born at Waverley Abbey House, near Farnham, Surrey, Thomson was the son of John Buncombe Poulett Thomson, a London merchant, by his wife Charlotte, daughter of John Jacob. His father was the head of J. Thomson, T. Bonar and Company, a successful trading firm that had dealings with |
Baldwin Act (1849)
Baldwin is a Germanic name, composed of the elements ''bald'' "bold" and ''win'' "friend". People * Baldwin (name) Places Canada * Baldwin, York Regional Municipality, Ontario * Baldwin, Ontario, in Sudbury District * Baldwin's Mills, Quebec United States * Baldwin County, Alabama * Baldwin, Florida * Baldwin, Georgia * Baldwin County, Georgia * Baldwin, Illinois * Baldwin, Iowa * Baldwin, Louisiana * Baldwin, Maine * Baldwin, Maryland * Baldwin, Michigan * Baldwyn, Mississippi * Baldwin, Chemung County, New York * Baldwin, Nassau County, New York ** Baldwin (LIRR station) * Baldwin, North Dakota * Baldwin, Pennsylvania * Baldwin, Wisconsin * Baldwin (town), Wisconsin Other places * Baldwin Street, in Dunedin, New Zealand, the world's steepest street *Baldwin Hills, neighborhood in Los Angeles, California * Montgomery, Powys, named in Welsh "Trefaldwyn", meaning "The Town of Baldwin" Companies * Baldwin Locomotive Works, one of the world's largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1841 In Law
Events January–March * January 20 – Charles Elliot of the United Kingdom, and Qishan of the Qing dynasty, agree to the Convention of Chuenpi. * January 26 – Britain occupies Hong Kong. Later in the year, the first census of the island records a population of about 7,500. * January 27 – The active volcano Mount Erebus in Antarctica is discovered, and named by James Clark Ross. * January 28 – Ross discovers the "Victoria Barrier", later known as the Ross Ice Shelf. On the same voyage, he discovers the Ross Sea, Victoria Land and Mount Terror. * January 30 – A fire ruins and destroys two-thirds of the villa (modern-day city) of Mayagüez, Puerto Rico. * February 4 – First known reference to Groundhog Day in North America, in the diary of a James Morris. * February 10 – The Act of Union (''British North America Act'', 1840) is proclaimed in Canada. * February 11 – The two colonies of the Canadas are merged, into the United Province of Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1841 In Canada
Events from the year 1841 in Canada. Incumbents * Monarch: Victoria Federal government * Parliament: 1st (starting June 15) Governors * Governor General of the Province of Canada: Charles Poulett Thomson, 1st Baron Sydenham * Governor of New Brunswick: William MacBean George Colebrooke *Governor of Nova Scotia: Lucius Cary, 10th Viscount Falkland * Civil Governor of Newfoundland: John Harvey * Governor of Prince Edward Island: Henry Vere Huntley * Governor of Canada West: John Clitherow then Richard Downes Jackson Premiers *Joint Premiers of the Province of Canada — ** William Henry Draper, Canada West Premier **Samuel Harrison, Canada East Premier Events *February 10 – The Union of Upper and Lower Canada establishes the Province of Canada. *June 15 – The 1st Parliament of the Province of Canada meets at Kingston. *October 2 – The Canada Gazette publishes its first issue. *December 20 – The Kingston Common Council establishes a police force. *The Dawn Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British North America, British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of 1837–1838. The Act of Union 1840, passed on 23 July 1840 by the British Parliament and proclaimed by the Monarchy of Great Britain, Crown on 10 February 1841, merged the Colonies of Upper Canada and Lower Canada by abolishing their separate parliaments and replacing them with a Parliament of the Province of Canada, single one with two houses, a Legislative Council of the Province of Canada, Legislative Council as the upper chamber and the Legislative Assembly of the Province of Canada, Legislative Assembly as the lower chamber. In the aftermath of the Rebellions of 1837–1838, unification of the two Canadas was driven by two factors. Firstly, Upper Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_badge.jpg)

