|
Distributed Version Control
In software development, distributed version control (also known as distributed revision control) is a form of version control in which the complete codebase, including its full history, is mirrored on every developer's computer. Compared to centralized version control, this enables automatic management Branching (version control), branching and Merge (version control), merging, speeds up most operations (except pushing and fetching), improves the ability to work offline, and does not rely on a single location for backups. Git (software), Git, the world's most popular version control system, is a distributed version control system. In 2010, software development author Joel Spolsky described distributed version control systems as "possibly the biggest advance in software development technology in the [past] ten years". Distributed vs. centralized Distributed version control systems (DVCS) use a peer-to-peer approach to version control, as opposed to the client–server model, clien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
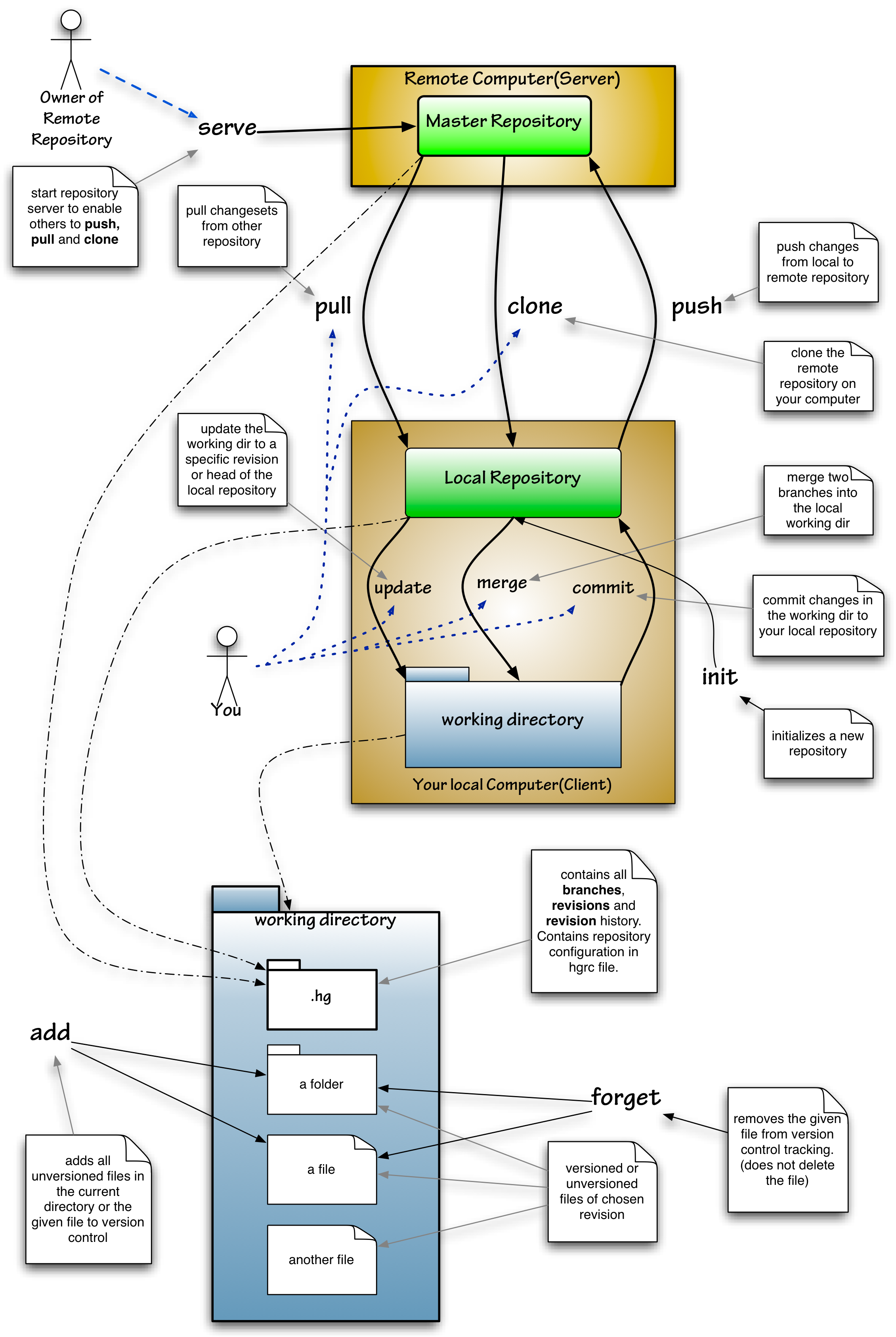
Git Session
Git () is a distributed version control software system, system that tracks versions of computer file, files. It is often used to control source code by Programmer, programmers who are software development, developing software collaboratively. Design goals of Git include speed, data integrity, and support for Distributed computing, distributed, non-linear workflows — thousands of parallel Branching (version control), branches running on different computers. "So I'm writing some scripts to try to track things a whole lot faster." As with most other distributed version control systems, and unlike most client–server systems, Git maintains a local copy of the entire Repository (version control), repository, also known as "repo", with history and version-tracking abilities, independent of Computer network, network access or a central Server (computing), server. A repository is stored on each computer in a standard directory (computing), directory with additional, Hidden f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
:Category:Software Using Distributed Version Control
{{category explanation, software which uses, or can use, a distributed version control In software development, distributed version control (also known as distributed revision control) is a form of version control in which the complete codebase, including its full history, is mirrored on every developer's computer. Compared to centr ... system as a storage repository, but is not ''itself'' a distributed version control system (or a user interface wrapper for one). Some software may support more than one DRCS back-end Distributed version control systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comparison Of Version-control Software
The following tables describe attributes of notable version control and software configuration management (SCM) systems that can be used to compare and contrast the various systems. For SCM software not suitable for source code, see Comparison of open-source configuration management software. General information The following table contains relatively general attributes of version-control software systems, including: *Repository model, the relationship between copies of the source code repository ** Client–server, users access a master repository via a client; typically, their local machines hold only a working copy of a project tree. Changes in one working copy must be committed to the master repository before they are propagated to other users. ** Distributed, repositories act as peers, and users typically have a local repository with version history available, in addition to their working copies. *Concurrency model, how changes to the working copy are managed to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
List Of Version-control Software
This is a list of notable version control software systems. Common attributes *Openness, whether the software is ''open'' source or ''proprietary'' *Repository model, how working and shared source code is handled **Shared, all developers use the same file system ** Client–server, users access a master repository server via a client; typically, a client machine holds only a working copy of a project tree; changes in one working copy are committed to the master repository before becoming available to other users **Distributed, repositories act as peers; typically each user has a local repository clone with complete version history in addition to their working files Active * AccuRev roprietary, client-server– source configuration management tool with integrated issue tracking based on "Streams" that manages parallel and global development; replication server is also available; now owned by Micro Focus * Autodesk Vault roprietary, client-server– Version control tool speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Version Control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code text files, but generally any type of file. Version control is a component of software configuration management. A ''version control system'' is a software tool that automates version control. Alternatively, version control is embedded as a feature of some systems such as word processors, spreadsheets, collaborative groupware, web docs, and content management systems, e.g., Help:Page history, Wikipedia's page history. Version control includes viewing old versions and enables Reversion (software development), reverting a file to a previous version. Overview As teams develop software, it is common to Software deployment, deploy multiple versions of the same software, and for different developers to work on one or more different versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
BitKeeper
BitKeeper is a discontinued software tool for distributed revision control of computer source code. Originally developed as proprietary software by BitMover Inc., a privately held company based in Los Gatos, California, it was released as open-source software under the Apache License, Apache-2.0 license on 9 May 2016. BitKeeper is no longer being developed. History BitKeeper was originally developed by BitMover Inc., a privately held company from Los Gatos, California owned by Larry McVoy, who had previously designed TeamWare. BitKeeper and the Linux kernel BitKeeper was first mentioned as a solution to some of the growing pains that Linux was having in September 1998. Early access betas were available in May 1999 and on May 4, 2000, the first public release of BitKeeper was made available. BitMover used to provide access to the system for certain Open-source software, open-source or free-software projects, one of which was the source code of the Linux kernel. The license for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mercurial (software)
Mercurial is a distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is supported on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and other Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD and macOS. Mercurial's major design goals include high performance and scalability, decentralization, fully distributed collaborative development, robust handling of both plain text and binary files, and advanced branching and merging capabilities, while remaining conceptually simple. It includes an integrated web-interface. Mercurial has also taken steps to ease the transition for users of other version control systems, particularly Subversion. Mercurial is primarily a command-line driven program, but graphical user interface extensions are available, e.g. TortoiseHg, and several IDEs offer support for version control with Mercurial. All of Mercurial's operations are invoked as arguments to its driver program hg (a reference to Hg – the chemical symbol of the element mercury). Olivia Mackall originated Mercur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Darcs
Darcs is a distributed version control system created by David Roundy. Key features include the ability to choose which changes to accept from other repositories, interaction with either other local (on-disk) repositories or remote repositories via SSH, HTTP, or email, and an unusually interactive interface. The developers also emphasize the use of advanced software tools for verifying correctness: the expressive type system of the functional programming language Haskell enforces some properties, and randomized testing via QuickCheck verifies many others. The name is a recursive acronym for Darcs Advanced Revision Control System. Model Darcs treats patches as first-class citizens. For the user, a repository can be seen as a set of patches, where each patch is not necessarily ordered with respect to other patches, i.e. the set of patches is only a partially ordered set. In many cases patches can be independently transmitted between various repositories. Many branching, mergin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monotone (software)
Monotone is an open source software tool for distributed revision control. It tracks revisions to files, groups sets of revisions into changesets, and tracks history across renames. The focus of the project is on integrity over performance. Monotone is designed for distributed operation, and makes heavy use of cryptographic primitives to track file revisions (via the SHA-1 secure hash) and to authenticate user actions (via RSA cryptographic signatures). History Milestones Monotone version 0.26 introduced major changes to the internal database structures, including a new structure known by Monotone developers as a ''roster''. Monotone databases created with version 0.26 can not exchange revisions with older Monotone databases. Older databases must first be upgraded to the new format. The new netsync protocol is incompatible with earlier versions of Monotone. As Git inspiration In April 2005, Monotone became the subject of increased interest in the FOSS community a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GNU Arch
GNU arch software is a distributed revision control system that is part of the GNU Project and licensed under the GNU General Public License. It is used to keep track of the changes made to a source tree and to help programmers combine and otherwise manipulate changes made by multiple people or at different times. As of 2009, GNU arch's official status is deprecation, and only security fixes are applied. Bazaar (or 'bzr') has since also been made an official GNU project and can thus be considered the replacement for GNU arch. It is not a fork of arch. Features Being a distributed, decentralized versioning system, each revision stored using arch is uniquely globally identifiable; such identifier can be used in a distributed setting to easily merge or "cherry-pick" changes from completely disparate sources. Being decentralized means that there is no need for a central server for which developers have to be authorized in order to contribute. As with other systems, a full re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Code Review
Code review (sometimes referred to as peer review) is a software quality assurance activity in which one or more people examine the source code of a computer program, either after implementation or during the development process. The persons performing the checking, excluding the author, are called "reviewers". At least one reviewer must not be the code's author. Code review differs from related software quality assurance techniques like static code analysis, self-checks, testing, and pair programming. Static analysis relies primarily on automated tools, self-checks involve only the author, testing requires code execution, and pair programming is performed continuously during development rather than as a separate step. Goal Although direct discovery of quality problems is often the main goal, code reviews are usually performed to reach a combination of goals: * ''Improving code quality'' Improve internal code quality and maintainability through better readability, uniformit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |