|
Distributed Object
In distributed computing, distributed objects are objects (in the sense of object-oriented programming) that are distributed across different address spaces, either in different processes on the same computer, or even in multiple computers connected via a network, but which work together by sharing data and invoking methods. This often involves location transparency, where remote objects appear the same as local objects. The main method of distributed object communication is with remote method invocation, generally by message-passing: one object sends a message to another object in a remote machine or process to perform some task. The results are sent back to the calling object. Distributed objects were popular in the late 1990s and early 2000s, but have since fallen out of favor. The term may also generally refer to one of the extensions of the basic object concept used in the context of distributed computing, such as ''replicated objects'' or ''live distributed objects''. * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
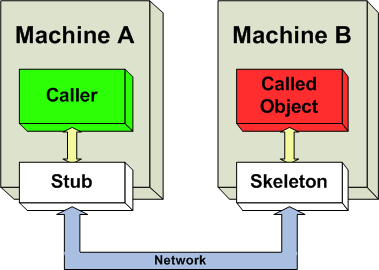
Distributed Object Communication
In a distributed computing environment, distributed object communication realizes communication between distributed objects. The main role is to allow objects to access data and invoke methods on remote objects (objects residing in non-local memory space). Invoking a method on a remote object is known as remote method invocation (RMI) or remote invocation, and is the object-oriented programming analog of a remote procedure call (RPC). Class stubs and skeletons The widely used approach on how to implement the communication channel is realized by using stubs and skeletons. They are generated objects whose structure and behavior depends on chosen communication protocol, but in general provide additional functionality that ensures reliable communication over the network. In RMI, a stub (which is the bit on the client) is defined by the programmer as an interface. The rmic (rmi compiler) uses this to create the class stub. The stub performs type checking. The skeleton is defined in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap'n Proto
Cap’n Proto is a data serialization format and Remote Procedure Call (RPC) framework for exchanging data between computer programs. The high-level design focuses on speed and security, making it suitable for network as well as inter-process communication. Cap'n Proto was created by the former maintainer of Google's popular Protocol Buffers framework (Kenton Varda) and was designed to avoid some of its perceived shortcomings. Technical overview IDL Schema Like most RPC frameworks dating as far back as Sun RPC and OSF DCE RPC (and their object-based descendants CORBA and DCOM), Cap'n Proto uses an Interface Description Language (IDL) to generate RPC libraries in a variety of programming languages - automating many low level details such as handling network requests, converting between data types, etc. The Cap'n Proto interface schema uses a C-like syntax and supports common primitives data types (booleans, integers, floats, etc.), compound types (structs, lists, enum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragmented Object
{{multiple issues, {{technical, date=June 2014 {{context, date=February 2018 In computing, fragmented objects are truly distributed objects. It is a novel design principle extending the traditional concept of stub based distribution. In contrast to distributed objects, they are physically distributed and encapsulate the distribution in the object itself. Parts of the object - named fragments - may exist on different nodes and provide the object's interface. Each client accessing a fragmented object by its unique object identity presumes a local fragment. Fragmented objects may act like a RPC-based infrastructure or a (caching) smart proxy as well. Therefore, clients cannot distinguish between the access of a local object, a local stub or a local fragment. Full transparency is gained by the following characteristics of fragmented objects. Arbitrary internal communication Arbitrary protocols may be chosen for the internal communication between the fragments. For instance, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruby Programming Language
Ruby is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language which supports multiple programming paradigms. It was designed with an emphasis on programming productivity and simplicity. In Ruby, everything is an object, including primitive data types. It was developed in the mid-1990s by Yukihiro "Matz" Matsumoto in Japan. Ruby is dynamically typed and uses garbage collection and just-in-time compilation. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented, and functional programming. According to the creator, Ruby was influenced by Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel, Ada, BASIC, Java and Lisp. History Early concept Matsumoto has said that Ruby was conceived in 1993. In a 1999 post to the ''ruby-talk'' mailing list, he describes some of his early ideas about the language: Matsumoto describes the design of Ruby as being like a simple Lisp language at its core, with an object system like that of Smalltalk, blocks inspired by higher-ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Ruby
Distributed Ruby or DRb allows Ruby programs to communicate with each other on the same machine or over a network. DRb uses remote method invocation (RMI) to pass commands and data between processes. See also * Java remote method invocation In computing, the Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI) is a Java API that performs remote method invocation, the object-oriented equivalent of remote procedure calls (RPC), with support for direct transfer of serialized Java classes and di ... * Rinda (Ruby programming language) External links DRb RDoc Documentation Ruby (programming language) Inter-process communication {{programming-software-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC programming language and first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000 and introduced new features such as list comprehensions, cycle-detecting garbage collection, reference counting, and Unicode support. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision that is not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2 was discontinued with version 2.7.18 in 2020. Python consistently ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PYthon Remote Objects
Python may refer to: Snakes * Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia ** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia * Python (mythology), a mythical serpent Computing * Python (programming language), a widely used programming language * Python, a native code compiler for CMU Common Lisp * Python, the internal project name for the PERQ 3 computer workstation People * Python of Aenus (4th-century BCE), student of Plato * Python (painter), (ca. 360–320 BCE) vase painter in Poseidonia * Python of Byzantium, orator, diplomat of Philip II of Macedon * Python of Catana, poet who accompanied Alexander the Great * Python Anghelo (1954–2014) Romanian graphic artist Roller coasters * Python (Efteling), a roller coaster in the Netherlands * Python (Busch Gardens Tampa Bay), a defunct roller coaster * Python (Coney Island, Cincinnati, Ohio), a steel roller coaster Vehicles * Python (automobile maker), an Australian car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JavaSpaces
A tuple space is an implementation of the associative memory paradigm for parallel/distributed computing. It provides a repository of tuples that can be accessed concurrently. As an illustrative example, consider that there are a group of processors that produce pieces of data and a group of processors that use the data. Producers post their data as tuples in the space, and the consumers then retrieve data from the space that match a certain pattern. This is also known as the blackboard metaphor. Tuple space may be thought as a form of distributed shared memory. Tuple spaces were the theoretical underpinning of the Linda language developed by David Gelernter and Nicholas Carriero at Yale University in 1986. Implementations of tuple spaces have also been developed for Java ( JavaSpaces), Lisp, Lua, Prolog, Python, Ruby, Smalltalk, Tcl, and the .NET Framework. Object Spaces Object Spaces is a paradigm for development of distributed computing applications. It is characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DDObjects
DDObjects is a remoting framework for Borland Delphi and C++ Builder. A main goal while developing DDObjects has not been only to keep the code one has to implement in order to utilize DDObjects as simple as possible but also very close to Delphi's usual style of event-driven programming. DDObjects supports remote method calls, server callbacks, asynchronous calls, asynchronous callbacks, stateful and -less objects and other features. DDObjects doesn't mimic other implementations as DCOM or CORBA, which are generalized to a least common denominator, but makes use of Delphi's rich type system including Objects, Exceptions, Records, Sets and Enumerations. DDObjects uses plain XML and HTTP as protocol, contains a broker component, a sourcecode generator as well as some new visual The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the vis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Component Object Model
Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) is a proprietary Microsoft technology for communication between software components on networked computers. DCOM, which originally was called "Network OLE", extends Microsoft's COM, and provides the communication substrate under Microsoft's COM+ application server infrastructure. The extension COM into Distributed COM was due to extensive use of DCE/RPC (Distributed Computing Environment/Remote Procedure Calls) – more specifically Microsoft's enhanced version, known as MSRPC. In terms of the extensions it added to COM, DCOM had to solve the problems of: * Marshalling – serializing and deserializing the arguments and return values of method calls "over the wire". *Distributed garbage collection – ensuring that references held by clients of interfaces are released when, for example, the client process crashed, or the network connection was lost. *Combining significant numbers of objects in the client's browser into a single transm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CORBA
The Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) is a standard defined by the Object Management Group (OMG) designed to facilitate the communication of systems that are deployed on diverse platforms. CORBA enables collaboration between systems on different operating systems, programming languages, and computing hardware. CORBA uses an object-oriented model although the systems that use the CORBA do not have to be object-oriented. CORBA is an example of the distributed object paradigm. Overview CORBA enables communication between software written in different languages and running on different computers. Implementation details from specific operating systems, programming languages, and hardware platforms are all removed from the responsibility of developers who use CORBA. CORBA normalizes the method-call semantics between application objects residing either in the same address-space (application) or in remote address-spaces (same host, or remote host on a network). Versio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java RMI
In computing, the Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI) is a Java API that performs remote method invocation, the object-oriented equivalent of remote procedure calls (RPC), with support for direct transfer of serialized Java classes and distributed garbage-collection. The original implementation depends on Java Virtual Machine (JVM) class-representation mechanisms and it thus only supports making calls from one JVM to another. The protocol underlying this Java-only implementation is known as Java Remote Method Protocol (JRMP). In order to support code running in a non-JVM context, programmers later developed a CORBA version. Usage of the term RMI may denote solely the programming interface or may signify both the API and JRMP, IIOP, or another implementation, whereas the term RMI-IIOP (read: RMI over IIOP) specifically denotes the RMI interface delegating most of the functionality to the supporting CORBA implementation. The basic idea of Java RMI, the distributed garbag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |