|
Distortion Synthesis
Distortion synthesis is a group of sound synthesis techniques which modify existing sounds to produce more complex sounds (or timbres), usually by using non-linear circuits or mathematics.Nb. Some authors refer to these techniques as 'modulation synthesis'; e.g. Chapter 6 of While some synthesis methods achieve sonic complexity by using many oscillators, distortion methods create a frequency spectrum which has many more components than oscillators. Some distortion techniques are: FM synthesis, waveshaping synthesis, and discrete summation formulas. FM synthesis Frequency modulation synthesis distorts the carrier frequency of an oscillator by modulating it with another signal. The distortion can be controlled by means of a modulation index. The method known as phase distortion synthesis is similar to FM. Waveshaping synthesis Waveshaping synthesis changes an original waveform by responding to its amplitude in a non-linear fashion. It can generate a bandwidth-limited spectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Synthesis
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis and frequency modulation synthesis. These sounds may be altered by components such as filters, which cut or boost frequencies; envelopes, which control articulation, or how notes begin and end; and low-frequency oscillators, which modulate parameters such as pitch, volume, or filter characteristics affecting timbre. Synthesizers are typically played with keyboards or controlled by sequencers, software or other instruments, and may be synchronized to other equipment via MIDI. Synthesizer-like instruments emerged in the United States in the mid-20th century with instruments such as the RCA Mark II, which was controlled with punch cards and used hundreds of vacuum tubes. The Moog synthesizer, developed by Robert Moog and first sold in 1964 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Distortion Synthesis
Phase distortion (PD) synthesis is a synthesis method introduced in 1984 by Casio in its CZ range of synthesizers. In outline, it is similar to phase modulation synthesis as championed by Yamaha Corporation (under the name of frequency modulation), in the sense that both methods dynamically change the harmonic content of a carrier waveform by influence of another waveform (modulator) in the time domain. However, the application and results of the two methods are quite distinct. Casio made five different synthesizers using their original concept of PD synthesis (with variations). The later VZ-1 and co's synthesis method Interactive phase distortion is much more similar to the aforementioned phase modulation, rather than a direct evolution of phase distortion; see below. Generating harmonic content Casio's implementation of PD used oscillators generated by modulator and carrier waveforms, synchronised to each other per-cycle. The modulators were various angular waves that could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band-limited
Bandlimiting is the limiting of a signal's frequency domain representation or spectral density to zero above a certain finite frequency. A band-limited signal is one whose Fourier transform or spectral density has bounded support. A bandlimited signal may be either random (stochastic) or non-random ( deterministic). In general, infinitely many terms are required in a continuous Fourier series representation of a signal, but if a finite number of Fourier series terms can be calculated from that signal, that signal is considered to be band-limited. Sampling bandlimited signals A bandlimited signal can be fully reconstructed from its samples, provided that the sampling rate exceeds twice the maximum frequency in the bandlimited signal. This minimum sampling rate is called the Nyquist rate. This result, usually attributed to Nyquist and Shannon, is known as the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. An example of a simple deterministic bandlimited signal is a sinusoid of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inharmonic
In music, inharmonicity is the degree to which the frequencies of overtones (also known as partials or partial tones) depart from whole multiples of the fundamental frequency ( harmonic series). Acoustically, a note perceived to have a single distinct pitch in fact contains a variety of additional overtones. Many percussion instruments, such as cymbals, tam-tams, and chimes, create complex and inharmonic sounds. Music harmony and intonation depends strongly on the harmonicity of tones. An ideal, homogeneous, infinitesimally thin or infinitely flexible string or column of air has exactly harmonic modes of vibration. In any real musical instrument, the resonant body that produces the music tone—typically a string, wire, or column of air—deviates from this ideal and has some small or large amount of inharmonicity. For instance, a very thick string behaves less as an ideal string and more like a cylinder (a tube of mass), which has natural resonances that are not whole numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the other harmonics are known as ''higher harmonics''. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a '' harmonic series''. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz. In music, harmonics are used on string instruments and wind instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio Amplifier
An audio power amplifier (or power amp) is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power electronic audio signals, such as the signal from a radio receiver or an electric guitar pickup, to a level that is high enough for driving loudspeakers or headphones. Audio power amplifiers are found in all manner of sound systems including sound reinforcement, public address and home audio systems and musical instrument amplifiers like guitar amplifiers. It is the final electronic stage in a typical audio playback chain before the signal is sent to the loudspeakers. The preceding stages in such a chain are low power audio amplifiers which perform tasks like pre-amplification of the signal (this is particularly associated with record turntable signals, microphone signals and electric instrument signals from pickups, such as the electric guitar and electric bass), equalization (e.g., adjusting the bass and treble), tone controls, mixing different input signals or adding electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
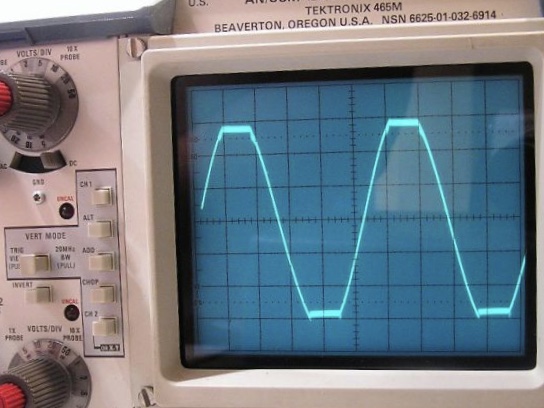
Clipping (audio)
Clipping is a form of waveform distortion that occurs when an amplifier is overdriven and attempts to deliver an output voltage or current beyond its maximum capability. Driving an amplifier into clipping may cause it to output power in excess of its power rating. In the frequency domain, clipping produces strong harmonics in the high-frequency range (as the clipped waveform comes closer to a squarewave). The extra high-frequency weighting of the signal could make tweeter damage more likely than if the signal was not clipped. In some cases, the distortion associated with clipping is unwanted, and is visible on an oscilloscope even if it is inaudible. However, clipping is often used in music for artistic effect, especially in heavier genres. Overview When an amplifier is pushed to create a signal with more power than its power supply can produce, it will amplify the signal only up to its maximum capacity, at which point the signal can be amplified no further. As the signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude & semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves, square waves or triangle waves ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value (DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveshaper
In electronic music, waveshaping is a type of distortion synthesis in which complex spectra are produced from simple tones by altering the shape of the waveforms. Uses Waveshapers are used mainly by electronic musicians to achieve an extra-abrasive sound. This effect is most used to enhance the sound of a music synthesizer by altering the waveform or vowel. Rock musicians may also use a waveshaper for heavy distortion of a guitar or bass. Some synthesizers or virtual software instruments have built-in waveshapers. The effect can make instruments sound noisy or overdriven. In digital modeling of analog audio equipment such as tube amplifiers, waveshaping is used to introduce a static, or memoryless, nonlinearity to approximate the transfer characteristic of a vacuum tube or diode limiter. How it works A waveshaper is an audio effect that changes an audio signal by mapping an input signal to the output signal by applying a fixed or variable mathematical function, calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer. The carrier is higher in frequency than the modulation signal. In radio communication the modulated carrier is transmitted through space as a radio wave to a radio receiver. Another purpose is to transmit multiple channels of information through a single communication medium, using frequency-division multiplexing (FDM). For example in cable television which uses FDM, many carrier signals, each modulated with a different television channel, are transported through a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbres
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish different instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe and a clarinet, both woodwind instruments). In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctively with its own unique tone color. Experienced musicians are able to distinguish between different instruments of the same type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)