|
Disposition Index
Disposition index (DI) is the product of insulin sensitivity times the amount of insulin secreted in response to blood glucose levels. Insulin resistant individuals can maintain normal responses to blood glucose due to the fact that higher levels of insulin are secreted as long as the beta cells of the pancreas are able to increase their output of insulin to compensate for the insulin resistance. But the ratio of the incremental increase in plasma insulin associated with an incremental increase in plasma glucose (disposition index) provides a better measure of beta cell function than the plasma insulin response to a glucose challenge. Loss of function of the beta cells, reducing their capacity to compensate for insulin resistance, results in a lower disposition index. Disposition index is used as a measure of beta cell function and the ability of the body to dispose of a glucose load. Thus a lowering of disposition index predicts the conversion of insulin resistance to diabetes me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood, but sulfate depletion may be the important factor. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. There are multiple ways to measure insulin resistance such as fasting insulin levels or glucose tolerance tests, but these are not often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats ( triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Sugar Level
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blood of a 70 kg (154 lb) human at all times. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level at the expense of glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle. In humans, a blood glucose level of 4 grams, or about a teaspoon, is critical for normal function in a number of tissues, and the human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasting, sedentary individuals. A persistent elevation in blood glucose leads to glucose toxicity, which contributes to cell dysfunction and the pathology grouped together as complications of diabetes. Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes (journal)
''Diabetes'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published since 1952 by the American Diabetes Association. It covers research about the physiology and pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus including any aspect of laboratory, animal or human research. Emphasis is on investigative reports focusing on areas such as the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications, normal and pathologic pancreatic islet function and intermediary metabolism, pharmacological mechanisms of drug and hormone action, and biochemical and molecular aspects of normal and abnormal biological processes. Diabetes also publishes abstracts presented at the ADA's annual meeting, Scientific Sessions, as a supplement. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 9.337, and 5 years impact factor of 10.509 ranking it 8th out of 240 journals in the category "Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism". See also * American Diabetes Association The American Diabetes Asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
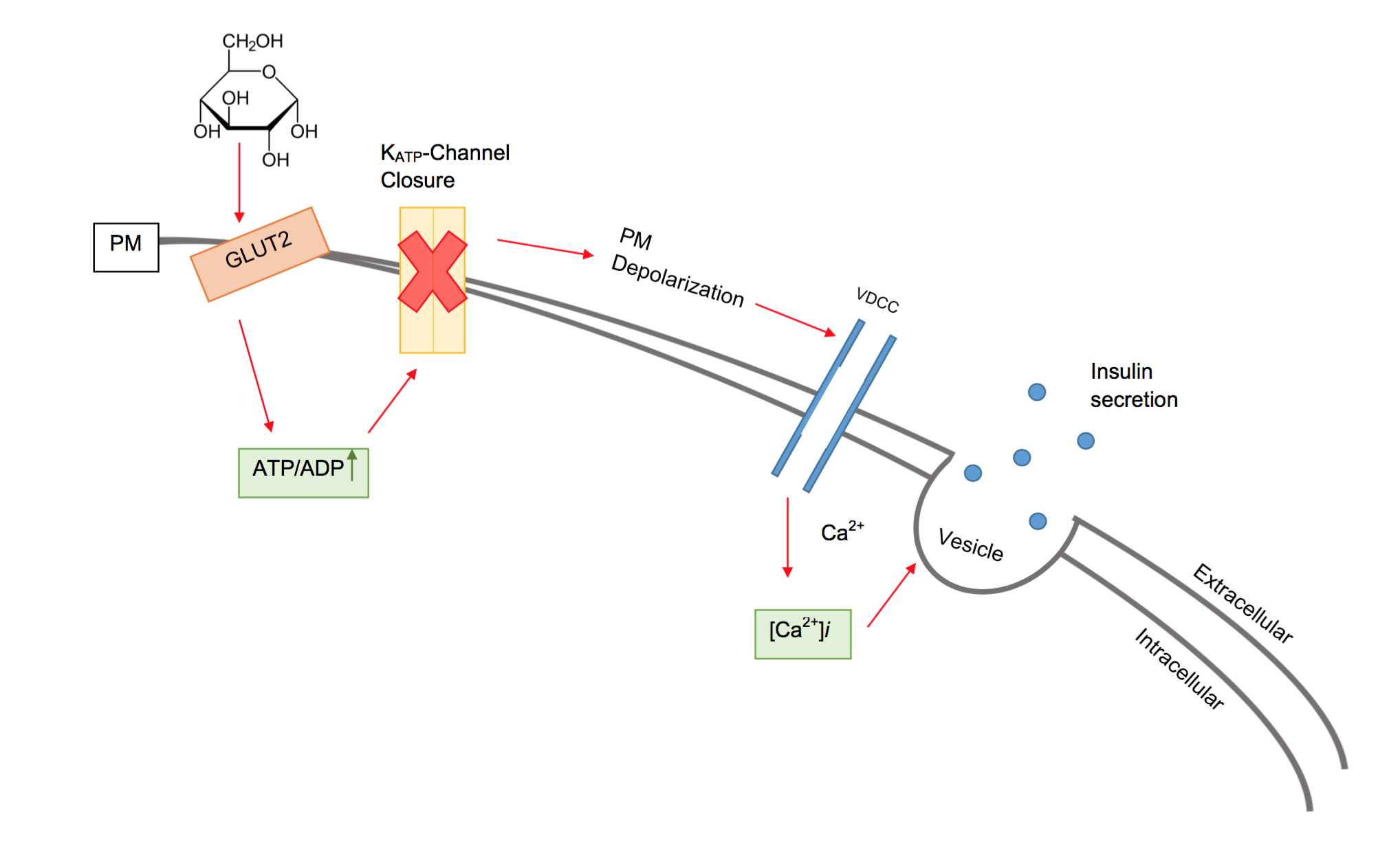
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are a type of cell found in pancreatic islets that synthesize and secrete insulin and amylin. Beta cells make up 50–70% of the cells in human islets. In patients with Type 1 diabetes, beta-cell mass and function are diminished, leading to insufficient insulin secretion and hyperglycemia. Function The primary function of a beta cell is to produce and release insulin and amylin. Both are hormones which reduce blood glucose levels by different mechanisms. Beta cells can respond quickly to spikes in blood glucose concentrations by secreting some of their stored insulin and amylin while simultaneously producing more. Primary cilia on beta cells regulate their function and energy metabolism. Cilia deletion can lead to islet dysfunction and type 2 diabetes. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, it simultaneously increases proinsulin biosynthesis, mainly through translational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose Tolerance Test
The glucose tolerance test (GTT, not to be confused with GGT test) is a medical test in which glucose is given and blood samples taken afterward to determine how quickly it is cleared from the blood. The test is usually used to test for diabetes, insulin resistance, impaired beta cell function, and sometimes reactive hypoglycemia and acromegaly, or rarer disorders of carbohydrate metabolism. In the most commonly performed version of the test, an ''oral glucose tolerance test'' (OGTT), a standard dose of glucose is ingested by mouth and blood levels are checked two hours later. Many variations of the GTT have been devised over the years for various purposes, with different standard doses of glucose, different routes of administration, different intervals and durations of sampling, and various substances measured in addition to blood glucose. History The glucose tolerance test was first described in 1923 by Jerome W. Conn. The test was based on the previous work in 1913 by A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may also include increased hunger, feeling tired, and sores that do not heal. Often symptoms come on slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, strokes, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the limbs which may lead to amputations. The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primarily to type 1 diabetes and gestational diabetes. In type 1 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Care
''Diabetes Care'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal published since 1978 by the American Diabetes Association. The journal covers research in the following five categories: 1) clinical care/education/nutrition/psychosocial research, 2) epidemiology/health services research, 3) emerging treatments and technologies, 4) pathophysiology/complications, and 5) cardiovascular and metabolic risk. The journal also publishes clinically relevant review articles, letters to the editor, and commentaries. The current Editor-in-Chief is Steven Kahn, MD. The journal has a 2020 impact factor of 19.112. See also * American Diabetes Association * ''Diabetes Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...'' References External links * {{Official website, http://care.diabetesjournal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Predisposition
A genetic predisposition is a genetic characteristic which influences the possible phenotypic development of an individual organism within a species or population under the influence of environmental conditions. In medicine, genetic susceptibility to a disease refers to a genetic predisposition to a health problem, which may eventually be triggered by particular environmental or lifestyle factors, such as tobacco smoking or diet. Genetic testing is able to identify individuals who are genetically predisposed to certain diseases. Behavior Predisposition is the capacity humans are born with to learn things such as language and concept of self. Negative environmental influences may block the predisposition (ability) one has to do some things. Behaviors displayed by animals can be influenced by genetic predispositions. Genetic predisposition towards certain human behaviors is scientifically investigated by attempts to identify patterns of human behavior that seem to be invaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proceedings Of The National Academy Of Sciences Of The United States Of America
''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America'' (often abbreviated ''PNAS'' or ''PNAS USA'') is a peer-reviewed multidisciplinary scientific journal. It is the official journal of the National Academy of Sciences, published since 1915, and publishes original research, scientific reviews, commentaries, and letters. According to '' Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 12.779. ''PNAS'' is the second most cited scientific journal, with more than 1.9 million cumulative citations from 2008 to 2018. In the mass media, ''PNAS'' has been described variously as "prestigious", "sedate", "renowned" and "high impact". ''PNAS'' is a delayed open access journal, with an embargo period of six months that can be bypassed for an author fee ( hybrid open access). Since September 2017, open access articles are published under a Creative Commons license. Since January 2019, ''PNAS'' has been online-only, although print issues a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Exercise
Aerobic exercise (also known as endurance activities, cardio or cardio-respiratory exercise) is physical exercise of low to high intensity that depends primarily on the aerobic energy-generating process. "Aerobic" is defined as "relating to, involving, or requiring oxygen", and refers to the use of oxygen to meet energy demands during exercise via aerobic metabolism adequately. Aerobic exercise is performed by repeating sequences of light-to-moderate intensity activities for extended periods of time. Aerobic exercise may be better referred to as "solely aerobic", as it is designed to be low-intensity enough that all carbohydrates are aerobically turned into energy via mitochondrial ATP production. Mitochondria are organelles that rely on oxygen for the metabolism of carbs, proteins, and fats. Examples of cardiovascular or aerobic exercise are medium- to long-distance running or jogging, swimming, cycling, stair climbing and walking. History Archibald Hill, a British physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |