|
Discounted Maximum Loss
Discounted maximum loss, also known as worst-case risk measure, is the present value of the worst-case scenario for a financial portfolio. In investment, in order to protect the value of an investment, one must consider all possible alternatives to the initial investment. How one does this comes down to personal preference; however, the worst possible alternative is generally considered to be the benchmark against which all other options are measured. The present value of this worst possible outcome is the discounted maximum loss. Definition Given a finite state space S, let X be a portfolio with profit X_s for s\in S. If X_,...,X_ is the order statistic the discounted maximum loss is simply -\delta X_, where \delta is the discount factor. Given a general probability space (\Omega,\mathcal,\mathbb), let X be a portfolio with discounted return \delta X(\omega) for state \omega \in \Omega. Then the discounted maximum loss can be written as -\operatorname \delta X = -\sup \delta \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Measure
In financial mathematics, a risk measure is used to determine the amount of an asset or set of assets (traditionally currency) to be kept in reserve. The purpose of this reserve is to make the risks taken by financial institutions, such as banks and insurance companies, acceptable to the regulator. In recent years attention has turned towards convex and coherent risk measurement. Mathematically A risk measure is defined as a mapping from a set of random variables to the real numbers. This set of random variables represents portfolio returns. The common notation for a risk measure associated with a random variable X is \rho(X). A risk measure \rho: \mathcal \to \mathbb \cup \ should have certain properties: ; Normalized : \rho(0) = 0 ; Translative : \mathrm\; a \in \mathbb \; \mathrm \; Z \in \mathcal ,\;\mathrm\; \rho(Z + a) = \rho(Z) - a ; Monotone : \mathrm\; Z_1,Z_2 \in \mathcal \;\mathrm\; Z_1 \leq Z_2 ,\; \mathrm \; \rho(Z_2) \leq \rho(Z_1) Set-valued In a situatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
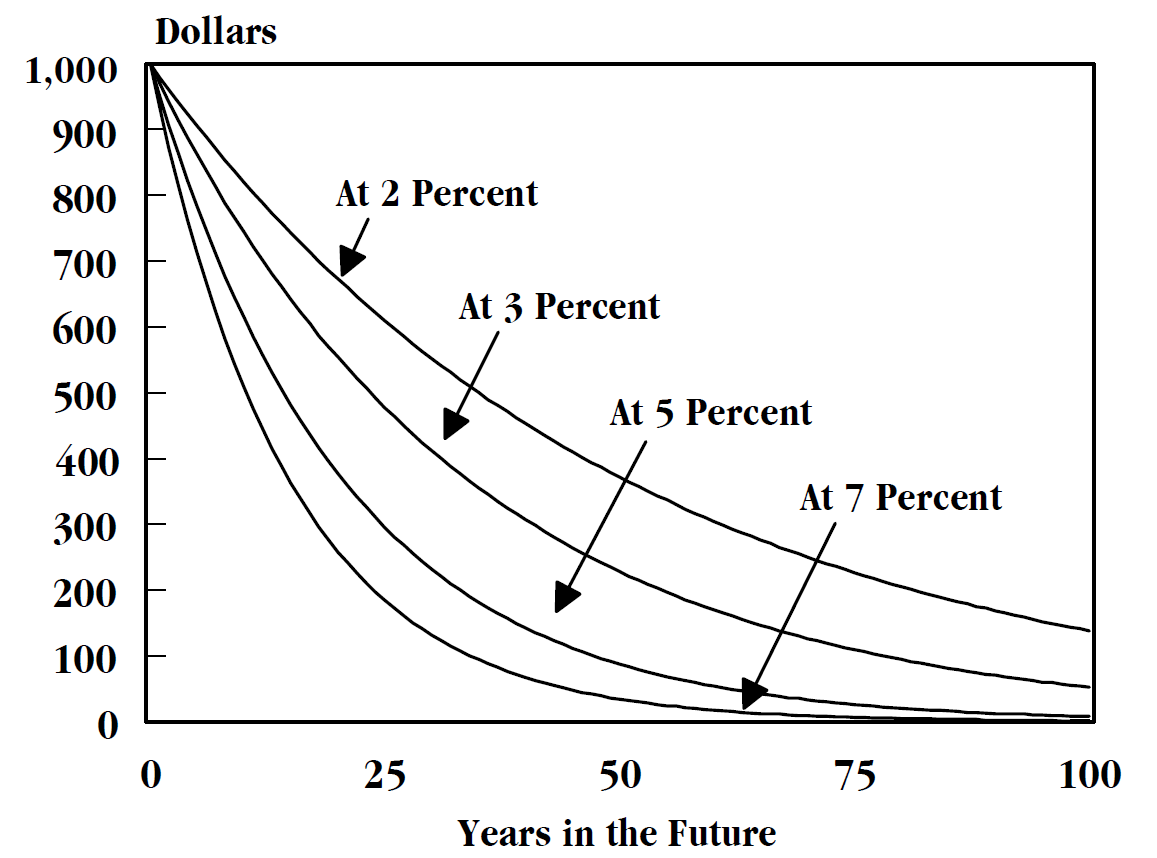
Present Value
In economics and finance, present value (PV), also known as present discounted value, is the value of an expected income stream determined as of the date of valuation. The present value is usually less than the future value because money has interest-earning potential, a characteristic referred to as the time value of money, except during times of zero- or negative interest rates, when the present value will be equal or more than the future value. Time value can be described with the simplified phrase, "A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow". Here, 'worth more' means that its value is greater than tomorrow. A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because the dollar can be invested and earn a day's worth of interest, making the total accumulate to a value more than a dollar by tomorrow. Interest can be compared to rent. Just as rent is paid to a landlord by a tenant without the ownership of the asset being transferred, interest is paid to a lender by a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portfolio (finance)
In finance, a portfolio is a collection of investments. Definition The term “portfolio” refers to any combination of financial assets such as stocks, bonds and cash. Portfolios may be held by individual investors or managed by financial professionals, hedge funds, banks and other financial institutions. It is a generally accepted principle that a portfolio is designed according to the investor's risk tolerance, time frame and investment objectives. The monetary value of each asset may influence the risk/reward ratio of the portfolio. When determining asset allocation, the aim is to maximise the expected return and minimise the risk. This is an example of a multi-objective optimization problem: many efficient solutions are available and the preferred solution must be selected by considering a tradeoff between risk and return. In particular, a portfolio A is dominated by another portfolio A' if A' has a greater expected gain and a lesser risk than A. If no portfolio domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Statistic
In statistics, the ''k''th order statistic of a statistical sample is equal to its ''k''th-smallest value. Together with rank statistics, order statistics are among the most fundamental tools in non-parametric statistics and inference. Important special cases of the order statistics are the minimum and maximum value of a sample, and (with some qualifications discussed below) the sample median and other sample quantiles. When using probability theory to analyze order statistics of random samples from a continuous distribution, the cumulative distribution function is used to reduce the analysis to the case of order statistics of the uniform distribution. Notation and examples For example, suppose that four numbers are observed or recorded, resulting in a sample of size 4. If the sample values are :6, 9, 3, 8, the order statistics would be denoted :x_=3,\ \ x_=6,\ \ x_=8,\ \ x_=9,\, where the subscript enclosed in parentheses indicates the th order statistic of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discount Factor
Discounting is a financial mechanism in which a debtor obtains the right to delay payments to a creditor, for a defined period of time, in exchange for a charge or fee.See "Time Value", "Discount", "Discount Yield", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Market", "Market Value" and "Opportunity Cost" in Downes, J. and Goodman, J. E. ''Dictionary of Finance and Investment Terms'', Baron's Financial Guides, 2003. Essentially, the party that owes money in the present purchases the right to delay the payment until some future date.See "Discount", "Compound Interest", "Efficient Markets Hypothesis", "Efficient Resource Allocation", "Pareto-Optimality", "Price", "Price Mechanism" and "Efficient Market" in Black, John, ''Oxford Dictionary of Economics'', Oxford University Press, 2002. This transaction is based on the fact that most people prefer current interest to delayed interest because of mortality effects, impatience effects, and salience effects. The discount, or charge, is the difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Space
In probability theory, a probability space or a probability triple (\Omega, \mathcal, P) is a mathematical construct that provides a formal model of a random process or "experiment". For example, one can define a probability space which models the throwing of a die. A probability space consists of three elements:Stroock, D. W. (1999). Probability theory: an analytic view. Cambridge University Press. # A sample space, \Omega, which is the set of all possible outcomes. # An event space, which is a set of events \mathcal, an event being a set of outcomes in the sample space. # A probability function, which assigns each event in the event space a probability, which is a number between 0 and 1. In order to provide a sensible model of probability, these elements must satisfy a number of axioms, detailed in this article. In the example of the throw of a standard die, we would take the sample space to be \. For the event space, we could simply use the set of all subsets of the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Infimum
In mathematics, the concepts of essential infimum and essential supremum are related to the notions of infimum and supremum, but adapted to measure theory and functional analysis, where one often deals with statements that are not valid for ''all'' elements in a set, but rather ''almost everywhere'', i.e., except on a set of measure zero. While the exact definition is not immediately straightforward, intuitively the essential supremum of a function is the smallest value that is greater than or equal to the function values everywhere while ignoring what the function does at a set of points of measure zero. For example, if one takes the function f(x) that is equal to zero everywhere except at x=0 where f(0)=1, then the supremum of the function equals one. However, its essential supremum is zero because we are allowed to ignore what the function does at the single point where f is peculiar. The essential infimum is defined in a similar way. Definition As is often the case in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Shortfall
Expected shortfall (ES) is a risk measure—a concept used in the field of financial risk measurement to evaluate the market risk or credit risk of a portfolio. The "expected shortfall at q% level" is the expected return on the portfolio in the worst q\% of cases. ES is an alternative to value at risk that is more sensitive to the shape of the tail of the loss distribution. Expected shortfall is also called conditional value at risk (CVaR), average value at risk (AVaR), expected tail loss (ETL), and superquantile. ES estimates the risk of an investment in a conservative way, focusing on the less profitable outcomes. For high values of q it ignores the most profitable but unlikely possibilities, while for small values of q it focuses on the worst losses. On the other hand, unlike the discounted maximum loss, even for lower values of q the expected shortfall does not consider only the single most catastrophic outcome. A value of q often used in practice is 5%. Expected shortfall is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherent Risk Measure
In the fields of actuarial science and financial economics there are a number of ways that risk can be defined; to clarify the concept theoreticians have described a number of properties that a risk measure might or might not have. A coherent risk measure is a function that satisfies properties of monotonicity, sub-additivity, homogeneity, and translational invariance. Properties Consider a random outcome X viewed as an element of a linear space \mathcal of measurable functions, defined on an appropriate probability space. A functional \varrho : \mathcal → \R \cup \ is said to be coherent risk measure for \mathcal if it satisfies the following properties: Normalized : \varrho(0) = 0 That is, the risk when holding no assets is zero. Monotonicity : \mathrm\; Z_1,Z_2 \in \mathcal \;\mathrm\; Z_1 \leq Z_2 \; \mathrm ,\; \mathrm \; \varrho(Z_1) \geq \varrho(Z_2) That is, if portfolio Z_2 always has better values than portfolio Z_1 under almost all scenarios then the risk of Z_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interest Rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, the compounding frequency, and the length of time over which it is lent, deposited, or borrowed. The annual interest rate is the rate over a period of one year. Other interest rates apply over different periods, such as a month or a day, but they are usually annualized. The interest rate has been characterized as "an index of the preference . . . for a dollar of present ncomeover a dollar of future income." The borrower wants, or needs, to have money sooner rather than later, and is willing to pay a fee—the interest rate—for that privilege. Influencing factors Interest rates vary according to: * the government's directives to the central bank to accomplish the government's goals * the currency of the principal sum lent or borrowed * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |