|
Dirk Coetsee
Dirk Coetzee/Coetsee (1655 – 1725) was the Hoofdheemraad (Chancellor) of the District of Stellenbosch and Drakenstein in South Africa for most of the 1690s and early 1700s. He also served as captain of the Stellenbosch Infantry and deacon of the Stellenbosch Moederkerk ( Dutch Reformed Mother Church) at different points in time. As captain of the Stellenbosch Infantry, which comprised mostly Huguenots, he provided military backing for a rebellion which began in 1706 against the Governor of the Cape Colony, Willem Adriaan van der Stel, whom the vrijburghers (free burghers, i.e. citizens of the colony not in the employ of the Dutch East India Company) had accused of tyranny, corruption and racketeering. Coetsee was imprisoned in the dungeon of the Castle of Good Hope along with the other leaders of the Huguenots but he was released after a year. The rebellion ultimately succeeded in 1707 when the Dutch East India Company recalled the Governor and other colonial officials. An accou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellenbosch
Stellenbosch (; )A Universal Pronouncing Gazetteer. Thomas Baldwin, 1852. Philadelphia: Lippincott, Grambo & Co.A Grammar of Afrikaans. Bruce C. Donaldson. 1993. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter. is a town in the Western Cape province of South Africa, situated about east of Cape Town, along the banks of the Eerste River at the foot of the Stellenbosch Mountain. The town became known as the City of Oaks or ''Eikestad'' in Afrikaans and Dutch language, Dutch due to the large number of oak trees that were planted by its founder, Simon van der S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellenbosch Mountain
Stellenbosch Mountain (Afrikaans: Stellenbosberg or Die Groteberg) is a mountain forming a prominent landmark overlooking the town of Stellenbosch in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. The mountain forms part of the Coetsenburg Estate, the Jonkershoek Nature Reserve, the Assegaaibosch Nature Reserve and the larger Hottentots-Holland Mountains Catchment Area. Geology The peak of Stellenbosch Mountain is 1,156m. The source of the Blaauwklippen (Blouklip) River is near the peak. The range is primarily composed of Table Mountain Sandstone. The climate is typically Mediterranean; warm and temperate, classified as Csb by the Köppen-Geiger system. However, it is generally much cooler and more verdant than other areas in the Western Cape, with annual precipitation at 802mm and an average temperature of 16.4 °C. In winter, there is much more rainfall than in summer. Snow is not unusual on the peak during winter. The Hottentots Holland Mountains, of which the Stellenbosc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Couches, Saône-et-Loire
Couches () is a commune in the Saône-et-Loire department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac .... Sights Chateau The chateau complex includes a number of structures from different periods. The chateau is often called the chateau of Margaret of Burgundy, Queen of France, wife of Louis X of France, who was confined to the Chateau Gaillard after allegedly committing adultery. She died there after apparent ill treatment in 1315. One version of the story is that she did not die in the Chateau Gaillard, but escaped and was taken in by her cousin, Marie of Couches, and housed in the chateau and died there in 1333. Image:CouchesChateau1.JPG, Chateau Image:CouchesChateau2.JPG, Chateau Image:CouchesChateau3.JPG, Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—most recently part of the Eastern Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour. Although it is derived from the Latin word ''feodum'' or ''feudum'' (fief), which was used during the Medieval period, the term ''feudalism'' and the system which it describes were not conceived of as a formal political system by the people who lived during the Middle Ages. The classic definition, by François Louis Ganshof (1944), François Louis Ganshof (1944). ''Qu'est-ce que la féodalité''. Translated into English by Philip Grierson as ''Feudalism'', with a foreword by F. M. Stenton, 1st ed.: New York and London, 1952; 2nd ed: 1961; 3rd ed.: 1976. describes a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seigneur
''Seigneur'' is an originally feudal title in France before the Revolution, in New France and British North America until 1854, and in the Channel Islands to this day. A seigneur refers to the person or collective who owned a ''seigneurie'' (or ''seigneury'')—a form of land tenure—as a fief, with its associated rights over person and property. A seigneur could be an individual—male or female (''seigneuresse''), noble or non-noble (''roturier'')—or a collective entity such a religious community, monastery, seminary, college, or parish. This form of lordship was called ''seigneurie'', the rights that the seigneur was entitled to were called ''seigneuriage'', and the jurisdiction exercised was ''seigneur justicier'' over his fief. In the wake of the French Revolution, seigneurialism was repealed in France on 4 August 1789 and in the Province of Canada on 18 December 1854. Since then, the feudal title has only been applicable in the Channel Islands and for sovereign princ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancien Régime
''Ancien'' may refer to * the French word for "ancient, old" ** Société des anciens textes français * the French for "former, senior" ** Virelai ancien ** Ancien Régime ** Ancien Régime in France {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bretons
The Bretons (; br, Bretoned or ''Vretoned,'' ) are a Celts, Celtic ethnic group native to Brittany. They trace much of their heritage to groups of Common Brittonic, Brittonic speakers who emigrated from Dumnonia, southwestern Great Britain, particularly Cornwall and Devon, mostly during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. They migrated in waves from the 3rd to 9th century (most heavily from 450 to 600) into Armorica, which was subsequently named Brittany after them. The main traditional language of Brittany is Breton language, Breton (''Brezhoneg''), spoken in Lower Brittany (i.e., the western part of the peninsula). Breton is spoken by around 206,000 people as of 2013. The other principal minority language of Brittany is Gallo language, Gallo; Gallo is spoken only in Upper Brittany, where Breton is less dominant. As one of the Brittonic languages, Breton is related closely to Cornish language, Cornish and more distantly to Welsh language, Welsh, while the Gallo language is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bezanson Hugues (1491–1532?), was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle (department), Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutheranism, Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the ''dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bezanson Hugues (1491–1532?), was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the '' dragonnades'' to forcibly convert Protestants, and then finally revoked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
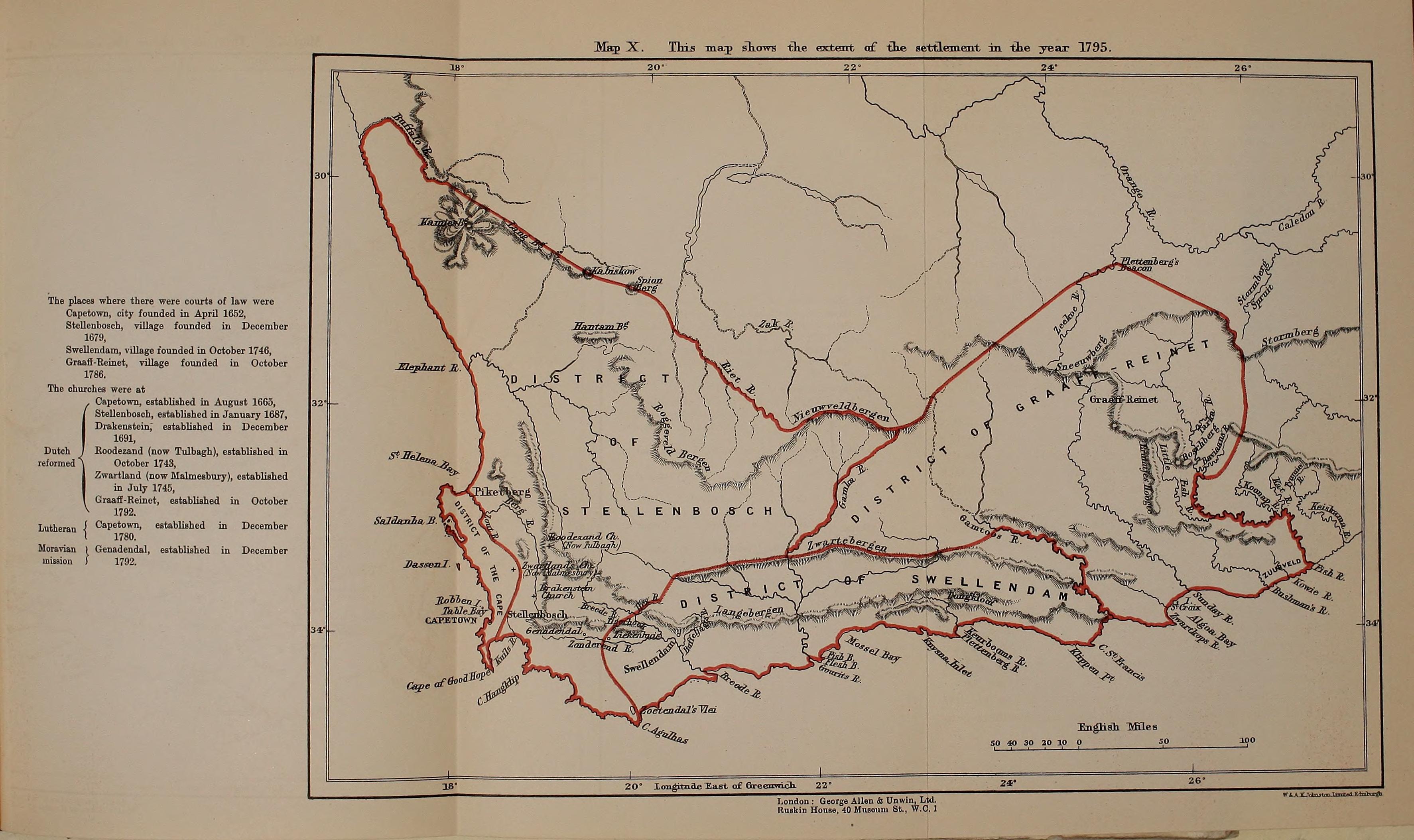
Invasion Of The Cape Colony
The Invasion of the Cape Colony, also known as the Battle of Muizenberg, was a British military expedition launched in 1795 against the Dutch Cape Colony at the Cape of Good Hope. The Dutch colony at the Cape, established and controlled by the United East India Company in the seventeenth century, was at the time the only viable South African port for ships making the journey from Europe to the European colonies in the East Indies. It therefore held vital strategic importance, although it was otherwise economically insignificant. In the winter of 1794, during the French Revolutionary Wars, French troops entered the Dutch Republic, which was reformed into the Batavian Republic. In response, Great Britain launched operations against the Dutch Empire to use its facilities against the French Navy. The British expedition was led by Vice-Admiral Sir George Keith Elphinstone and sailed in April 1795, arriving off Simon's Town at the Cape in June. Attempts were made to negotiate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Establishment
''The Establishment'' is a term used to describe a dominant social group , group or elite that controls a polity or an organization. It may comprise a closed social group that selects its own members, or entrenched elite structures in specific institutions. One can refer to any relatively small social class , class or group of people who can exercise control as ''The Establishment''. Conversely, in the jargon of sociology, anyone who does not belong to ''The Establishment'' may be labelled an Emic and etic, outsider (as opposed to an "insider"). Anti-authoritarianism, Anti-authoritarian Anti-establishment, anti-establishment ideologies question the legitimacy of establishments, seeing their influence on society as Criticism of democracy, undemocratic. The term in its modern sense was popularized by the British journalist Henry Fairlie, who in September 1955 in the London magazine ''The Spectator'' defined the network of prominent, well-connected people as "the Establishment". H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |