|
Diprotodon Australis
''Diprotodon'' ( Ancient Greek: "two protruding front teeth") is an extinct genus of marsupial from the Pleistocene of Australia, containing one species, ''D. optatum''. The earliest finds date to 1.77 million to 780,000 years ago, but most specimens are dated to after 110,000 years ago. Its massive fossils were first unearthed in 1830 in Wellington Caves, New South Wales, before any serious scientists were active on the continent, and were variably guessed to belong to rhinos, elephants, hippos, or dugongs. ''Diprotodon'', formally described by Sir Richard Owen in 1838, was the first named Australian fossil creature, and set Owen on a path to becoming the foremost authority of his time on other marsupials and Australian megafauna so enigmatic to European science. ''Diprotodon'' is the largest known marsupial to have ever lived, far dwarfing its closest living relatives, wombats and koalas. It grew as large as at the shoulders, over from head to tail, and possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koala
The koala or, inaccurately, koala bear (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the wombats. The koala is found in coastal areas of the mainland's eastern and southern regions, inhabiting Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, and South Australia. It is easily recognisable by its stout, tailless body and large head with round, fluffy ears and large, spoon-shaped nose. The koala has a body length of and weighs . Fur colour ranges from silver grey to chocolate brown. Koalas from the northern populations are typically smaller and lighter in colour than their counterparts further south. These populations possibly are separate subspecies, but this is disputed. Koalas typically inhabit open ''Eucalyptus'' woodland, as the leaves of these trees make up most of their diet. Because this eucalypt diet has limited nutritional and calor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Rock Art
Indigenous Australian art includes art made by Aboriginal Australian and Torres Strait Islander peoples, including collaborations with others. It includes works in a wide range of media including painting on leaves, bark painting, wood carving, rock carving, watercolour painting, sculpting, ceremonial clothing and sand painting; art by Indigenous Australians that pre-dates European colonisation by thousands of years, up to the present day. Traditional Indigenous art There are several types of and methods used in making Aboriginal art, including rock painting, dot painting, rock engravings, bark painting, carvings, sculptures, weaving and string art. Australian Aboriginal art is the oldest unbroken tradition of art in the world. Stone art Rock art, including painting and engraving or carving (petroglyphs), can be found at sites throughout Australia. Examples of rock art have been found that are believed to depict extinct megafauna such as ''Genyornis'' and ''Thylacoleo'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunyip
The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in swamps, billabongs, creeks, riverbeds, and waterholes. Name The origin of the word ''bunyip'' has been traced to the Wemba-Wemba or Wergaia language of the Aboriginal people of Victoria, in South-Eastern Australia. The word ''bunyip'' is usually translated by Aboriginal Australians today as "devil" or "evil spirit". This contemporary translation may not accurately represent the role of the bunyip in pre-contact Aboriginal mythology or its possible origins before written accounts were made. Some modern sources allude to a linguistic connection between the bunyip and Bunjil, "a mythic 'Great Man' who made the mountains, rivers, man, and all the animals". The word ''bahnyip'' first appeared in the ''Sydney Gazette'' in 1812. It was used by James Ives to describe "a large black animal like a seal, with a terrible voice which creates terror among the blacks". Distribution The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Aboriginal Religion And Mythology
Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology is the sacred spirituality represented in the stories performed by Aboriginal Australians within each of the language groups across Australia in their ceremonies. Aboriginal spirituality includes the Dreamtime (''the Dreaming''), songlines, and Aboriginal oral literature. Aboriginal spirituality often conveys descriptions of each group's local cultural landscape, adding meaning to the whole country's topography from oral history told by ancestors from some of the earliest recorded history. Most of these spiritualities belong to specific groups, but some span the whole continent in one form or another. Antiquity An Australian linguist, R. M. W. Dixon, recording Aboriginal myths in their original languages, encountered coincidences between some of the landscape details being told about within various myths, and scientific discoveries being made about the same landscapes. In the case of the Atherton Tableland, myths tell of the orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Australian
Aboriginal Australians are the various Indigenous peoples of the Australian mainland and many of its islands, such as Tasmania, Fraser Island, Hinchinbrook Island, the Tiwi Islands, and Groote Eylandt, but excluding the Torres Strait Islands. The term Indigenous Australians refers to Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders collectively. It is generally used when both groups are included in the topic being addressed. Torres Strait Islanders are ethnically and culturally distinct, despite extensive cultural exchange with some of the Aboriginal groups. The Torres Strait Islands are mostly part of Queensland but have a separate governmental status. Aboriginal Australians comprise many distinct peoples who have developed across Australia for over 50,000 years. These peoples have a broadly shared, though complex, genetic history, but only in the last 200 years have they been defined and started to self-identify as a single group. Australian Aboriginal identity has cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Extinction Event
The Quaternary period (from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present) has seen the extinctions of numerous predominantly megafaunal species, which have resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity and the extinction of key ecological strata across the globe. The most prominent event in the Late Pleistocene is differentiated from previous Quaternary pulse extinctions by the widespread absence of ecological succession to replace these extinct species, and the regime shift of previously established faunal relationships and habitats as a consequence. The earliest casualties were incurred at 130,000 BCE (the start of the Late Pleistocene), in Australia ~ 60,000 years ago, in Americas ~ 15,000 years ago, coinciding in time with the early human migrations. However, the great majority of extinctions in Afro-Eurasia and the Americas occurred during the transition from the Pleistocene to the Holocene epoch (13,000 BCE to 8,000 BCE). This extinction wave di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pouch (marsupial)
The pouch is a distinguishing feature of female marsupials, monotremes and possibly most extinct non-placental mammals including eutherians like ''Zalambdalestes'' (and rarely in the males as in the water opossumNogueira, José Carlos, et al.Morphology of the male genital system of Chironectes minimus and comparison to other didelphid marsupials. Journal of mammalogy 85.5 (2004): 834-841. and the extinct thylacine); the name marsupial is derived from the Latin ''marsupium'', meaning "pouch". Marsupials give birth to a live but relatively undeveloped fetus called a joey. When the joey is born it crawls from inside the mother to the pouch. The pouch is a fold of skin with a single opening that covers the teats. Inside the pouch, the blind offspring attaches itself to one of the mother’s teats and remains attached for as long as it takes to grow and develop to a juvenile stage. Variations Pouches are different amongst different marsupials, two kinds distinguishable (on the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thylacoleo
''Thylacoleo'' ("pouch lion") is an extinct genus of carnivorous marsupials that lived in Australia from the late Pliocene to the late Pleistocene (2 million to 46 thousand years ago). Some of these marsupial lions were the largest mammalian predators in Australia of their time, with ''Thylacoleo carnifex'' approaching the weight of a lioness. The estimated average weight for the species ranges from . Taxonomy The genus was first published in 1859, erected to describe the type species ''Thylacoleo carnifex''. The new taxon was established in examination of fossil specimens provided to Richard Owen. The familial alliance takes its name from this description, the so-called marsupial lions of Thylacoleonidae. The colloquial name "marsupial lion" alludes to the superficial resemblance to the placental lion and its ecological niche as a large predator. ''Thylacoleo'' is not closely related to the modern lion (''Panthera leo''). Genus: ''Thylacoleo'' (''Thylacopardus'') – Australia' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygyny In Animals
Polygyny (; from Neo-Greek πολυγυνία, from πολύ- ''poly-'', "many", and γυνή ''gyne'', "woman" or "wife") is a mating system in which one male lives and mates with multiple females but each female only mates with a single male. Systems where several females mate with several males are defined either as promiscuity or polygynandry. Lek mating is frequently regarded as a form of polygyny, because one male mates with many females, but lek-based mating systems differ in that the male has no attachment to the females with whom he mates, and that mating females lack attachment to one another.Clutton-Brock T.H. (1989). ‘Review lecture: mammalian mating systems.' ''Proceedings of the Royal Society of London''. Series B, Biological Sciences 236: 339–372. Polygyny is typical of one-male, multi-female groupsBoyd, R., & Silk, J. B. (2009). How Humans Evolved (preferably the downloadable pdf version): WW Norton & Company, New York. and can be found in many species includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatheria
Metatheria is a mammalian clade that includes all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. First proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1880, it is a more inclusive group than the marsupials; it contains all marsupials as well as many extinct non-marsupial relatives. There are three extant subclasses of mammals, one being metatherians: #monotremes: egg laying mammals like the platypus and the echidna, #metatheria: marsupials, which includes three American orders ( Didelphimorphia, Paucituberculata and Microbiotheria) and four Australasian orders (Notoryctemorphia, Dasyuromorphia, Peramelemorphia and Diprotodontia), and the # eutherians: placental mammals, consisting of four superorders divided into 21 orders. Metatherians belong to a subgroup of the northern tribosphenic mammal clade or Boreosphenida. They differ from all other mammals in certain morphologies like their dental formula, which includes about five upper and four lower incisors, a canine, three pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilophodont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_BHL21155651.jpg)


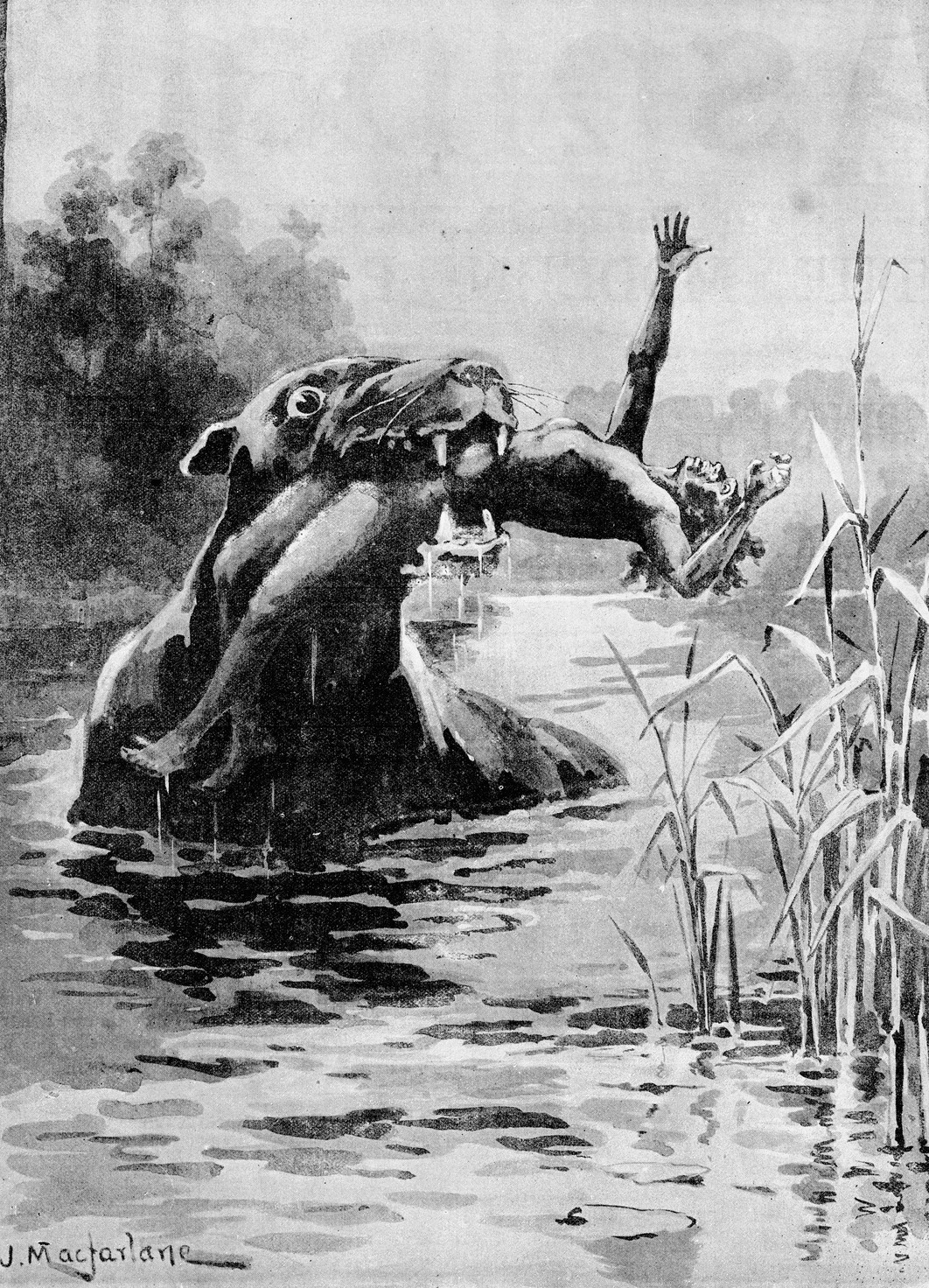



.jpg)

