|
Diogo Botelho Pereira
Diogo Botelho Pereira was a 16th-century Portuguese nobleman, colonial official, navigator and cartographer. He famously undertook a daring voyage by sea from India back to Portugal aboard a fusta. Born in Portuguese India, Botelho was the son of Iria Pereira and António Real, captain of Fort Emmanuel of Cochin. In India, Botelho learned to navigate and compiled detailed portolan charts for the Portuguese navy, in the service of which he commanded ships of the Portuguese India Armadas and participated in military expeditions. Coming to Lisbon, King John III granted him an official title of ''fidalgo'', but Pereira fell out of royal favour over disagreements with the monarch regarding his proper compensation for services to the Crown, and was instead banished to India in perpetuity. This motivated his audacious enterprise of sailing a minuscule vessel from India back to Portugal, between November 1535 and May 1536, bearing the first news of the construction of the Portuguese fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusta By Jan Huygen Van Linschoten
The fusta or fuste (also called foist) was a narrow, light and fast ship with shallow draft, powered by both oars and sail—in essence a small galley. It typically had 12 to 18 two-man rowing benches on each side, a single mast with a lateen (triangular) sail, and usually carried two or three guns. The sail was used to cruise and save the rowers’ energy, while the oars propelled the ship in and out of harbor and during combat. The fusta was the favorite ship of the North African Barbary pirates, corsairs of Salé and the Barbary Coast. Its speed, mobility, capability to move without wind, and its ability to operate in shallow water—crucial for hiding in coastal waters before pouncing on a passing ship—made it ideal for war and piracy. It was mainly with fustas that the Barbarossa brothers, Aruj, Baba Aruj and Barbarossa (Ottoman admiral), Khair ad Din, carried out the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman conquest of North Africa and the rescue of Mudéjars and Moriscos from Spain af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusta
The fusta or fuste (also called foist) was a narrow, light and fast ship with shallow draft, powered by both oars and sail—in essence a small galley. It typically had 12 to 18 two-man rowing benches on each side, a single mast with a lateen (triangular) sail, and usually carried two or three guns. The sail was used to cruise and save the rowers’ energy, while the oars propelled the ship in and out of harbor and during combat. The fusta was the favorite ship of the North African corsairs of Salé and the Barbary Coast. Its speed, mobility, capability to move without wind, and its ability to operate in shallow water—crucial for hiding in coastal waters before pouncing on a passing ship—made it ideal for war and piracy. It was mainly with fustas that the Barbarossa brothers, Baba Aruj and Khair ad Din, carried out the Ottoman conquest of North Africa and the rescue of Mudéjars and Moriscos from Spain after the fall of Granada, and that they and the other North Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the Kingdom of Portugal. The capital of Portuguese India served as the governing centre of a string of military forts and trade posts scattered all over the Indian Ocean. The first viceroy, Francisco de Almeida established his base of operations at Fort Manuel, after the Kingdom of Cochin negotiated to become a protectorate of Portugal in 1505. With the Portuguese conquest of Goa from the Bijapur Sultanate in 1510, Goa became the major anchorage for the Portuguese Armadas arriving in India. The capital of the viceroyalty was transferred from Cochin in the Malabar region to Goa in 1530. From 1535, Mumbai (Bombay) was a harbour of Portuguese India as '' Bom Bahia'', unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Emmanuel
Fort Emmanuel, also known as Fort Manuel, is a ruined fort located at Fort Kochi Beach in Kochi (Cochin), Kerala, India. It is a bastion of the Portuguese and a symbol of the strategic alliance between the Maharaja of Kochi and the Kingdom of Portugal. Named after Manuel I of Portugal, it was the first European Portuguese fort in Asia.Logan, William. ''Malabar''. District Manual. Asian Educational Services, 1887. History In September 1503 the chief of Kochi granted permission to Afonso de Albuquerque to build Fort Emmanuel near the waterfront of the Arabian Sea. The construction was commenced on 26 September, and "it took the shape of a square with flanking bastions at the corners mounted with ordnance". The walls were made of double rows of coconut tree stems securely fastened together and with earth rammed firmly between; it was further protected by a wet ditch. The fort was christened on the morning of 1 October 1503 "Emmanuel", after the King of Portugal.Logan, Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese India Armadas
The Portuguese Indian Armadas ( pt, Armadas da Índia) were the fleets of ships funded by the Crown of Portugal, and dispatched on an annual basis from Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal to Portuguese India, India. The principal destination was Portuguese in Goa and Bombay-Bassein, Goa, and previously Portuguese Cochin, Cochin. These armadas undertook the ''Carreira da Índia'' ('India Run') from Portugal, following the maritime discovery of the Cape route, to the Indian Subcontinent by Vasco da Gama in 1497–99. During the Dutch Malabar, Dutch occupation of Cochin and the Battle_of_Goa_(1638), Dutch siege of Goa, the harbour of ''Bom Bahia'', now known as Mumbai (Bombay), off the coast of the northern Konkan region, served as the standard diversion for the Naval fleet, armadas. The India run For a long time after its discovery by Vasco da Gama, the sea route to India via the Cape of Good Hope was dominated by the Portuguese Indian armada – the annual fleet dispatched from Portug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III Of Portugal
John III ( pt, João III ; 7 June 1502 – 11 June 1557), nicknamed The Pious (Portuguese: ''o Piedoso''), was the King of Portugal and the Algarves from 1521 until his death in 1557. He was the son of King Manuel I and Maria of Aragon, the third daughter of King Ferdinand II of Aragon and Queen Isabella I of Castile. John succeeded his father in 1521 at the age of nineteen. During his rule Portuguese possessions were extended in Asia and in the New World through the Portuguese colonization of Brazil. John III's policy of reinforcing Portugal's bases in India (such as Goa) secured Portugal's monopoly over the spice trade of cloves and nutmeg from the Maluku Islands. On the eve of his death in 1557, the Portuguese empire had a global dimension and spanned almost . During his reign, the Portuguese became the first Europeans to make contact with Japan (during the Muromachi period). He abandoned the Muslim territories in North Africa in favor of the trade with India and investme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fidalgo
''Fidalgo'' (, ), from Galician and Portuguese —equivalent to nobleman, but sometimes literally translated into English as "son of somebody" or "son of some (important family)"—is a traditional title of Portuguese nobility that refers to a member of the titled or untitled nobility. A ''fidalgo'' is comparable in some ways to the French '' gentilhomme'' (the word also implies nobility by birth or by charge) and to the Italian '' nobile''. The title was abolished after the overthrow of the monarchy in 1910 and is also a family surname. Origins and etymology The word has the same etymological and historical roots as its Spanish cognate, ''hidalgo''. Although ''algo'' generally means "something", in this expression the word specifically denotes "riches" or "wealth" and thus was originally synonymous with ''rico homem'' (literally, "a rich man"). Corominas, Joan and José A Pascual (1981). "Hijo" in ''Diccionario crítico etimológico castellano e hispánico'', Vol. G-Ma (3). Mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
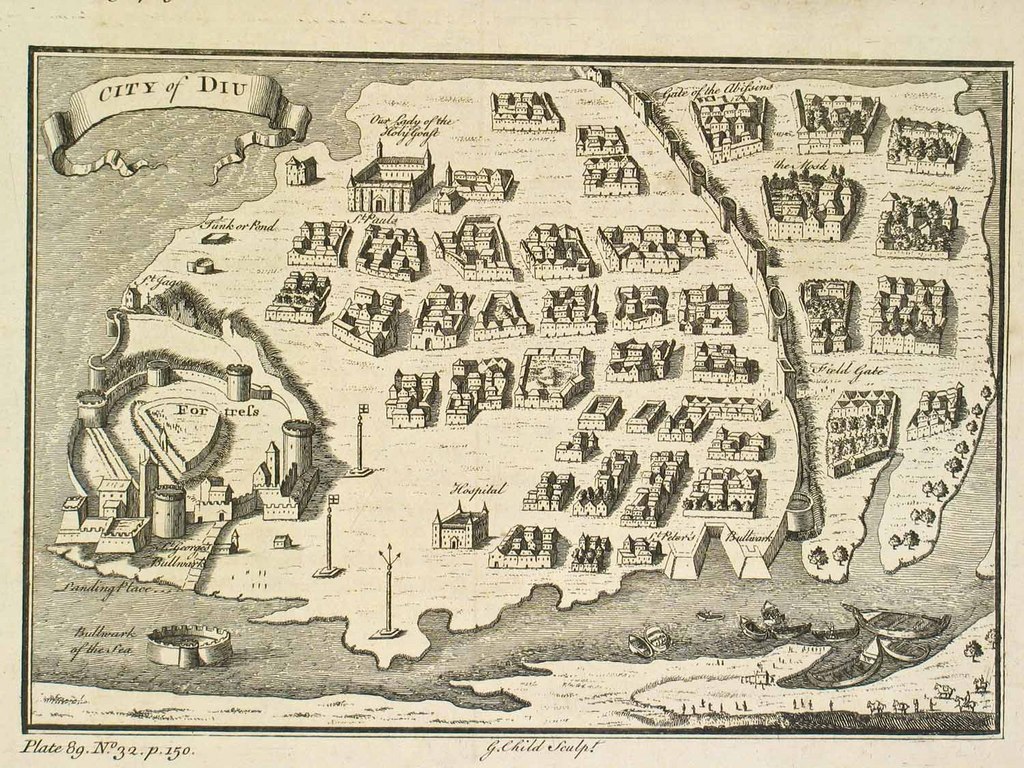
Diu Fortress
The Diu Fortress (Portuguese: ''Fortaleza de Diu'' or formally ''Fortaleza de São Tomé'') is a Portuguese-built fortification located on the west coast of India in Diu. The fortress was built as part of Portuguese India's defensive fortifications at the eastern tip of the island of Diu during the 16th century. The fortress, which borders on the town of Diu, was built in 1535 subsequent to a defense alliance forged by Bahadur Shah, the Sultan of Gujarat and the Portuguese when Humayun, the Mughal Emperor attempted to annex this territory. It was strengthened over the years, till 1546. The Portuguese ruled over this territory from 1537 until the Indian invasion of December 1961. Today it is a landmark of Diu and one of the Seven Wonders of Portuguese Origin in the World. History Before the Portuguese built the fortress in 1535, the ancient history of the place was linked to several Kings and Dynasties; the earliest quoted is of the Puranic period, followed by the Mauryans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese São Tomé And Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe islands were a colony of the Portuguese Empire from its discovery in 1470 until 1975, when independence was granted by Portugal. History The Portuguese explorers João de Santarém and Pêro Escobar discovered the islands around 1470,Francisco, Agostinho, p.24 which they found uninhabited.Grivetti, Shapiro, p. 1849 The São Tomé island was named by the Portuguese in honor of Saint Thomas, as they discovered the island on his feast day, while the Príncipe island (Prince's island) was named in honor of Afonso, Prince of Portugal, his father's favorite. The first attempt of settlement in the islands began in 1485, when the Portuguese Crown granted to João de Paiva the São Tomé island. However, this attempt was not successful, because the settlers were unable to produce food in the specific conditions and climate that the islands offered, and because of the tropical diseases that affected the settlers. It was only in 1493 when King John II of Portuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors Of Portuguese São Tomé And Príncipe
The islands of São Tomé and Príncipe were discovered and claimed by Portugal in the 1470s. A Portuguese colony was established in 1485. Each island was governed as a separate entity until 1753, when they were united as a single crown colony. In 1951, the islands became an overseas province of Portugal. Autonomy was granted in 1974 and independence was granted on 12 July 1975. São Tomé Portuguese Colony (1485–1522) * 24 September 1485 – 3 February 1490 João de Paiva, Captain * 3 February 1490 – 29 July 1493 João Pereira, Captain * 29 July 1493 – 28 April 1499 Álvaro de Caminha, Captain * 11 December 1499 – c.1510 Fernão de Melo, Captain * c.1510 – c.1516 .... * c.1516 – c.1517 Diogo de Alcáçova, Captain * c.1517–1522 João de Melo, Captain Portuguese Crown Colony (1522–1641) * 1522 – 15.. Vasco Estevens, Captain * 15.. – 1531 .... * 1531 – c.1535 Henrique Pereira, Captain * c.1535–1541 Gonçalo Álvares, Governor [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th-century Portuguese People
The 16th century begins with the Julian year 1501 ( MDI) and ends with either the Julian or the Gregorian year 1600 ( MDC) (depending on the reckoning used; the Gregorian calendar introduced a lapse of 10 days in October 1582). The 16th century is regarded by historians as the century which saw the rise of Western civilization and the Islamic gunpowder empires. The Renaissance The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ... in Italy and Europe saw the emergence of important artists, authors and scientists, and led to the foundation of important subjects which include accounting and political science. Copernicus proposed the Copernican heliocentrism, heliocentric universe, which was met with strong resistance, and Tycho Brahe refuted the theory of celestial spheres through o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Explorers
Portuguese maritime exploration resulted in the numerous territories and maritime routes recorded by the Portuguese as a result of their intensive maritime journeys during the 15th and 16th centuries. Portuguese sailors were at the vanguard of European exploration, chronicling and mapping the coasts of Africa and Asia, then known as the East Indies, and Canada and Brazil (the West Indies), in what came to be known as the Age of Discovery. Methodical expeditions started in 1419 along West Africa's coast under the sponsorship of prince Henry the Navigator, with Bartolomeu Dias reaching the Cape of Good Hope and entering the Indian Ocean in 1488. Ten years later, in 1498, Vasco da Gama led the first fleet around Africa to India, arriving in Calicut and starting a maritime route from Portugal to India. Portuguese explorations then proceeded to southeast Asia, where they reached Japan in 1542, forty-four years after their first arrival in India. In 1500, the Portuguese nobleman Pedro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |