|
Dioctophyma
''Dioctophyme'' is a monotypic genus of nematodes belonging to the family Dioctophymidae. The only species is ''Dioctophyme renale ''Dioctophyme renale'', commonly referred to as the giant kidney worm, is a parasitic nematode (roundworm) whose mature form is found in the kidneys of mammals. ''D. renale'' is distributed worldwide, but is less common in Africa and Oceania. ...''. The species is found in Northern America and Japan. References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q18606983, from2=Q5279085 Nematodes Nematode genera Monotypic animal genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioctophyme Renale
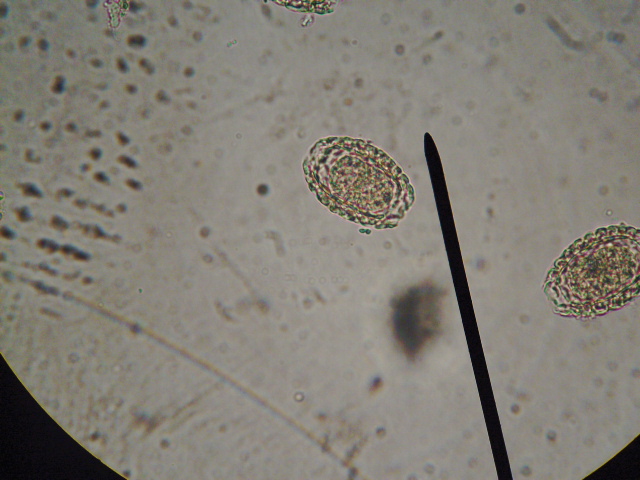
''Dioctophyme renale'', commonly referred to as the giant kidney worm, is a parasitic nematode (roundworm) whose mature form is found in the kidneys of mammals. ''D. renale'' is distributed worldwide, but is less common in Africa and Oceania. It affects fish eating mammals, particularly mink and dogs. Human infestation is rare, but results in kidney destruction, usually of one kidney and hence not fatal. A 2019 review listed a total of 37 known human cases of dioctophymiasis in 10 countries with the highest number (22) in China. Upon diagnosis through tissue sampling, the only treatment is surgical excision. Synonyms Dioctophymosis, dioctophymiasis, giant kidney worm, kidney worm infection, ''Dioctophyme renale'' infection History of discovery ''Dioctophyme renale'' was discovered in 1583. Almost two centuries later, in 1782, Johann Goeze first described ''D. renale'' upon discovering the worms in a dog kidney. The family Dioctophymidae has only one genus (''Dioctophyme' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioctophymidae
Dioctophymatidae is a family of nematodes belonging to the order Ascaridida. Genera: * ''Dioctophyma'' Collet-Meygret, 1802 * ''Dioctophyme'' * ''Eustrongylides'' * ''Hystrichis ''Hystrichis'' is a genus of nematode worm with a spinose anterior end, resembling the introvert of priapulids. Species of ''Hystrichis'' live mainly in the digestive tract The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary can ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q21220654 Nematodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Genus
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with Arthropod, arthropods, Tardigrade, tardigrades and other moulting animalia, animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike platyhelminthe, flatworms, have tubular digestion, digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematodes
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode Genera
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over time. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity published in the mega journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |